Java学习之==>异常体系
一、定义
程序运行时总是会遇到各种各样的问题,Java中的异常体系就是针对这些问题提出的统一的处理方案。在Java中,将这些各种各样的问题进行归类后,统一称为异常。
二、分类
我们先来看看下面这个图:

- 错误(Error)
- 虚拟机错误(VirtualMachineError),如:资源耗尽、内存溢出;
- 异常(Exception)
- 运行时异常(RuntimeException)
- 受检异常(Checked Exception)
由上图可以看出来,Java的异常体系由 Throwable 类作为超类,两个直接子类是 Error 类和 Exception 类分别代表错误和异常。其中,异常又包括运行时异常(RuntimeException)和受检异常(Checked Exception),下面将介绍这些错误和异常的区别:
1、错误(Error)和异常(Exception)
Error 是程序无法处理的错误,它是由Java虚拟机(JVM)产生和抛出的,比如:OutOfMemoryError、ThreadDeath等。这些异常发生时,Java虚拟机(JVM)一般会选择线程终止。
Exception 是程序本身可以处理的异常,这种异常分两大类,运行时异常和受检异常,程序中可以处理这些异常。
2、运行时异常(RuntimeException)和受检异常(Checked Exception)
运行时异常都是RuntimeException类及其子类异常,如NullPointerException、IndexOutOfBoundsException等,此类异常属于不可查异常,一般是由程序逻辑错误引起的,在程序中可以选择捕获处理,也可以不处理。
受检异常是除RuntimeException以外的异常,类型上都属于Exception类及其子类。从程序语法角度讲是必须进行处理的异常,如果不处理,程序就不能编译通过。如IOException、SQLException等,在程序中,通常不会自定义该类异常,而是直接使用系统提供的异常类。
三、异常的处理
1、受检异常
通常,我们在处理受检异常时有三种方式:
第一种:在方法名后面使用关键字throws抛出异常,同时在调用该方法时需要使用try..catch来处理该异常
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { try { demo01(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private static void demo01() throws FileNotFoundException { new FileInputStream(new File("test.log")); } }
第二种:直接使用try..catch处理,自己抛出,自己处理
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { demo01(); } private static void demo01() { try { new FileInputStream(new File("test.log")); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
第三种:使用try..catch,在try里面把异常声明出来,然后再catch
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { demo01(); } private static void demo01() { try (FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("test.log"))) { } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果如下:

2、运行时异常
在编译时,运行时异常不会被发现,所以不要要求在代码中一定要处理这些异常。但是,如果程序员愿意,也可以使用 try...catch...finally 来处理这些异常。对于这些异常,发生的原因多半是代码写的有问题,我们应该修正代码,而不是去通过异常处理器处理。
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { demo01(0); } private static void demo01(Integer num) { if (num == 0) { throw new ArithmeticException("分母不能为0"); } int result = 1024/num; } }
上面这种情况,如果没有 if() 代码,程序在运行过程中会抛出异常中断程序,虽然我们增加了 if() 代码块主动抛出了异常增加了异常的可读性,但是程序仍然会中断。正确的处理方式是我们可以在 if() 代码块下进行一些其他逻辑的处理,从而程序不会走到除法分支,从而不会报错。这就是上面所说的,运行时异常,我们通常需要去优化代码逻辑,而不是处理异常。
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { demo01(0); } private static void demo01(Integer num) { try { int result = 1024/num; }catch (ArithmeticException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println("处理完毕"); } } }
这种情况是使用 try...catch...finally 捕获异常再进行处理。
四、异常处理流程
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { demo01(0); System.out.println("-------------"); demo01(1); } private static int demo01(Integer num) { try { // 这里是正常的业务代码,要被我处理的代码, System.out.println("AAA"); int result = 1024 / num; System.out.println("BBB"); return result; } catch (Exception e) { // 这里是出了问题时怎么处理的 System.out.println("CCC"); return -1; } finally { // 最后的收尾动作,finally中不要写retrun,不然前面的结果不能返回 System.out.println("DDD"); return -2; } } }
运行结果:

先执行try中的代码块,如果没有报错则在return前执行finally中的代码块
如果try中的代码块有报错,则执行catch中的代码块,在return前执行finally中的代码块
如果finally中有return,则不会执行try中代码块的return和catch中的代码块,所以一般finally中的代码块一般不写return
五、常用写法
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { demo01(); } private static void demo01() { try { // 被检查的代码块 new FileInputStream(new File("test.log")); }catch (IllegalStateException ex){ // 第一个要处理的异常 ex.printStackTrace(); }catch (IllegalFormatException ex){ // 第二个要处理的异常 ex.printStackTrace(); }catch (IllegalArgumentException ex){ // 第三个要处理的异常 ex.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException ex){ // 第四个要处理的异常 ex.printStackTrace(); }finally { // 最终怎么做 System.out.println("异常处理完成"); } } }
六、自定义异常
如果要自定义异常类,则继承Exception类即可,因此这样的自定义异常都属于受检异常(checked exception)。如果要自定义运行时异常,则继承自类RuntimeException。按照惯例,自定义的异常应该总是包含如下的构造函数:
- 一个无参构造函数;
- 一个带有String参数的构造函数,并传递给父类的构造函数;
- 一个带有String参数和Throwable参数,并都传递给父类构造函数;
- 一个带有Throwable 参数的构造函数,并传递给父类的构造函数;
如下:

public class TestException extends RuntimeException { public TestException() { } public TestException(String message) { super(message); } public TestException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public TestException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } }
调用如下:
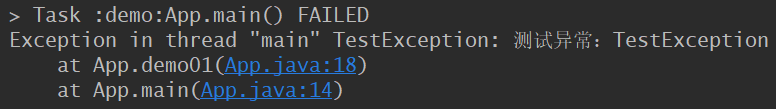
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { demo01(); } private static void demo01() { throw new TestException("测试异常:TestException"); } }
运行结果:
七、异常方法分析
常用的异常方法包括以下三个,通过源码来分析以下它们的使用:
- printStackTrace()
- getStackTrace()
- getMessage()

public StackTraceElement[] getStackTrace() { return getOurStackTrace().clone(); } private synchronized StackTraceElement[] getOurStackTrace() { // Initialize stack trace field with information from // backtrace if this is the first call to this method if (stackTrace == UNASSIGNED_STACK || (stackTrace == null && backtrace != null) /* Out of protocol state */) { int depth = getStackTraceDepth(); stackTrace = new StackTraceElement[depth]; for (int i=0; i < depth; i++) stackTrace[i] = getStackTraceElement(i); } else if (stackTrace == null) { return UNASSIGNED_STACK; } return stackTrace; }
getStackTrace()返回的是通过getOurStackTrace方法获取的StackTraceElement[]数组,而这个StackTraceElement是ERROR的每一个cause by的信息。

public void printStackTrace() { printStackTrace(System.err); } /** * Prints this throwable and its backtrace to the specified print stream. * * @param s {@code PrintStream} to use for output */ public void printStackTrace(PrintStream s) { printStackTrace(new Throwable.WrappedPrintStream(s)); } private void printStackTrace(Throwable.PrintStreamOrWriter s) { // Guard against malicious overrides of Throwable.equals by // using a Set with identity equality semantics. Set<Throwable> dejaVu = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<Throwable, Boolean>()); dejaVu.add(this); synchronized (s.lock()) { // Print our stack trace s.println(this); StackTraceElement[] trace = getOurStackTrace(); for (StackTraceElement traceElement : trace) s.println("\tat " + traceElement); // Print suppressed exceptions, if any for (Throwable se : getSuppressed()) se.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, SUPPRESSED_CAPTION, "\t", dejaVu); // Print cause, if any Throwable ourCause = getCause(); if (ourCause != null) ourCause.printEnclosedStackTrace(s, trace, CAUSE_CAPTION, "", dejaVu); } }
printStackTrace()返回的是一个void值,但是可以看到其方法内部将当前传入打印流锁住,然后同样通过getOurStackTrace方法获取的StackTraceElement[]数组,只不过printStackTrace()方法直接打印出来了。而getStackTrace()则是得到数组,使用者可以根据自己的需求去得到打印信息,相比printStackTrace()会更详细一些。

/** * Specific details about the Throwable. For example, for * {@code FileNotFoundException}, this contains the name of * the file that could not be found. * * @serial */ private String detailMessage; /** * Returns the detail message string of this throwable. * * @return the detail message string of this {@code Throwable} instance * (which may be {@code null}). */ public String getMessage() { return detailMessage; }
getMessage()只是获取到了异常的名称。
八、Java异常体系设计分析
我们先来看看Java异常体系的继承机构

Throwable是所有子类的基类,分为 Exception 和 Error 两个分支,Exception 和 Error 又分别有他们自己的子类,层层继承。
再来看看所有类中实现的方法:
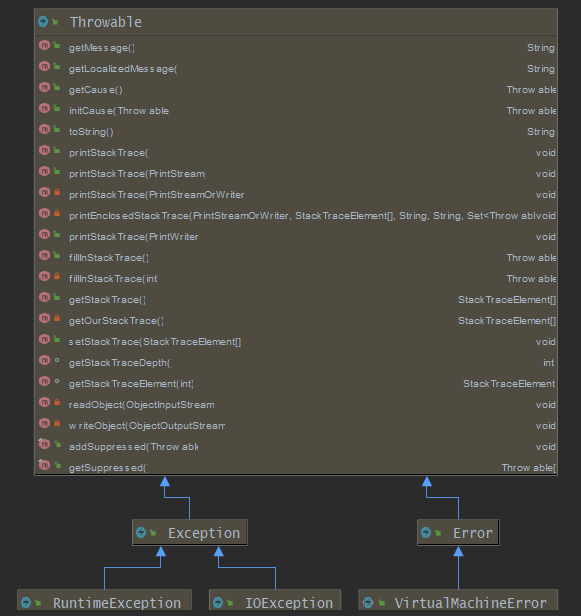
我们看到除了基类 Throwable 以外,其他所有的子类都没有实现任何方法。
我们随便来看几个类:

public class Exception extends Throwable { static final long serialVersionUID = -3387516993124229948L; /** * Constructs a new exception with {@code null} as its detail message. * The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by a * call to {@link #initCause}. */ public Exception() { super(); } public Exception(String message) { super(message); } public Exception(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public Exception(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } protected Exception(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } }

public class Error extends Throwable { static final long serialVersionUID = 4980196508277280342L; /** * Constructs a new error with {@code null} as its detail message. * The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by a * call to {@link #initCause}. */ public Error() { super(); } public Error(String message) { super(message); } public Error(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public Error(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } protected Error(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } }

public class RuntimeException extends Exception { static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897190745766939L; /** Constructs a new runtime exception with {@code null} as its * detail message. The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be * initialized by a call to {@link #initCause}. */ public RuntimeException() { super(); } public RuntimeException(String message) { super(message); } public RuntimeException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public RuntimeException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } protected RuntimeException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } }
从以上代码可以看出,所有子类中的构造方法都调用父类的构造方法,最终调用的都是 Throwable 中实现的构造方法。除Throwable 以外,所有类都没有其他方法实现。
九、面试
Java异常体系如何设计、分类的?
相信如果看完了上面的文章,大家应该知道了这个问题怎么回答了吧!!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号