高并发下的HashMap,ConcurrentHashMap
参照:
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/dzNq50zBQ4iDrOAhM4a70A
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/1yWSfdz0j-PprGkDgOomhQ
JDK1.7 多线程下死循环
源代码:
/** * Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a * larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the * number of keys in this map reaches its threshold. * * If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not * resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE. * This has the effect of preventing future calls. * * @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two; * must be greater than current capacity unless current * capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value * is irrelevant). */ void resize( int newCapacity) { // 当前数组 Entry[] oldTable = table; // 当前数组容量 int oldCapacity = oldTable.length ; // 如果当前数组已经是默认最大容量MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ,则将临界值改为Integer.MAX_VALUE 返回 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } // 使用新的容量创建一个新的链表数组 Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; // 将当前数组中的元素都移动到新数组中 transfer(newTable); // 将当前数组指向新创建的数组 table = newTable; // 重新计算临界值 threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); } /** * Transfers all entries from current table to newTable. */ void transfer(Entry[] newTable) { // 当前数组 Entry[] src = table; // 新数组长度 int newCapacity = newTable.length ; // 遍历当前数组的元素,重新计算每个元素所在数组位置 for (int j = 0; j < src. length; j++) { // 取出数组中的链表第一个节点 Entry<K,V> e = src[j]; if (e != null) { // 将旧链表位置置空 src[j] = null; // 循环链表,挨个将每个节点插入到新的数组位置中 do { // 取出链表中的当前节点的下一个节点 Entry<K,V> next = e. next; // 重新计算该链表在数组中的索引位置 int i = indexFor(e. hash, newCapacity); // 将下一个节点指向newTable[i] e. next = newTable[i]; // 将当前节点放置在newTable[i]位置 newTable[i] = e; // 下一次循环 e = next; } while (e != null); } } }
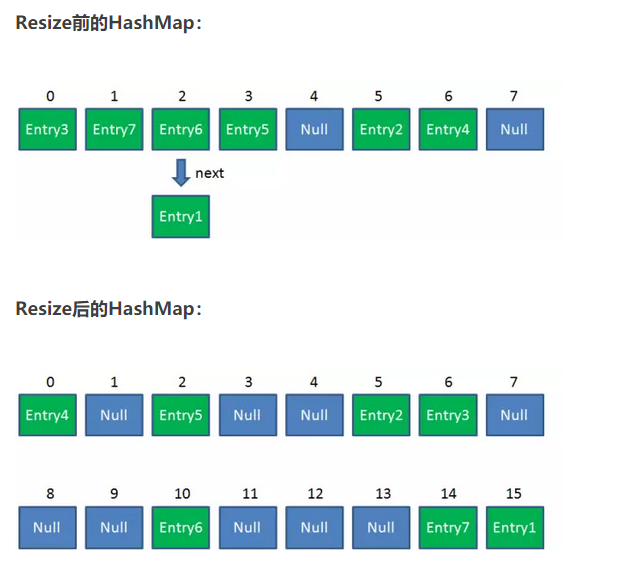
resize步骤:
1.扩容
创建一个新的Entry空数组,长度是原数组的2倍。
2.ReHash
遍历原Entry数组,把所有的Entry重新Hash到新数组。为什么要重新Hash呢?因为长度扩大以后,Hash的规则也随之改变。
ConcuttrntHashMap
改变线程安全的方法:
- HashTable
- Collections.synchronizedMap
性能是个为你,无论是读操作还是写操作,都会给整个集合加锁

利用 ConcurrentHashMap
Segment是什么呢?Segment本身就相当于一个HashMap对象。
同HashMap一样,Segment包含一个HashEntry数组,数组中的每一个HashEntry既是一个键值对,也是一个链表的头节点。
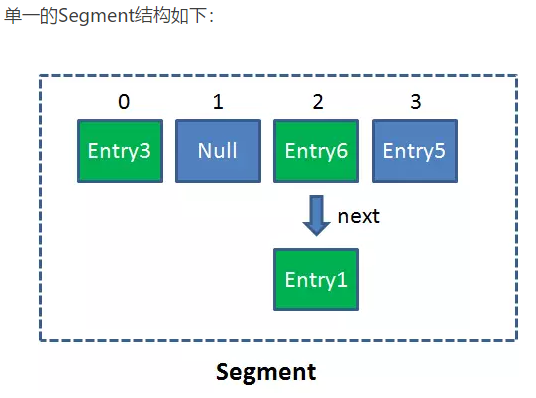
在ConcurrentHashMap集合中有多少个呢?有2的N次方个segment

ConcurrentHashMap优势就是采用了[锁分段技术]
每个segment就好比一个自治区,读写操作高度自治,segment之间相互不影响
- 不同Segment的写入是可以并发执行的。
- 同一Segment的写和读是可以并发执行的。
- Segment的写入是需要上锁的,因此对同一Segment的并发写入会被阻塞。
Get方法:
1.为输入的Key做Hash运算,得到hash值。
2.通过hash值,定位到对应的Segment对象
3.再次通过hash值,定位到Segment当中数组的具体位置。
Put方法:
1.为输入的Key做Hash运算,得到hash值。
2.通过hash值,定位到对应的Segment对象
3.获取可重入锁
4.再次通过hash值,定位到Segment当中数组的具体位置。
5.插入或覆盖HashEntry对象。
6.释放锁。
ConcurrentHashMap读写都需要二次定位
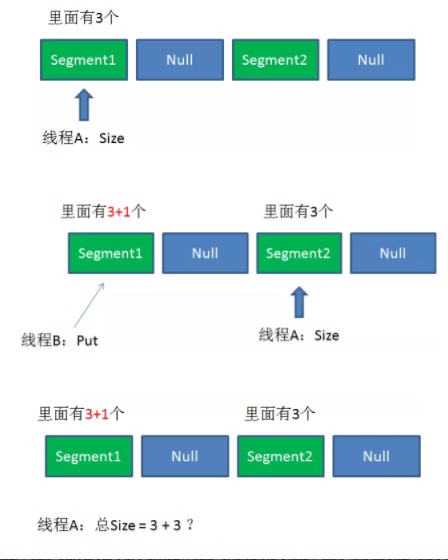
size的一致性问题?
源代码:
public int size() { // Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to // continuous async changes in table, resort to locking. final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments; int size; boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bits long sum; // sum of modCounts long last = 0L; // previous sum int retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retry try { for (;;) { if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation } sum = 0L; size = 0; overflow = false; for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) { Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j); if (seg != null) { sum += seg.modCount; int c = seg.count; if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0) overflow = true; } } if (sum == last) break; last = sum; } } finally { if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) segmentAt(segments, j).unlock(); } } return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size; }
1.遍历所有的Segment。
2.把Segment的元素数量累加起来。
3.把Segment的修改次数累加起来。
4.判断所有Segment的总修改次数是否大于上一次的总修改次数。如果大于,说明统计过程中有修改,重新统计,尝试次数+1;如果不是。说明没有修改,统计结束。
5.如果尝试次数超过阈值,则对每一个Segment加锁,再重新统计。
6.再次判断所有Segment的总修改次数是否大于上一次的总修改次数。由于已经加锁,次数一定和上次相等。
7.释放锁,统计结束。
为了尽量不锁住所有Segment,首先乐观地假设Size过程中不会有修改。当尝试一定次数,才无奈转为悲观锁,锁住所有Segment保证强一致性。



