五Spring-AOP--6AOP调用逻辑源码分析
五Spring-AOP--6AOP调用逻辑源码分析
5.6.2 AOP调用逻辑
当被代理类的被AOP增强的方法执行时,会调用invoke。
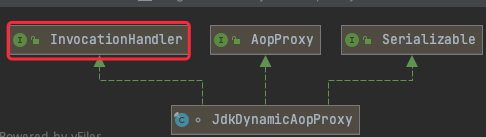
以JdkDynamicAopProxy为例分析,其本身是InvocationHandler,方法调用的处理器,因此代理方法调用时,会调用invoke方法,实现拦截
//Implementation of {@code InvocationHandler.invoke}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
//AdvisedSupport.targetSource获取被代理的类(targetsource包装真实target类)
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
//是否需要对外暴露代理对象
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
//将proxy设置入AopContext,然后可以从AopContext中获取代理对象
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
//获取被代理真实类
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
/**……………………………………………………………………………………………获取当前method的interceptor的chain……………………………………………………*/
//TAG1 AdvisedSupport.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
//调用this.AdvisedSupport的getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice方法,获取当前method的interceptor的chain
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
//表示当前target的method没有被AOP增强所拦截
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
//直接调用method方法并返回,不做AOP增强
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
/**………………………………………………………………AOP链式调用核心入口……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
//TAG2 invocation.proceed()
//proceed实现链式调用
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
//targetSource释放代理的target对象
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
TAG1 AdvisedSupport.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
AdvisedSupport作为当前JdkDynamicAopProxy的内部属性,其内包含了拦截器chain的信息。
AdvisedSupport.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice的执行逻辑如下图:

public class AdvisedSupport extends ProxyConfig implements Advised {
//advisor链。当一个Advice添加,会被wrap成advisor后添加到当前list
private List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
/** method为key,List<advisorChain>为value的methodCache缓存对象 */
private transient Map<MethodCacheKey, List<Object>> methodCache;
//提供advisorChainFactory。factory提供
AdvisorChainFactory advisorChainFactory = new DefaultAdvisorChainFactory();
//根据此配置,确定给定方法的MethodInterceptor列表
//该方法用来获取代理的方法上,对应的有效的所有的拦截器interceptor链
//将DefaultAdvisorChainFactory的方法代理到getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice上
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
//以待拦截的method对象,创建MethodCacheKey--缓存中的key
MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
//查询缓存
List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached == null) {
/**…………………………………………………………………………生成拦截器chain………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//TAG1.1 advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
//DefaultAdvisorChainFactory:生成通知器链的工厂,实现了interceptor链的获取过程
cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
this, method, targetClass);
//缓存中存储(MethodCacheKey(method),InterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice)
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
}
return cached;
}
TAG1.1 advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
//DefaultAdvisorChainFactory:生成拦截器链
public class DefaultAdvisorChainFactory implements AdvisorChainFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// 拿到代理里面所有的通知们:getAdvisors
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(config.getAdvisors().length);
Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass);
//通过registry将advisor转换为interceptors
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
//遍历ProxyConfig中缓存的当前class的advisors集合
for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) { //1
//advisor为PointcutAdvisor的处理逻辑
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { //2
// 转换为PointcutAdvisor
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
//当当前advisor匹配到targetclass时(也就是目标类需要被此advisor增强拦截)
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { //3
/**…………………………………………………………………………………………构造拦截器链chain……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
//TAG1.1.1 registry.getInterceptors(advisor)
//registry.getInterceptors将advisor转换为MethodInterceptor,并创建拦截器链chain返回
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
//如果当前当前advisor内的methodmatcher,能匹配到当前class的method上
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) { //4
// 动态匹配
//(动态匹配,就是即使两个参数的match方法返回true,在运行时,最后依然会调用这个三个参数的matches方法)
if (mm.isRuntime()) { //5
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
//全部MethodInterceptors分别转换为InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
//如果mm.isRuntime为true动态匹配,chain链传入的是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象,在ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed的调用环节,匹配方法用的是三个参数的matches
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
} //5
// 静态匹配
else {
//直接将interceptors添加入list
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
} //4
} //3
} //2
//当advisor为引介introduction时的处理逻辑
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}
}
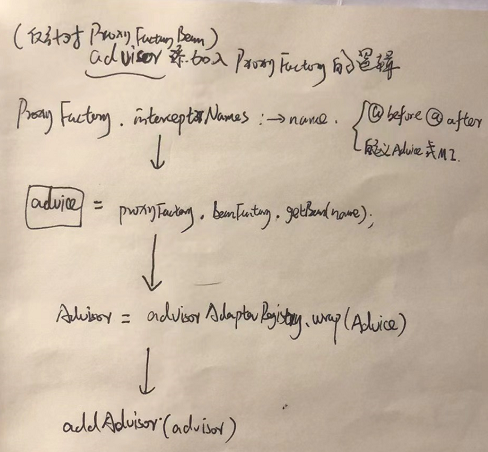
TIPS:Advice-Advisor-MethodInterceptor转化逻辑全过程
构建拦截器链chain的逻辑:
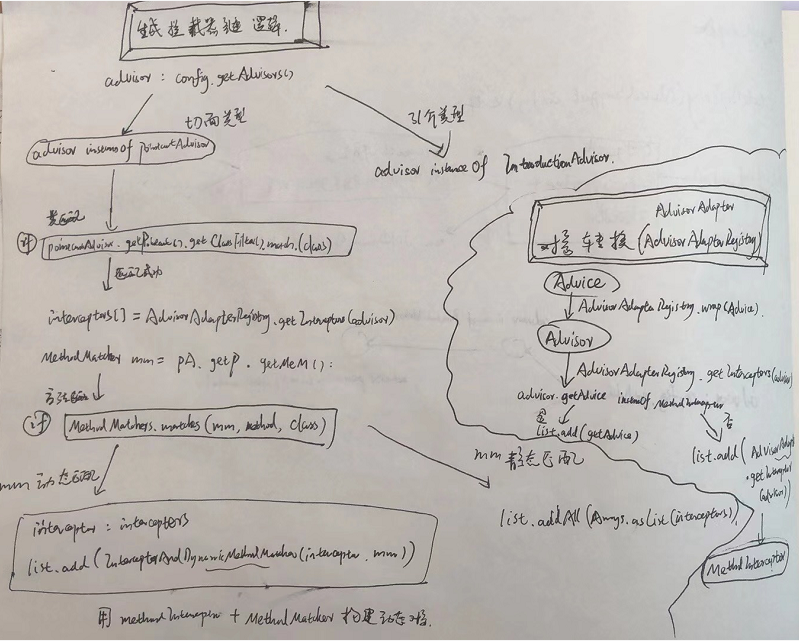
首先通过pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter.match(targetClass),判断当前对象targetClass是否需要切面增强,如果需要,通过AdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInterceptors(advisor),转换为interceptors对象;然后获取MethodMatcher,如果匹配到当前方法,且mm为动态匹配,那么将构建InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm),加入list;如果为静态匹配,构建 interceptors直接加入list。
这个chain链,会在ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed中调用(动态匹配的需要调用methodMatcher的三个参数的matches来做匹配),详情看[5.4.4.2 ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed方法。](# 5.4.4.2 ReflectiveMethodInvocation)
图一:advice的获取并转换为advisor,并add入proxyFactory:
图二:从proxyFactory中注册的advisor,转换为可执行的拦截器链,在proxy执行到代理方法时,拦截器链执行。
注意:
从可知上面的过程,aopProxy的方法拦截,是动态拦截,生成的proxy类,只是一个动态代理的对象,具体方法或者拦截器的增强,是在执行到proxy的特定方法时,触发拦截器链执行,来完成代理增强的逻辑。
借助[DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry](#5.5.5 DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry)将Advisor集合转换成MethodInterceptor

TAG1.1.1 registry.getInterceptors(advisor)
public class DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry implements AdvisorAdapterRegistry, Serializable {
//通知器适配器集合
private final List<AdvisorAdapter> adapters = new ArrayList<>(3);
// 默认就支持这几种类型的适配器(AdvisorAdapter能将advisor转换为AOP可以拦截识别的MethodInterceptor对象)
public DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry() {
registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter());
registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter());
registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter());
}
@Override
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(3);
//从advisor获取advice
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
//如果advice是MethodInterceptor类型,直接加入interceptors
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
//遍历注册在registry内的
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
//如果当前adapter支持转换当前advice
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
/**………………………………………………………………………………………………将advisor转换为methodinterceptor………………………………………………………… */
//TAG1.1.1.1 adapter.getInterceptor(advisor)
//通过getInterceptor转换,并添加入拦截器链interceptors上
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[0]);
}
//注册AdvisorAdapter,存入缓存adapters中List<AdvisorAdapter>的advisor转换器list
@Override
public void registerAdvisorAdapter(AdvisorAdapter adapter) {
this.adapters.add(adapter);
}
TAG1.1.1.1 adapter.getInterceptor(advisor)
这里,以MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter为例:
class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
@Override
public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
return (advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice);
}
//将advisor.getAdvice------>转换为对应的methodInterceptor
@Override
public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice) advisor.getAdvice();
//TAG1.1.1.1.1 MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice);
}
}
TAG1.1.1.1.1 MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
// 都转为了AOP联盟的MethodInterceptor 从而实现拦截统一的拦截工作
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
//转换后的interceptor持有MethodBeforeAdvice实例
private MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
//方法被拦截时,执行invoke,这里会执行增强的方法 advice.before
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//因为是methodBeforeAdvice,方法前增强,所以这里在执行链式调用mi.proceed之前,调用advice.before方法
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
/**………………………………………………………………………………………………链式调用的关键…………………………………………………………………………………………………… */
// 最终调用,实现了链式调用的效果
return mi.proceed();
}
}
在调用时候,methodinterceptor的invoke,会按照执行的方位点before、after、throw等,选择advice.before/after执行,然后,执行MethodInvocation.proceed,这里是实现链式调用的关键。
TAG2 invocation.proceed()
首先,创建方法的反射调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation
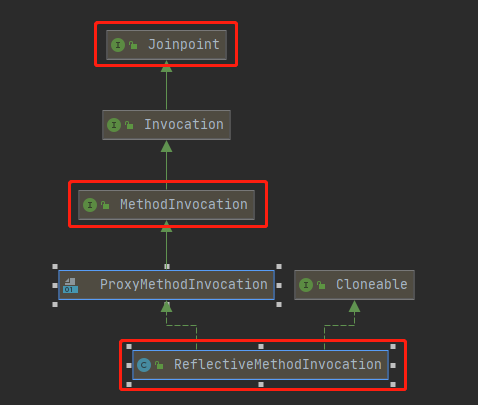
反射方法调用类,用反射method.invoke来调用target对象的目标方法,以及拦截器链chain,完成AOP的增强。子类通过重写invokeJoinpoint方法,来改变行为。
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
/**缓存了MethodInterceptor and InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher对象的list
调用的时候,需要进行动态确认,其类型前者还是后者 */
protected final List<?> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
@Nullable
//反射来调用joinpoint
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments);
}
/**该类实现proceed方法,来递归地执行chain链*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
//当执行到chain链中最后一个时,反射调用joinpoint点处的方法代码
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
//从缓存中逐个获取chain中的对象
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
/**……………………………………处理获取的chain中对象是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher的情况……………………………………………………*/
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
//获取当前target的Class对象
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
//当前代理方法动态匹配成功时,执行interceptor.invoke,调用拦截器方法
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
//如果当前拦截器,没有匹配上当前jointpoint内的method方法,执行proceed,进行chain链表中下一个调用
else {
//递归调用--------------完成链式调用的关键
return proceed();
}
}
/** ……………………………………………………………………判断获取的chain中对象是MethodInterceptor………………………………………………………………*/
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
//直接invoke调用
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
ReflectiveMethodInvocation的方法调用中,proceed执行拦截器链的逻辑如下:
1 通过执行proceed方法,执行拦截器链执行;
2 List<?> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers缓存当前joinpoint的拦截器链(joinpoint是一个待增强的method点),逐个获取chain中的属性;
3 判断对象是MethodInterceptor 还是 InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher,执行不同的逻辑:
3.1 如果是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher,即动态匹配拦截器,要调用InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher.methodMatcher.match方法判断当前拦截器是否需要拦截,
3.1.1 如果是,执行dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
3.1.2 如果不是,直接proceed(),递归调用,执行chain中下一个;
3.2 如果是MethodInterceptor,直接反射调用mi.invoke。
4 完成链式调用的关键,在3.1.2的proceed方法上。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号