自定义资源支持:K8s Device Plugin 从原理到实现

本文主要分析 k8s 中的 device-plugin 机制工作原理,并通过实现一个简单的 device-plugin 来加深理解。
1. 背景
默认情况下,k8s 中的 Pod 只能申请 CPU 和 Memory 这两种资源,就像下面这样:
resources:
requests:
memory: "1024Mi"
cpu: "100m"
limits:
memory: "2048Mi"
cpu: "200m"
随着 AI 热度越来越高,更多的业务 Pod 需要申请 GPU 资源,GPU 环境搭建指南:如何在裸机、Docker、K8s 等环境中使用 GPU 中我们分析了如何在 k8s 环境中使用 GPU,就是靠 Device Plugin 机制,通过该机制使得 k8s 能感知到节点上的 GPU 资源,就像原生的 CPU 和 Memory 资源一样使用。
实际上在早期,K8s 也提供了一种名为 alpha.kubernetes.io/nvidia-gpu 的资源来支持 NVIDIA GPU,不过后面也发现了很多问题,每增加一种资源都要修改 k8s 核心代码,k8s 社区压力山大。于是在 1.8 版本引入了 device plugin 机制,通过插件形式来接入其他资源,设备厂家只需要开发对应的 xxx-device-plugin 就可以将资源接入到 k8s 了。
ps:类似的还有引入
CSI让存储插件从 Kubernetes 内部(in-tree)代码库中分离出来,改为独立的、可插拔的外部组件(out-of-tree),还有CRI、CNI等等,这里的 Device Plugin 也能算作其中的一种。
Device Plugin 有两层含义,下文中根据语义自行区分:
- 首先它可以代表 k8s 中的 Device Plugin framework
- 其次也可以代表厂家的具体实现,比如 NVIDIA/k8s-device-plugin,就是用于接入 NVIDIA GPU 资源的 Device Plugin 实现
2. 原理
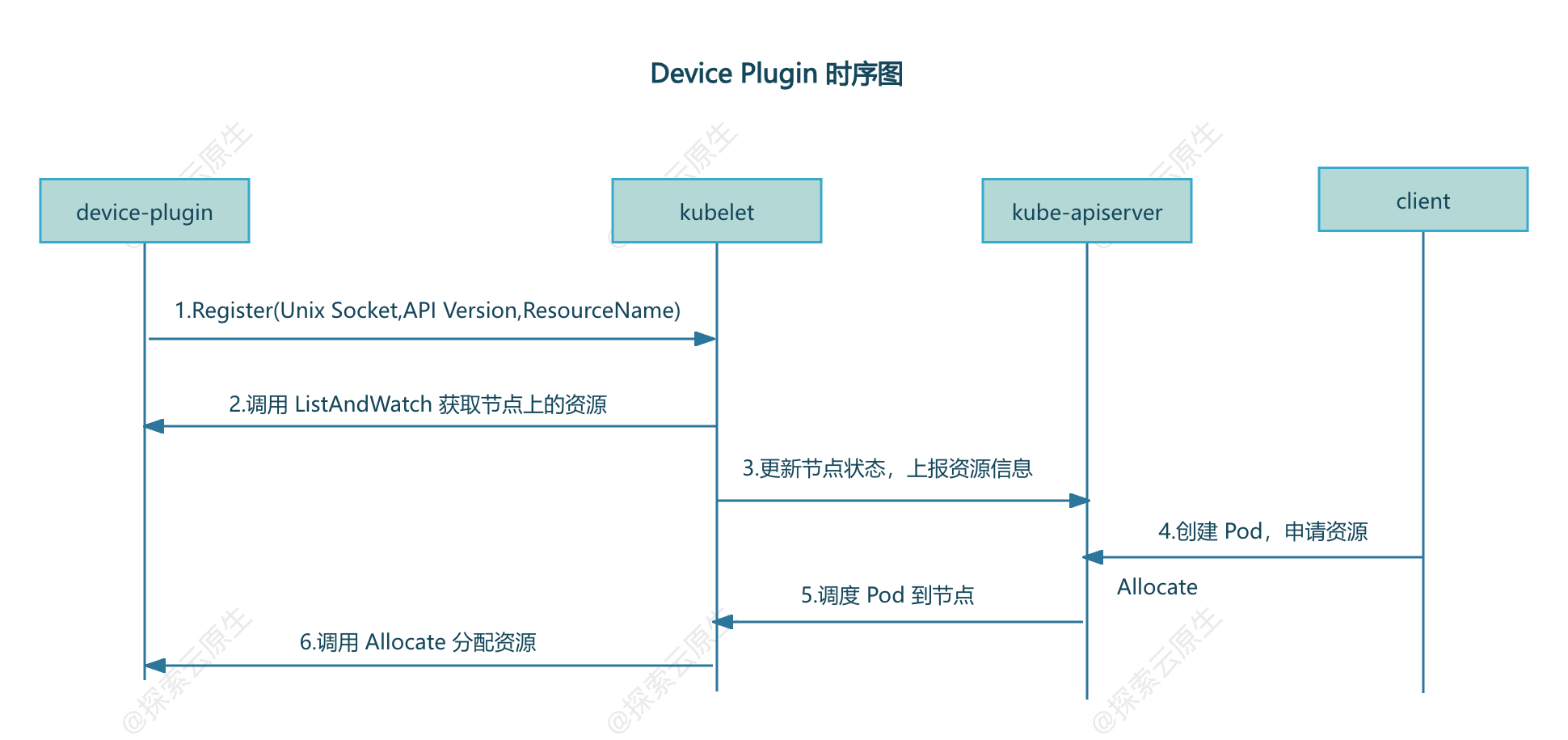
Device Plugin 的工作原理其实不复杂,可以分为 插件注册 和 kubelet 调用插件两部分。
- 插件注册:DevicePlugin 启动时会想节点上的 Kubelet 发起注册,这样 Kubelet就可以感知到该插件的存在了
- kubelet 调用插件:注册完成后,当有 Pod 申请对于资源时,kubelet 就会调用该插件 API 实现具体功能
如 k8s 官网上的图所示:
Kubelet 部分
为了提供该功能,Kubelet 新增了一个 Registration gRPC service:
service Registration {
rpc Register(RegisterRequest) returns (Empty) {}
}
device plugin 可以调用该接口向 Kubelet 进行注册,注册接口需要提供三个参数:
-
device plugin 对应的 unix socket 名字:后续 kubelet 根据名称找到对应的 unix socket,并向插件发起调用
-
device plugin 调 API version:用于区分不同版本的插件
-
device plugin 提供的 ResourceName:遇到不能处理的资源申请时(CPU和Memory之外的资源),Kubelet 就会根据申请的资源名称来匹配对应的插件
- ResourceName 需要按照
vendor-domain/resourcetype格式,例如nvidia.com/gpu。
- ResourceName 需要按照
device plugin 部分
要进行设备管理,device plugin 插件需要实现以下接口:
-
GetDevicePluginOptions:这个接口用于获取设备插件的信息,可以在其返回的响应中指定一些设备插件的配置选项,可以看做是插件的元数据 -
ListAndWatch:该接口用于列出可用的设备并持续监视这些设备的状态变化。 -
GetPreferredAllocation:将分配偏好信息提供给 device plugin,以便 device plugin 在分配时可以做出更好的选择
Allocate:该接口用于向设备插件请求分配指定数量的设备资源。PreStartContainer: 该接口在容器启动之前调用,用于配置容器使用的设备资源。
只有
ListAndWatch和Allocate两个接口是必须的,其他都是可以选的。
工作流程
一般所有的 Device Plugin 实现最终都会以 Pod 形式运行在 k8s 集群中,又因为需要管理所有节点,因此都会以 DaemonSet 方式部署。
device plugin 启动之后第一步就是向 Kubelet 注册,让 Kubelet 知道有一个新的设备接入了。
为了能够调用 Kubelet 的 Register 接口,Device Plugin Pod 会将宿主机上的 kubelet.sock 文件(unix socket)挂载到容器中,通过 kubelet.sock 文件发起调用以实现注册。
集群部署后,Kubelet 就会启动,
-
1)Kubelet 启动 Registration gRPC 服务(kubelet.sock),提供 Register 接口
-
2)device-plugin 启动后,通过 kubelet.sock 调用 Register 接口,向 Kubelet 进行注册,注册信息包括 device plugin 的 unix socket,API Version,ResourceName
-
3)注册成功后,Kubelet 通过 device-plugin 的 unix socket 向 device plugin 调用 ListAndWatch, 获取当前节点上的资源
-
4)Kubelet 向 api-server 更新节点状态来记录上一步中发现的资源
- 此时
kubelet get node -oyaml就能查看到 Node 对象的 Capacity 中多了对应的资源
5)用户创建 Pod 并申请该资源,调度完成后,对应节点上的 kubelet 调用 device plugin 的 Allocate 接口进行资源分配
- 此时
大致如下:
【Kubernetes 系列】持续更新中,搜索公众号【探索云原生】订阅,阅读更多文章。

3. 实现
device plugin 实现大致分为三部分:
- 1)启动时向 Kubelet 发起注册
- 注意监控 kubelet 的重启,一般是使用
fsnotify类似的库监控 kubelet.sock 的重新创建事件。如果 kubelet.sock 重新创建了,则认为 kubelet 是重启了,那么需要重新注册
- 注意监控 kubelet 的重启,一般是使用
- 2)gRPC Server:主要是实现
ListAndWatch和Allocate两个方法
实现 gRPC Server
简单起见,这里只实现了ListAndWatch 和 Allocate 这两个必须的方法。
对 gRPC 不熟悉的童鞋可以看下这个 --> gRPC 系列教程
ListAndWatch
这是一个 gRPC 的 Stream 方法,建立长连接,可以持续向 Kubelet 发送设备的信息。
// ListAndWatch returns a stream of List of Devices
// Whenever a Device state change or a Device disappears, ListAndWatch
// returns the new list
func (c *GopherDevicePlugin) ListAndWatch(_ *pluginapi.Empty, srv pluginapi.DevicePlugin_ListAndWatchServer) error {
devs := c.dm.Devices()
klog.Infof("find devices:%s", String(devs))
err := srv.Send(&pluginapi.ListAndWatchResponse{Devices: devs})
if err != nil {
return errors.WithMessage(err, "send device failed")
}
klog.Infoln("waiting for device update")
for range c.dm.notify {
devs = c.dm.Devices()
klog.Infof("device update,new device list:%s", String(devs))
_ = srv.Send(&pluginapi.ListAndWatchResponse{Devices: devs})
}
return nil
}
发现设备的部分代码如下:
func (d *DeviceMonitor) List() error {
err := filepath.Walk(d.path, func(path string, info fs.FileInfo, err error) error {
if info.IsDir() {
klog.Infof("%s is dir,skip", path)
return nil
}
d.devices[info.Name()] = &pluginapi.Device{
ID: info.Name(),
Health: pluginapi.Healthy,
}
return nil
})
return errors.WithMessagef(err, "walk [%s] failed", d.path)
}
很简单,就是遍历查看 /etc/gophers 目录下的所有文件,每个文件都会当做一个设备。
然后再启动一个 Goroutine 监控设备的变化,即/etc/gophers 目录下文件有变化时通过 chan 发送通知,将最新的设备信息发送给 Kubelet。
func (d *DeviceMonitor) Watch() error {
klog.Infoln("watching devices")
w, err := fsnotify.NewWatcher()
if err != nil {
return errors.WithMessage(err, "new watcher failed")
}
defer w.Close()
errChan := make(chan error)
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
errChan <- fmt.Errorf("device watcher panic:%v", r)
}
}()
for {
select {
case event, ok := <-w.Events:
if !ok {
continue
}
klog.Infof("fsnotify device event: %s %s", event.Name, event.Op.String())
if event.Op == fsnotify.Create {
dev := path.Base(event.Name)
d.devices[dev] = &pluginapi.Device{
ID: dev,
Health: pluginapi.Healthy,
}
d.notify <- struct{}{}
klog.Infof("find new device [%s]", dev)
} else if event.Op&fsnotify.Remove == fsnotify.Remove {
dev := path.Base(event.Name)
delete(d.devices, dev)
d.notify <- struct{}{}
klog.Infof("device [%s] removed", dev)
}
case err, ok := <-w.Errors:
if !ok {
continue
}
klog.Errorf("fsnotify watch device failed:%v", err)
}
}
}()
err = w.Add(d.path)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("watch device error:%v", err)
}
return <-errChan
}
Allocate
Allocate 则是需要告知 kubelet 怎么将设备分配给容器,这里实现比较简单,就是在对应容器中增加一个环境变量,Gopher=$deviceId
// Allocate is called during container creation so that the Device
// Plugin can run device specific operations and instruct Kubelet
// of the steps to make the Device available in the container
func (c *GopherDevicePlugin) Allocate(_ context.Context, reqs *pluginapi.AllocateRequest) (*pluginapi.AllocateResponse, error) {
ret := &pluginapi.AllocateResponse{}
for _, req := range reqs.ContainerRequests {
klog.Infof("[Allocate] received request: %v", strings.Join(req.DevicesIDs, ","))
resp := pluginapi.ContainerAllocateResponse{
Envs: map[string]string{
"Gopher": strings.Join(req.DevicesIDs, ","),
},
}
ret.ContainerResponses = append(ret.ContainerResponses, &resp)
}
return ret, nil
}
简单看一下 NVIDIA 的 device plugin 是怎么实现 Allocate 的。
// Allocate which return list of devices.
func (plugin *NvidiaDevicePlugin) Allocate(ctx context.Context, reqs *pluginapi.AllocateRequest) (*pluginapi.AllocateResponse, error) {
responses := pluginapi.AllocateResponse{}
for _, req := range reqs.ContainerRequests {
if err := plugin.rm.ValidateRequest(req.DevicesIDs); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid allocation request for %q: %w", plugin.rm.Resource(), err)
}
response, err := plugin.getAllocateResponse(req.DevicesIDs)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to get allocate response: %v", err)
}
responses.ContainerResponses = append(responses.ContainerResponses, response)
}
return &responses, nil
}
核心其实是这个方法:
// updateResponseForDeviceListEnvvar sets the environment variable for the requested devices.
func (plugin *NvidiaDevicePlugin) updateResponseForDeviceListEnvvar(response *pluginapi.ContainerAllocateResponse, deviceIDs ...string) {
response.Envs[plugin.deviceListEnvvar] = strings.Join(deviceIDs, ",")
}
给容器添加了一个环境变量,value 为设备 id,具体 deviceID 提供了两种测量,可能是编号或者 uuid
const (
DeviceIDStrategyUUID = "uuid"
DeviceIDStrategyIndex = "index"
)
key 是一个变量 plugin.deviceListEnvvar,初始化如下:
plugin := NvidiaDevicePlugin{
deviceListEnvvar: "NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES",
socket: pluginPath + ".sock",
// ...
}
也就是说 NVIDIA 这个 device plugin 实现 Allocate 主要就是给容器增加了环境变量,例如:
NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES="0,1"
在文章 GPU 环境搭建指南:使用 GPU Operator 加速 Kubernetes GPU 环境搭建 中提到 GPU Operator 会使用 NVIDIA Container Toolit Installer 安装 NVIDIA Container Toolit。
这个 NVIDIA Container Toolit 的作用就是添加对 GPU 的支持,也包括了识别 NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES 这个环境变量,然后将对应设备挂载到容器里。
除此之外还会把设备挂载到容器里:
func (plugin *NvidiaDevicePlugin) apiDeviceSpecs(devRoot string, ids []string) []*pluginapi.DeviceSpec {
optional := map[string]bool{
"/dev/nvidiactl": true,
"/dev/nvidia-uvm": true,
"/dev/nvidia-uvm-tools": true,
"/dev/nvidia-modeset": true,
}
paths := plugin.rm.GetDevicePaths(ids)
var specs []*pluginapi.DeviceSpec
for _, p := range paths {
if optional[p] {
if _, err := os.Stat(p); err != nil {
continue
}
}
spec := &pluginapi.DeviceSpec{
ContainerPath: p,
HostPath: filepath.Join(devRoot, p),
Permissions: "rw",
}
specs = append(specs, spec)
}
return specs
}
核心为:
spec := &pluginapi.DeviceSpec{
ContainerPath: p,
HostPath: filepath.Join(devRoot, p),
Permissions: "rw",
}
这里指定了设备在宿主机上的 Path 和挂载到容器之后的 Path,后续就可以根据这些信息进行设备挂载了。
其他方法
另外几个方法非强制的,因此只做一个空实现。
// GetDevicePluginOptions returns options to be communicated with Device
// Manager
func (c *GopherDevicePlugin) GetDevicePluginOptions(_ context.Context, _ *pluginapi.Empty) (*pluginapi.DevicePluginOptions, error) {
return &pluginapi.DevicePluginOptions{PreStartRequired: true}, nil
}
// GetPreferredAllocation returns a preferred set of devices to allocate
// from a list of available ones. The resulting preferred allocation is not
// guaranteed to be the allocation ultimately performed by the
// devicemanager. It is only designed to help the devicemanager make a more
// informed allocation decision when possible.
func (c *GopherDevicePlugin) GetPreferredAllocation(_ context.Context, _ *pluginapi.PreferredAllocationRequest) (*pluginapi.PreferredAllocationResponse, error) {
return &pluginapi.PreferredAllocationResponse{}, nil
}
// PreStartContainer is called, if indicated by Device Plugin during registeration phase,
// before each container start. Device plugin can run device specific operations
// such as reseting the device before making devices available to the container
func (c *GopherDevicePlugin) PreStartContainer(_ context.Context, _ *pluginapi.PreStartContainerRequest) (*pluginapi.PreStartContainerResponse, error) {
return &pluginapi.PreStartContainerResponse{}, nil
}
向 Kubelet 进行注册
注册也是很简单,调用 deviceplugin 提供的 RegisterRequest 方法即可。
// Register registers the device plugin for the given resourceName with Kubelet.
func (c *GopherDevicePlugin) Register() error {
conn, err := connect(pluginapi.KubeletSocket, common.ConnectTimeout)
if err != nil {
return errors.WithMessagef(err, "connect to %s failed", pluginapi.KubeletSocket)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := pluginapi.NewRegistrationClient(conn)
reqt := &pluginapi.RegisterRequest{
Version: pluginapi.Version,
Endpoint: path.Base(common.DeviceSocket),
ResourceName: common.ResourceName,
}
_, err = client.Register(context.Background(), reqt)
if err != nil {
return errors.WithMessage(err, "register to kubelet failed")
}
return nil
}
监控 kubelet.sock 状态
使用 fsnotify 库监控 kubelet.sock 文件状态,通过 kubelet.sock 文件的变化来判断 kubelet 是否重启,当 kubelet 重启后 device plugin 也需要重启,然后注册到新的 kubelet.sock。
// WatchKubelet restart device plugin when kubelet restarted
func WatchKubelet(stop chan<- struct{}) error {
watcher, err := fsnotify.NewWatcher()
if err != nil {
return errors.WithMessage(err, "Unable to create fsnotify watcher")
}
defer watcher.Close()
go func() {
// Start listening for events.
for {
select {
case event, ok := <-watcher.Events:
if !ok {
continue
}
klog.Infof("fsnotify events: %s %v", event.Name, event.Op.String())
if event.Name == pluginapi.KubeletSocket && event.Op == fsnotify.Create {
klog.Warning("inotify: kubelet.sock created, restarting.")
stop <- struct{}{}
}
case err, ok := <-watcher.Errors:
if !ok {
continue
}
klog.Errorf("fsnotify failed restarting,detail:%v", err)
}
}
}()
// watch kubelet.sock
err = watcher.Add(pluginapi.KubeletSocket)
if err != nil {
return errors.WithMessagef(err, "Unable to add path %s to watcher", pluginapi.KubeletSocket)
}
return nil
}
为什么需要重新注册
因为Kubelet 中使用一个 map 来存储注册的插件,因此每次 Kubelet 重启都会丢失,所以我们在实现 device plugin 时就要监控 Kubelet 重启状态并重新注册。
Kubelet Register 方法 实现如下:
// /pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/plugin/v1beta1/server.go#L143-L165
func (s *server) Register(ctx context.Context, r *api.RegisterRequest) (*api.Empty, error) {
klog.InfoS("Got registration request from device plugin with resource", "resourceName", r.ResourceName)
metrics.DevicePluginRegistrationCount.WithLabelValues(r.ResourceName).Inc()
if !s.isVersionCompatibleWithPlugin(r.Version) {
err := fmt.Errorf(errUnsupportedVersion, r.Version, api.SupportedVersions)
klog.InfoS("Bad registration request from device plugin with resource", "resourceName", r.ResourceName, "err", err)
return &api.Empty{}, err
}
if !v1helper.IsExtendedResourceName(core.ResourceName(r.ResourceName)) {
err := fmt.Errorf(errInvalidResourceName, r.ResourceName)
klog.InfoS("Bad registration request from device plugin", "err", err)
return &api.Empty{}, err
}
if err := s.connectClient(r.ResourceName, filepath.Join(s.socketDir, r.Endpoint)); err != nil {
klog.InfoS("Error connecting to device plugin client", "err", err)
return &api.Empty{}, err
}
return &api.Empty{}, nil
}
核心在 connectClient 方法:
func (s *server) connectClient(name string, socketPath string) error {
c := NewPluginClient(name, socketPath, s.chandler)
s.registerClient(name, c)
if err := c.Connect(); err != nil {
s.deregisterClient(name)
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to connect to new client", "resource", name)
return err
}
go func() {
s.runClient(name, c)
}()
return nil
}
怎么保存这个 client 的呢?
func (s *server) registerClient(name string, c Client) {
s.mutex.Lock()
defer s.mutex.Unlock()
s.clients[name] = c
klog.V(2).InfoS("Registered client", "name", name)
}
定义如下:
type server struct {
socketName string
socketDir string
mutex sync.Mutex
wg sync.WaitGroup
grpc *grpc.Server
rhandler RegistrationHandler
chandler ClientHandler
clients map[string]Client // 使用 map 存储,并为持久化
}
main.go
main 方法分为三个部分:
- 1)启动 gRPC 服务
- 2)向 Kubelet 进行注册
- 3)监控 kubelet.sock 状态
func main() {
klog.Infof("device plugin starting")
dp := device_plugin.NewGopherDevicePlugin()
go dp.Run()
// register when device plugin start
if err := dp.Register(); err != nil {
klog.Fatalf("register to kubelet failed: %v", err)
}
// watch kubelet.sock,when kubelet restart,exit device plugin,then will restart by DaemonSet
stop := make(chan struct{})
err := utils.WatchKubelet(stop)
if err != nil {
klog.Fatalf("start to kubelet failed: %v", err)
}
<-stop
klog.Infof("kubelet restart,exiting")
}
4. 测试
部署
首先是部署 i-device-plugin,一般使用 DaemonSet 方式部署,完整 yaml 如下:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: i-device-plugin
namespace: kube-system
labels:
app: i-device-plugin
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: i-device-plugin
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: i-device-plugin
spec:
containers:
- name: i-device-plugin
image: docker.io/lixd96/i-device-plugin:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: "512Mi"
requests:
cpu: "0.1"
memory: "128Mi"
volumeMounts:
- name: device-plugin
mountPath: /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins
- name: gophers
mountPath: /etc/gophers
volumes:
- name: device-plugin
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins
- name: gophers
hostPath:
path: /etc/gophers
以 hostPath 方式将用到的两个目录挂载到 Pod 里:
- /var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins:请求 kubelet.sock 发起调用,同时将 device-plugin gRPC 服务的 sock 文件写入该目录供 kubelet 调用
- /etc/gophers:在该 Demo 中,把 /etc/gophers 目录下的文件作为设备,因此需要将其挂载到 Pod 里。
确保 i-device-plugin 已经启动。
[root@test ~]# kubectl -n kube-system get po
i-device-plugin-vnw6z 1/1 Running 0 17s
初始化
在该 Demo 中,把 /etc/gophers 目录下的文件作为设备,因此我们只需要到 /etc/gophers 目录下创建文件,模拟有新的设备接入即可。
mkdir /etc/gophers
touch /etc/gophers/g1
查看 device plugin 日志
[root@test ~]# kubectl -n kube-system logs -f i-device-plugin-vnw6z
I0719 13:52:24.674737 1 main.go:10] device plugin starting
I0719 13:52:24.675440 1 device_monitor.go:33] /etc/gophers is dir,skip
I0719 13:52:24.675679 1 device_monitor.go:49] watching devices
I0719 13:52:24.682141 1 api.go:22] find devices []
I0719 13:52:24.682315 1 api.go:29] waiting for device update
I0719 13:53:09.369381 1 device_monitor.go:70] fsnotify device event: /etc/gophers/g1 CREATE
I0719 13:53:09.370394 1 device_monitor.go:79] find new device [g1]
I0719 13:53:09.370445 1 device_monitor.go:70] fsnotify device event: /etc/gophers/g1 CHMOD
I0719 13:53:09.370659 1 api.go:32] device update,new device list [g1]
可以看到,已经感知到新增的设备了。
不出意外的话可以在 node 上看到新资源了
[root@test gophers]# k get node n1 -oyaml|grep capacity -A 7
capacity:
cpu: "4"
ephemeral-storage: 20960236Ki
hugepages-1Gi: "0"
hugepages-2Mi: "0"
lixueduan.com/gopher: "1"
memory: 8154984Ki
pods: "110"
果然,node capacity 中新增了lixueduan.com/gopher: "1"。
创建测试 Pod
接下来创建一个 Pod 申请该资源试试
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: gopher-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: gopher-container
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", "echo Hello, Kubernetes! && sleep 3600"]
resources:
requests:
lixueduan.com/gopher: "1"
limits:
lixueduan.com/gopher: "1"
Pod 启动成功
[root@test ~]# kubectl get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gopher-pod 1/1 Running 0 27s
之前分配设备是添加 Gopher=xxx 这个环境变量,现在看下是否正常分配
[root@test ~]# kubectl exec -it gopher-pod -- env|grep Gopher
Gopher=g1
ok,环境变量存在,可以看到分配给该 Pod 的设备是 g1。
新增设备
使用同样的 yaml 改下名称再创建一个 Pod
[root@test ~]# k get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gopher-pod 1/1 Running 0 3m9s
gopher-pod2 0/1 Pending 0 2s
因为只有一个 gopher 资源,因此第二个 Pod pending 了。
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning FailedScheduling 7s default-scheduler 0/1 nodes are available: 1 Insufficient lixueduan.com/gopher. preemption: 0/1 nodes are available: 1 No preemption victims found for incoming pod..
在创建一个设备
touch /etc/gophers/g2
device plugin 立马感知到了设备变化,相关日志如下:
I0719 14:01:00.308599 1 device_monitor.go:70] fsnotify device event: /etc/gophers/g2 CREATE
I0719 14:01:00.308986 1 device_monitor.go:79] find new device [g2]
I0719 14:01:00.309017 1 device_monitor.go:70] fsnotify device event: /etc/gophers/g2 CHMOD
I0719 14:01:00.309141 1 api.go:32] device update,new device list [g2,g1]
node 上的资源数量也更新为 2
[root@argo-1 ~]# k get node argo-1 -oyaml|grep capacity -A 7
capacity:
cpu: "4"
ephemeral-storage: 20960236Ki
hugepages-1Gi: "0"
hugepages-2Mi: "0"
lixueduan.com/gopher: "2"
memory: 8154984Ki
pods: "110"
然后 pod2 也可以正常启动了
[root@test ~]# kubectl get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gopher-pod 1/1 Running 0 4m31s
gopher-pod2 1/1 Running 0 84s
删除设备
然后删除 g2 设备
rm -rf /etc/gophers/g2
device plugin 也是能正常感知到,相关日志
I0719 14:03:55.904983 1 device_monitor.go:70] fsnotify device event: /etc/gophers/g2 REMOVE
I0719 14:03:55.905203 1 device_monitor.go:84] device [g2] removed
I0719 14:03:55.905267 1 api.go:32] device update,new device list [g1]
查看 Node 上的资源数量更新没有
[root@test ~]# k get node argo-1 -oyaml|grep capacity -A 7
capacity:
cpu: "4"
ephemeral-storage: 20960236Ki
hugepages-1Gi: "0"
hugepages-2Mi: "0"
lixueduan.com/gopher: "1"
memory: 8154984Ki
pods: "110"
对应资源也变成 1 个了,一切正常。
5. 小结
本文主要分析了 k8s 中的 Device Plugin 机制的工作原理,并实现了一个简单的 i-device-plugin来进一步加深理解。
Device Plugin 的工作原理其实不复杂,可以分为 插件注册 和 kubelet 调用插件两部分:
- 插件注册:DevicePlugin 启动时会想节点上的 Kubelet 发起注册,这样 Kubelet就可以感知到该插件的存在了
- kubelet 调用插件:注册完成后,当有 Pod 申请对于资源时,kubelet 就会调用该插件 API 实现具体功能
【Kubernetes 系列】持续更新中,搜索公众号【探索云原生】订阅,阅读更多文章。

6. 参考
https://github.com/NVIDIA/k8s-device-plugin




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号