第一次个人编程作业
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gdgy/CSGrade22-34 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 个人项目 - 作业 - 计科22级34班 - 班级博客 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) |
| 这个作业的目标 | 设计一个论文查重算法,给出一个原文文件和一个在这份原文上经过了增删改的抄袭版论文的文件,在答案文件中输出其重复率,并进行测试。 |
github地址:LAObeeDENG/3122004742: 软件工程第二次作业-个人项目-论文查重 (github.com)
一、需求
题目:论文查重
描述如下:
设计一个论文查重算法,给出一个原文文件和一个在这份原文上经过了增删改的抄袭版论文的文件,在答案文件中输出其重复率。
- 原文示例:今天是星期天,天气晴,今天晚上我要去看电影。
- 抄袭版示例:今天是周天,天气晴朗,我晚上要去看电影。
要求输入输出采用文件输入输出,规范如下:
- 从命令行参数给出:论文原文的文件的绝对路径。
- 从命令行参数给出:抄袭版论文的文件的绝对路径。
- 从命令行参数给出:输出的答案文件的绝对路径。
我们提供一份样例,课堂上下发,上传到班级群,使用方法是:orig.txt是原文,其他orig_add.txt等均为抄袭版论文。
注意:答案文件中输出的答案为浮点型,精确到小数点后两位
二、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 35 | 20 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 35 | 20 |
| Development | 开发**** | 425 | 565 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 180 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 60 | 35 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 15 | 15 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 15 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 60 | 60 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 120 | 180 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 30 | 20 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 80 | 75 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 45 | 45 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 25 | 20 |
| 合计 | 540 | 660 |
三、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
1. 设计思路
在设计计算模块时,目标是构建一个模块化、易维护的查重系统,能够综合余弦相似度和编辑距离两种算法的优势进行文本相似度的计算。本次采用了基于函数的设计而非面向对象的设计。这种设计更符合项目需求,也能保证清晰的逻辑结构。
2.函数设计
(1)文本读取与预处理函数
read_file(file_path):从文件中读取文本内容
preprocess_text(text):对读取的文本进行预处理,包括去除标点符号和多余空白字符;当文本字数大于800时,会去除长文本中的常见字,比如:“的”,“了”,“你”,“我”,“他”等等
(2)分词与词频统计:
segment_text(text):使用jieba库对文本进行分词,输出词语列表。
calculate_term_frequency(words):计算文本中每个词出现的频率。
(3)向量化与相似度计算:
text_to_vector(words, vocabulary):将分词后的文本转化为词频向量,构建用于计算余弦相似度的基础。
calculate_cosine_similarity(vec1, vec2):根据词频向量,计算两个文本的余弦相似度。
(4)编辑距离相似度:
calculate_edit_distance_similarity(text1, text2):计算两个文本的编辑距离,并根据编辑距离与文本长度之间的比例来衡量相似度。
(5)组合相似度计算:
similarity(text1, text2, cosine_weight, edit_distance_weight):将余弦相似度和编辑距离相似度加权计算得到最终的相似度值。
3.函数之间的关系
本算法共9个函数,各个函数之间的关系是线性依赖的,按照从文本处理到相似度计算的流程顺序调用,,具体流程如下:
(1)文件读取:从文件中读取原文和抄袭版文本。
(2)预处理:对读取的文本进行清理,去除标点和空白。
(3)分词:使用 jieba分词器将文本拆解成词语。
(4)词频统计和向量化:将词语列表转化为词频向量,准备进行余弦相似度计算。
(5)余弦相似度计算:通过余弦相似度算法,衡量两个文本的相似性。
(6)编辑距离计算:通过编辑距离算法,捕捉文本间的局部修改或顺序变化的影响。
(7)加权组合:将两种相似度按照设定的权重进行加权求和,得到最终的查重相似度。
算法流程图:

4.算法关键和独到之处
(1)余弦相似度:
主要用于计算长文本的全局相似度,适合长文本的查重,基于词频向量,忽略词的顺序变化。因此,适用于捕捉词语和语义的相似性,但对词序变化不敏感。
(2)编辑距离:
通过计算文本间的最小编辑操作(插入、删除、替换)的次数,捕捉局部修改或顺序变化的影响,对短文本或句子级别的比较非常有效。
(3)加权平均:
该模块的独到之处在于结合了两种不同的相似度算法,将全局相似度(余弦相似度)和局部变化(编辑距离)进行加权平均。通过设定不同权重(如 0.7 和 0.3),可以灵活调整两者对最终相似度的贡献。这种设计可以平衡文本整体相似和局部差异带来的影响,从而提高查重的准确性。
(4)去除停用词
停用词是指在语言中非常常见的词汇,它们虽然经常出现,但对文本的语义贡献较少,通常不会影响文本的核心内容,比如:“的”,“了”,“你”,“我”,“他”等等,因此在查重时将它们排除可以提高查重的准确性。
四、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
1.在pycharm中,我使用了利用line_profiler插件和line_profiler来检测每一个函数每一段代码所用的时间,查看每个模块的性能,便于性能分析。
2.我们先查看main函数的性能分析,similarity()函数部分占了99.9%最多的时间,约705毫秒,我们接着去查看similarity()函数
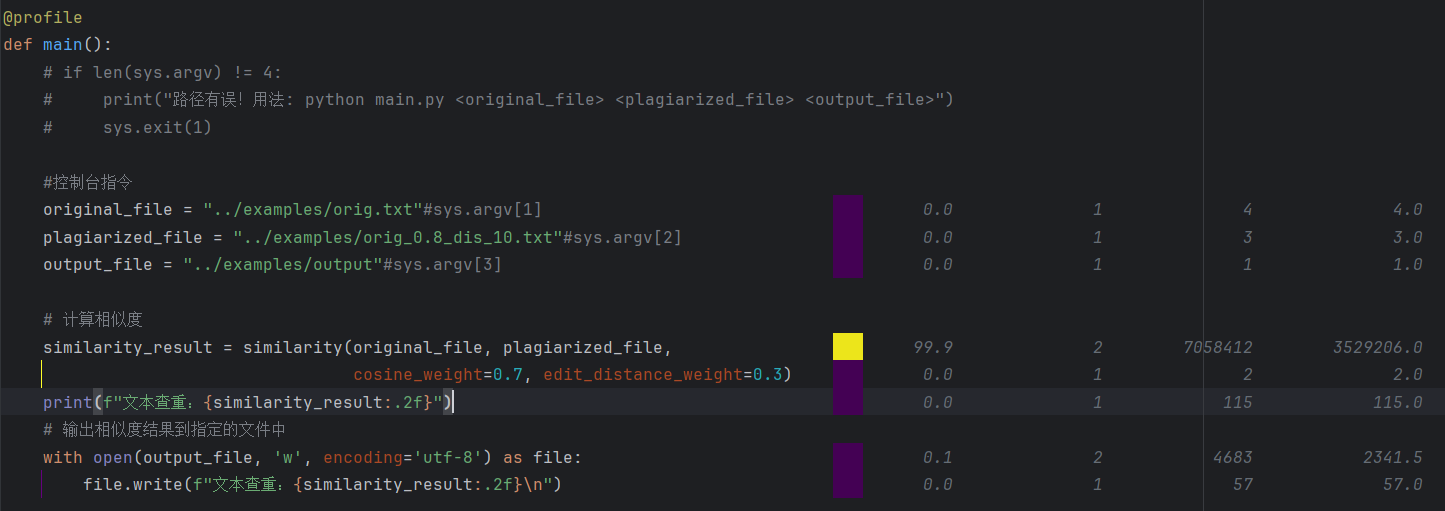
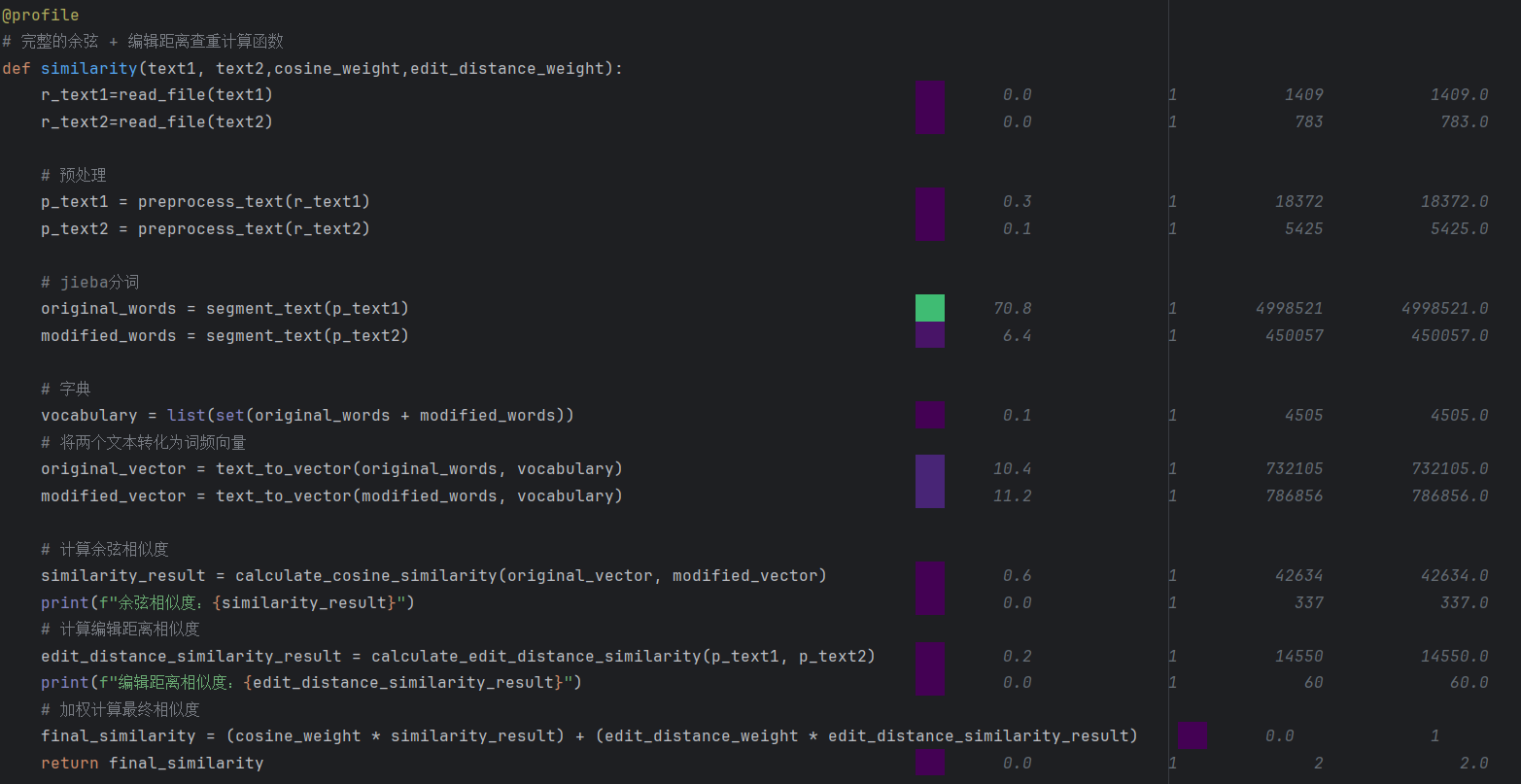
3.接着我们查看similarity(),可以看到jieba分词segment_text()这个语句占用时间最多,约545毫秒,总共消耗的时间占比到达77.2%
# jieba分词
original_words = segment_text(p_text1)
4.其次是转化词频向量text_to_vector(original_words, vocabulary)共占了21.6%,约151毫秒,所以可以考虑从这两个函数下手改进
# 将两个文本转化为词频向量
original_vector = text_to_vector(original_words, vocabulary)
modified_vector = text_to_vector(modified_words, vocabulary)
五.计算模块部分单元测试展示
1.测试预处理函数
# 测试1: 测试文本预处理函数 - 正常文本
def test1_preprocess_text_normal(self):
text = "今天是星期天,我去看电影了!"
expected_result = "今天是星期天我去看电影了"
print(preprocess_text(text))
self.assertEqual(preprocess_text(text), expected_result)
# 测试2: 测试文本预处理函数 - 特殊字符
def test2_preprocess_text_special_chars(self):
text = "today是 .星期天!!"
expected_result = "today是 星期天"
print(preprocess_text(text))
self.assertEqual(preprocess_text(text), expected_result)
# 测试3: 测试文本预处理函数 - 空字符串
def test3_preprocess_text_empty(self):
text = ""
expected_result = ""
self.assertEqual(preprocess_text(text), expected_result)
预处理函数的单元测试,测试了:预处理函数是否能正确去除正常文本中的标点符号和空格、多个连续特殊字符是否能被正确处理、字符串的处理情况。
测试的目标是能让预处理函数处理正常文本、特殊字符以及空字符串
作用是确保文本预处理功能在常规输入下工作正常同时对包含多个标点符号的文本和空输入的处理能力。
2.测试jieba分词
# 测试4: 测试jieba分词 - 中英文本
def test4_segment_text_normal(self):
text = "today is 星期天"
result = segment_text(text)
expected_words = ['today','is','星期', '天'] # 假设jieba分词结果
print(result)
self.assertGreater(len(result), 0)
self.assertTrue(any(word in result for word in expected_words))
# 测试5: 测试jieba分词 - 空字符串
def test5_segment_text_empty(self):
text = ""
result = segment_text(text)
self.assertEqual(result, [])
对jieba分词函数模块的测试,测试了中英文本的分词和空字符串的处理
测试目标是确认分词模块能够正常处理中英文词语和空字符串
测试结果应该是词结果中包含期望的关键词和返回空列表,符合预期。
3.测试词频向量生成函数
# 测试6: 测试词频向量生成 - 正常文本
def test6_text_to_vector_normal(self):
words = ['今天', '是', '星期天']
vocabulary = ['今天', '是', '星期', '天']
vector = text_to_vector(words, vocabulary)
expected_vector = np.array([1, 1, 0, 0])
np.testing.assert_array_equal(vector, expected_vector)
# 测试7: 测试词频向量生成 - 空文本
def test7_text_to_vector_empty(self):
words = []
vocabulary = ['今天', '是', '星期', '天']
vector = text_to_vector(words, vocabulary)
expected_vector = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0])
np.testing.assert_array_equal(vector, expected_vector)
测试词频向量生成函数是否能根据词汇表正确生成词频向量。测试词频向量生成函数对空输入的处理。
作用是确保词频向量化过程正确执行,词频分布符合预期以及确保函数在没有词的情况下生成全零向量。
测试结果也符合预期
4.测试余弦相似度和编辑距离相似度的计算
# 测试9: 测试余弦相似度 - 完全相同向量
def test9_cosine_similarity_identical(self):
vec1 = [1, 1, 1]
vec2 = [1, 1, 1]
similarity = calculate_cosine_similarity(vec1, vec2)
self.assertAlmostEqual(similarity, 1.0)
# 测试10: 测试编辑距离相似度 - 相近文本
def test10_edit_distance_similarity_close(self):
text1 = "今天是星期天"
text2 = "今天是周天"
similarity = calculate_edit_distance_similarity(text1, text2)
expected_similarity = 0.67 # 预期相似度
self.assertAlmostEqual(similarity, expected_similarity, places=2)
# 测试11: 测试编辑距离相似度 - 完全不同文本
def test11_edit_distance_similarity_different(self):
text1 = "今天是星期天"
text2 = "明天是工作日"
similarity = calculate_edit_distance_similarity(text1, text2)
self.assertLess(similarity, 0.5)
# 测试12: 测试编辑距离相似度 - 完全相同文本
def test12_edit_distance_similarity_identical(self):
text1 = "今天是星期天"
text2 = "今天是星期天"
similarity = calculate_edit_distance_similarity(text1, text2)
self.assertEqual(similarity, 1.0)
测试余弦相似度函数对正常向量的相似度计算和余弦相似度对完全相同向量的处理。也测试了编辑距离函数对相似文本的处理和编辑距离对完全不同文本的处理还有编辑距离对相同文本的相似度计算。
对于完全相同向量,余弦相似度计算值为1,对于相近文本和不同文本,余弦相似度要符合计算值。编辑距离相似度同样也是。
这个测试是为了确保两个相似度计算算法在各种文本下都不出错。
5.测试整体相似度最终计算函数
# 测试13: 测试相似度函数 - 正常相似文本
def test13_similarity_normal(self):
text1 = "../examples/orig.txt"
text2 = "../examples/orig_0.8_add.txt"
similarity_result = similarity(text1, text2, cosine_weight=0.7, edit_distance_weight=0.3)
self.assertGreater(similarity_result, 0.7) # 预期相似度大于0.7
# 测试14: 测试相似度函数 - 相同文本
def test14_similarity_identical(self):
text1 = "../examples/orig.txt"
text2 = "../examples/orig.txt"
similarity_result = similarity(text1, text2, cosine_weight=0.7, edit_distance_weight=0.3)
self.assertAlmostEqual(similarity_result, 1.0)
# 测试15: 测试相似度函数 - 完全不同文本
def test15_similarity_different(self):
text1 = "../examples/orig.txt"
text2 = "../examples/chaos.txt"
similarity_result = similarity(text1, text2, cosine_weight=0.7, edit_distance_weight=0.3)
print(f"文本查重:{similarity_result:.2f}")
self.assertLess(similarity_result, 0.1)
#测试16: 测试相似度函数 - 不存在的文本文件:报错
def test16_similarity_none(self):
text1 = "../examples/orig.txt"
text2 = "../examples/cccccc.txt"
similarity_result = similarity(text1, text2, cosine_weight=0.7, edit_distance_weight=0.3)
print(f"文本查重:{similarity_result:.2f}")
self.assertLess(similarity_result, 0.1)
最终计算函数把读路径,预处理,分词,向量化,计算相似度合为一体。测试了最终计算函数计算相似文本、相同文本、完全不同文本的处理。同时,测试了异常处理。
测试的作用是验证整体流程是否准确,结果是否合理,确保了不同文本的相似度较低。
最终测试结果也是符合预期,能够验证不同文本的区分能力,符合测试需求
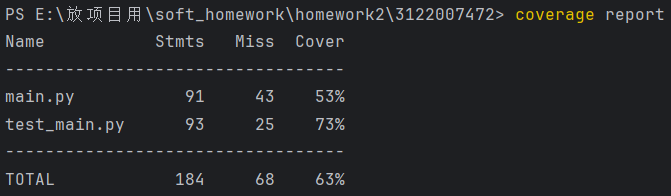
6.代码覆盖率
以下是测试代码的覆盖率,由Coverage得到
六、计算模块部分异常处理说明
def read_file(file_path):
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
return file.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"没找到文件: {file_path}")
读文件函数,如果没找到文件,则报错FileNotFoundError(f"没找到文件: {file_path}")
def similarity(text1, text2,cosine_weight,edit_distance_weight):
r_text1=read_file(text1)
r_text2=read_file(text2)
# 预处理
p_text1 = preprocess_text(r_text1)
p_text2 = preprocess_text(r_text2)
if not p_text1 or not p_text2:
raise ValueError("报错,空文件无法查重!请重新输入!")
在总重复度计算函数中,预处理过后的文本如果是空,则报错
def main():
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print("输入有误!用法: python main.py <original_file> <plagiarized_file> <output_file>")
sys.exit(1)
#控制台指令
original_file = sys.argv[1]
plagiarized_file = sys.argv[2]
output_file = sys.argv[3]
在main函数中,如果控制台输入有误,输入错误或少输入地址则报错



