初识消息中间件之 ==> ActiveMQ
一、消息队列概述
消息(Message)是指在应用间传送的数据。消息可以非常简单,比如只包含文本字符串,也可以更复杂,可能包含嵌入对象。
消息队列(Message Queue)是一种应用间的通信方式,消息发送后可以立即返回,由消息系统来确保消息的可靠传递。消息发布者只管把消息发布到 MQ 中而不用管谁来取,消息使用者只管从 MQ 中取消息而不管是谁发布的。这样发布者和使用者都不用知道对方的存在。
消息队列中间件是分布式系统中重要的组件,主要解决异步消息,流量削峰,应用耦合等问题。实现高性能,高可用,可伸缩和最终一致性架构。是大型分布式系统不可缺少的中间件。目前使用较多的消息队列产品有ActiveMQ,RabbitMQ,ZeroMQ,Kafka,MetaMQ,RocketMQ等。
生活中的例子
老式餐厅点餐后需呆在座位上等餐,中途不能离开去干别的事,如果离开去干别的事,餐好了,点餐人却不知道。
新式餐厅点餐后,餐厅会提供一个“电子盘”给顾客,顾客可以不用在店里等餐,可以去附近逛逛,买买东西,等餐好了,手上的“电子盘”就会响,通知顾客可以回去就餐了。
对比以上两种形式,第二种情形就像消息队列一样,点完餐以后就可以去处理别的事情,不用一直在餐厅等着。
二、消息队列的作用
上面说了消息队列主要解决了异步处理,流量削峰,应用耦合等三个方面的问题。
异步处理
场景说明:用户注册后,系统要发送注册邮件和注册短信。传统的方式有两种,串行模式和并行方式 。
串行模式:将注册信息存入数据库成功后,先发送注册邮件再发送注册短信,以上三个步骤都完成后,将成功的信息返回给客户端。
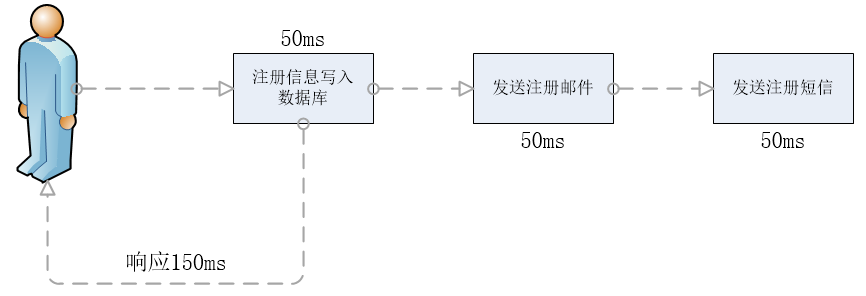
并行模式:将注册信息存入数据库成功后,发送邮件的同时发送注册短信,以上三个任务都完成后返回给客户端,与串行模式的差别是并行模式可以提高处理的时间。

假设每个业务结点的处理时间为50ms,不考虑网络开销,则串行模式的时间为150ms,并行模式的时间为100ms。
如果引入消息队列,能够大大缩短响应时间,如下:

用户注册信息写入数据库后,再将发送邮件和短信写入消息队列,然后直接返回注册结果,总共耗时55m,是并行的一半左右,是串行的三分之一左右,大大提高了系统的处理能力。
应用解耦
场景说明:用户下单后,订单系统需要通知库存系统。传统的做法是,订单系统调用库存系统的接口,如图所示:

传统模式的缺点:
- 假如库存系统无法访问,则订单减库存将失败,从而导致下单失败;
- 订单系统与库存系统耦合;
引入消息队列的方案如下:
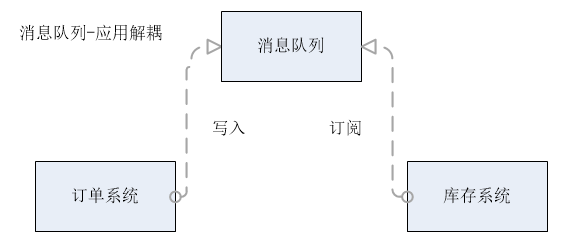
- 订单系统:用户下单后,订单系统完成持久化处理,将消息写入消息队列,返回用户订单下单成功。
- 库存系统:订阅下单的消息,采用拉/推的方式,获取下单信息,库存系统根据下单信息,进行库存操作。
- 假如:在下单时库存系统不能正常使用。也不影响正常下单,因为下单后,订单系统写入消息队列就不再关心其他的后续操作了。实现订单系统与库存系统的应用解耦。
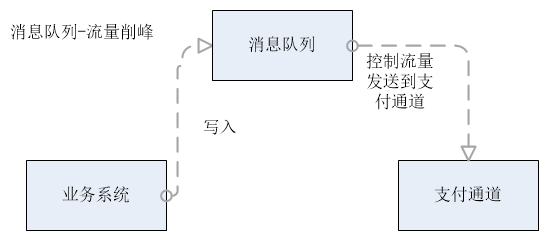
流量削峰
场景说明:业务系统处理能力远远大于支付渠道处理能力,假如不控制流量把全部请求往支付渠道发送,支付渠道可能会挂掉,导致整个业务不能成功。
这时引入消息队列,控制流量,让请求有序的进入支付渠道
日志处理
日志处理是指将消息队列用在日志处理中,比如 Kafka 的应用,解决大量日志传输的问题。架构简化如下:
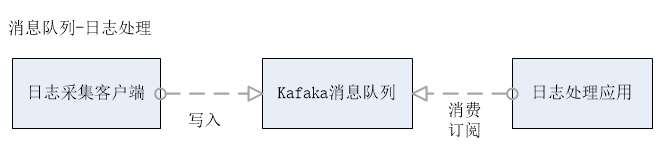
- 日志采集客户端,负责日志数据采集,定时写受写入Kafka队列;
- Kafka消息队列,负责日志数据的接收,存储和转发;
- 日志处理应用:订阅并消费kafka队列中的日志数据;
三、Active MQ
下载
http://activemq.apache.org/components/classic/download/
安装
直接解压,然后移动到指定目录即可。
>tar zxvf apache-activemq-5.15.10-bin.tar.gz >mv ./apache-activemq-5.15.10 /usr/local
启动
>/usr/local/activemq-5.15.10/bin/activemq start # 检查启动状态 [root@cbooy bin]# jps 3168 Jps 2268 activemq.jar # activemq启动的默认端口号 61616 [root@cbooy bin]# lsof -i:61616 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME java 2268 root 132u IPv6 15719 0t0 TCP *:61616 (LISTEN)
其他基本命令
> activemq restart # 重启 > activemq stop # 关闭 > activemq start > /activemq_home/logs/activemq.log # 落地相关信息,打印日志
指定配置文件的启动
./bin/activemq start xbean:/usr/local/activemq-5.15.10/conf/activemq.xml
后台图形化界面支持
- http://127.0.0.1:8161/admin
- 默认用户名/密码, admin/admin
- 图形化页面相关信息说明
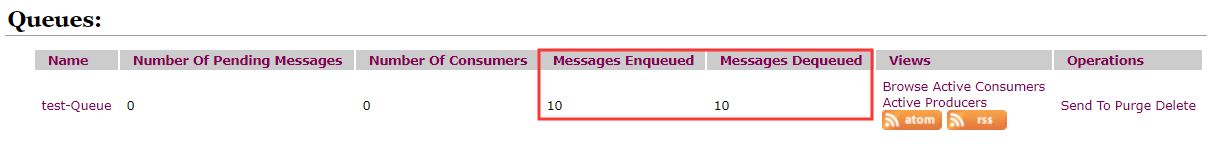
- Number Of Pending Messages
- 等待消费的消息
- 未出队列的数量
- Number Of Consumers
- 消费者数量
- Messages Enqueued
- 进队消息数,进入队列的总数包括出队的消息数
- Messages Dequeued
- 出队消息数,即消费者消费后的消息
- Number Of Pending Messages
四、Java操作ActiveMQ
依赖 jar 包
dependencies { compile('org.apache.activemq:activemq-all:5.15.9') compile('org.apache.activemq:activemq-pool:5.15.9') }
第一种模式:Queue
生产流程
- 创建连接工厂对象
- 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection)
- 从连接中建立一个会话(Session)
- 基于会话建立目的地(Queue)
- 基于会话创建生产者(Producer)
- 在会话的基础上创建一条消息(Message)
- 生产者将消息发出
- 资源关闭

public class Producer { // activemq服务的地址,默认通信端口为61616 private static final String URL = "tcp://192.168.182.128:61616"; // 定义队列的名称 private static final String QUEUE_NAME = "test-Queue"; public static void main(String[] args) { MessageProducer producer = null; Session session = null; Connection connection = null; try { // 创建连接工厂对象 ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(URL); // 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection) connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); connection.start(); // 从连接中建立一个会话(Session) session = connection.createSession(false, 1); // 基于会话建立队列(Queue) Queue queue = session.createQueue(QUEUE_NAME); // 基于会话创建生产者(Producer) producer = session.createProducer(queue); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // 在会话的基础上创建一条消息(Message) TextMessage textMessage = session.createTextMessage("test-mq:" + i); // 生产者将消息发出 producer.send(textMessage); } } catch (Exception ex) { throw new IllegalStateException(ex); // 资源关闭 } finally { try { if (null != producer) { producer.close(); } } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (null != session) { session.close(); } } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (null != connection) { connection.close(); } } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
执行以上代码后,我们可以在管理页面上看到如下情况:
 消费流程
消费流程
- 创建连接工厂对象
- 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection)
- 从连接中建立一个会话(Session)
- 基于会话建立目的地(Queue)
- 基于会话创建消费者(Consumer)
- 消费者接收消息
- 资源关闭

public class Consumer { // activemq服务地址,默认通信端口为61616 private static final String URL = "tcp://192.168.182.128:61616"; // 定义队列的名称 private static final String QUEUE_NAME = "test-Queue"; public static void main(String[] args) { MessageConsumer consumer = null; Session session = null; Connection connection = null; try { // 创建连接工厂对象 ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(URL); // 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection) connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); connection.start(); // 从连接中建立一个会话(Session) session = connection.createSession(false, 1); // 基于会话建立队列(Queue) Queue queue = session.createQueue(QUEUE_NAME); // 基于会话创建消费者(Consumer) consumer = session.createConsumer(queue); // 接收消息的第一种方式,阻塞式接收 // Message message = consumer.receive(); // System.out.println("consumer recive message = " + message); // 接收消息的第二种方式,使用监听器 consumer.setMessageListener(msg -> { TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) msg; try { System.out.println("textMessage = " + textMessage.getText()); } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } } }
执行以上代码后,我们可以在管理页面上看到如下情况:
我们这次先运行两个 Consumer,由于 Consumer 种没有关闭资源,所以会一直保持和 ActiveMQ的连接。
然后再运行 Producer,我们来看看现象:

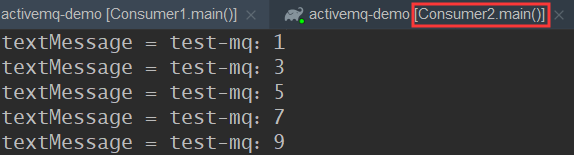
控制台打印的信息中,Consumer1 消费的信息都是偶数的,Consumer2 消费的信息都是奇数的,一条消息只能被一个Consumer消费。
第二种模式:Topic
生产流程
- 创建连接工厂对象
- 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection)
- 从连接中建立一个会话(Session)
- 基于会话建立目的地(Topic)
- 基于会话创建生产者(Producer)
- 在会话的基础上创建一条消息(Message)
- 生产者将消息发出
- 资源关闭

public class Producer { // activemq服务地址,默认通信端口为61616 private static final String URL = "tcp://192.168.182.128:61616"; // 定义队列的名称 private static final String TOPIC_NAME = "test-Topic"; public static void main(String[] args) { MessageProducer producer = null; Session session = null; Connection connection = null; try { // 创建连接工厂对象 ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(URL); // 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection) connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); connection.start(); // 从连接中建立一个会话(Session) session = connection.createSession(false, 1); // 基于会话建立目的地(Topic) Topic topic = session.createTopic(TOPIC_NAME); // 基于会话创建生产者(Producer) producer = session.createProducer(topic); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // 在会话的基础上创建一条消息(Message) TextMessage textMessage = session.createTextMessage("test-topic:" + i); // 生产者将消息发出 producer.send(textMessage); } } catch (Exception ex) { throw new IllegalStateException(ex); // 资源关闭 } finally { try { if (null != producer) { producer.close(); } } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (null != session) { session.close(); } } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (null != connection) { connection.close(); } } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
消费流程
- 创建连接工厂对象
- 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection)
- 从连接中建立一个会话(Session)
- 基于会话建立目的地(Topic)
- 基于会话创建消费者(Consumer)
- 消费者接收消息
- 资源关闭

public class Consumer1 { // activemq服务的地址,默认通信端口为61616 private static final String URL = "tcp://192.168.182.128:61616"; // 定义队列的名称 private static final String TOPIC_NAME = "test-Topic"; public static void main(String[] args) { MessageConsumer consumer = null; Session session = null; Connection connection = null; try { // 创建连接工厂对象 ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(URL); // 从工厂中建立一个连接并开启(Connection) connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); connection.start(); // 从连接中建立一个会话(Session) session = connection.createSession(false, 1); // 基于会话建立目的地(Topic) Topic topic = session.createTopic(TOPIC_NAME); // 基于会话创建消费者(Consumer) consumer = session.createConsumer(topic); // 接收消息的第一种方式,阻塞式接收 // Message message = consumer.receive(); // System.out.println("consumer recive message = " + message); // 接收消息的第二种方式,使用监听器 consumer.setMessageListener(msg -> { TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) msg; try { System.out.println("textMessage = " + textMessage.getText()); } catch (JMSException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } } }
Queue 模式和 Topic 模式,代码十分相似,一个是创建Queue,而另外一个是创建Topic。
现在我们来运行三个 Consumer,再运行 Producer,来看看现象
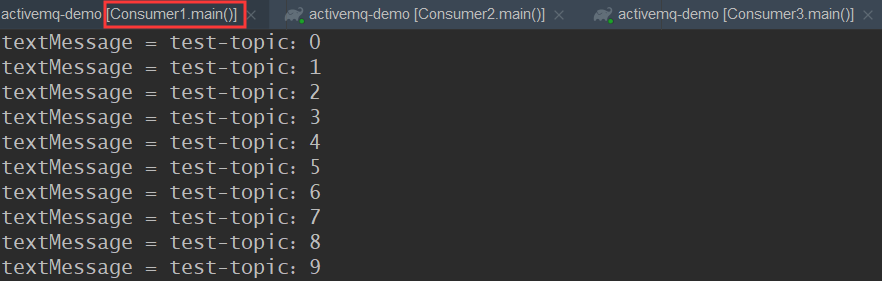
控制台打印的信息中,三个Consumer 都消费了所有消息,一条消息只能被多个 Consumer消费。
五、SpringBoot整合ActiveMQ
Queue模式
Producer端:
1、引入依赖

dependencies { implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web') implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop') testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test') // 导入activemq启动器依赖 implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-activemq') }
2、新建 application.yaml 配置文件并进行基本配置

server: port: 8888 servlet: context-path: /queue-producer spring: activemq: broker-url: tcp://192.168.182.128:61616
3、创建配置类

@EnableJms @Configuration public class ProducerConfig { @Bean public Queue createQueue(){ return new ActiveMQQueue("springboot-queue"); } }
4、创建 Producer 类

@Component public class QueueProducer { @Autowired private Queue queue; @Autowired private JmsMessagingTemplate jmsTemplate; public String sendMsg(String msg) { jmsTemplate.convertAndSend(queue, msg); return "send success"; } }
5、创建 Controller 接收消息

@Slf4j @RestController public class ProducerController { @Autowired private QueueProducer producer; @RequestMapping("/producer") public String produce(String msg) { log.info("spring boot produce msg={}", msg); return producer.sendMsg(msg); } }
6、创建启动类

@SpringBootApplication public class ProducerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ProducerApplication.class); } }
Consumer端:
1、引入依赖
和 Producer 端一样
2、新建 application.yaml 配置文件并进行基本配置

server: port: 9999 spring: activemq: broker-url: tcp://192.168.182.128:61616
3、创建 Consumer 类

@Slf4j @Component public class QueueConsumer { @JmsListener(destination = "springboot-queue") public void recive(String msg) { log.info("spring boot queue consumer receive msg={}", msg); } }
4、创建启动类

@EnableJms @SpringBootApplication public class ConsumerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class); } }
验证:
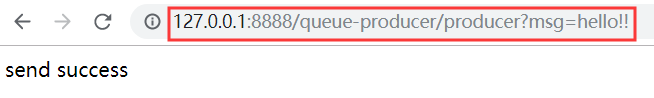


分别把 Producer端和 Consumer端都启动起来,然后在浏览器中发送 Get请求,Producer端接收请求并将消息发给 ActiveMQ服务端,然后 Consumer端接收到 ActiveMQ的消息。
Topic模式
topci模式的实现和queue模式基本一样,只是有一处不太一样, Producer端和 Consumer端的配置类都需要多配置一个 ContainerFactory,如下:
@Bean public JmsListenerContainerFactory topicListenerContainerFactory(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory){ DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory factory = new DefaultJmsListenerContainerFactory(); factory.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory); // topic类型消息必须设置为true,false则表示是queue类型 factory.setPubSubDomain(true); return factory; }
同时在 @JmsListener注解中,需要加上上面这个方法,如下:
@Slf4j @Component public class TopicConsumer { @JmsListener(destination = "springboot-topic",containerFactory = "topicListenerContainerFactory") public void recive(String msg){ log.info("spring boot topic consumer recive msg={} ",msg); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号