【20161114模拟赛】

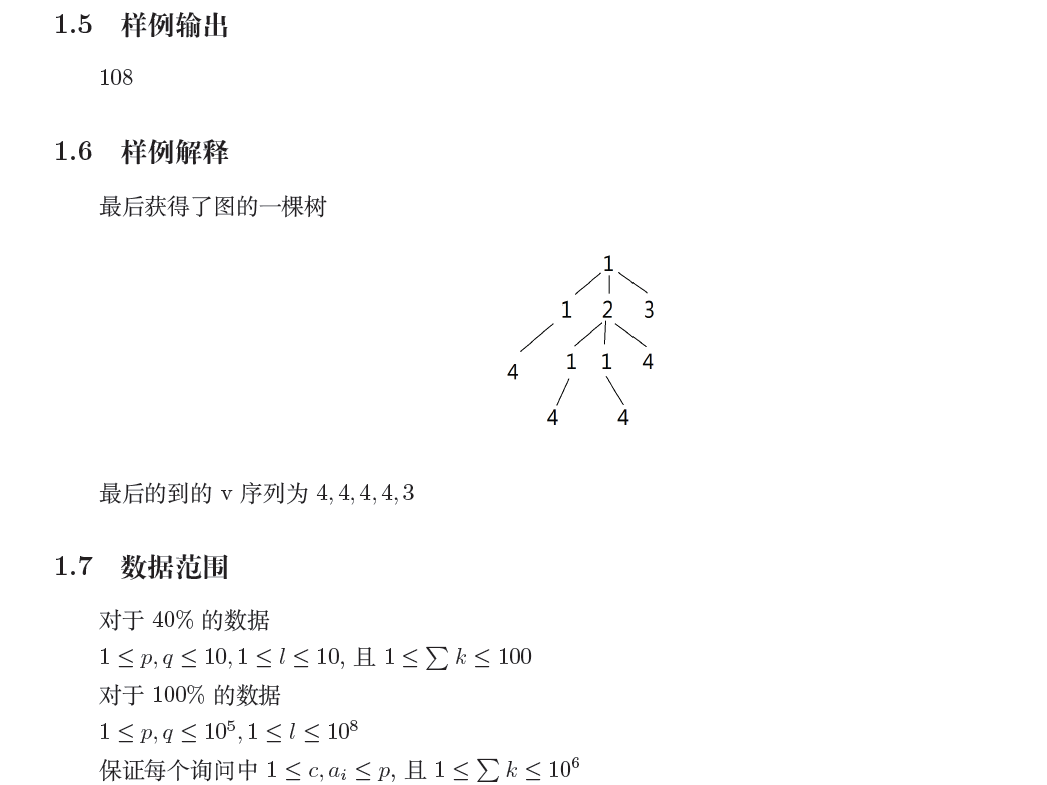
这题逆序做就好了。
然后我要记录当前的点要乘l的多少次方
在这里被卡了6个点。。因为这个最终的点数很大,指数也要mod,指数mod的应该是phi(mod),因为mod是个质数,所以应该%(mod-1)。
当然可以直接记录数值然后就避开这个问题。
1 #include<cstdio>
2 #include<cstdlib>
3 #include<cstring>
4 #include<iostream>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 typedef long long LL;///////
8 const LL N=1000100,M=1000100,mod=998244353;
9 LL n,m,L,cost[N],sum[N];
10 LL ql,q[M],st[M],qc[M];
11
12 LL quickpow(LL x,LL y)
13 {
14 LL ans=1;
15 while(y)
16 {
17 if(y&1) ans=ans*x%mod;
18 x=x*x%mod;
19 y/=2;
20 }
21 return ans;
22 }
23
24 int main()
25 {
26 freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
27 freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
28 scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&n,&m,&L);
29 for(LL i=1;i<=n;i++) cost[i]=i,sum[i]=1;
30 LL x,k,now;ql=0;
31 memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
32 for(LL i=1;i<=m;i++)
33 {
34 scanf("%I64d%I64d",&k,&qc[i]);
35 st[i]=ql+1;
36 for(LL j=1;j<=k;j++)
37 {
38 scanf("%I64d",&x);
39 q[++ql]=x;
40 }
41 }
42 st[m+1]=ql+1;
43 /*
44 for(LL i=1;i<=m;i++)
45 {
46 printf("%d\n",qc[i]);
47 for(LL j=st[i];j<st[i+1];j++)
48 printf("%d ",q[j]);
49 printf("\n");
50 }
51 */
52 LL t0,t1;
53 for(LL i=m;i>=1;i--)
54 {
55 x=qc[i];
56 t0=0,t1=0;
57 for(LL j=st[i];j<st[i+1];j++)
58 {
59 now=(cost[q[j]]*quickpow(L,t1))%mod;
60 t0=(t0+now)%mod;
61 t1=(t1+sum[q[j]])%(mod-1);
62 }
63 cost[x]=t0;sum[x]=t1;
64 // printf("cost %I64d = %I64d sum = %I64d\n",x,t0,t1);
65 }
66 printf("%I64d\n",cost[1]);
67 return 0;
68 }



这个c(n+k-1,k)也就是重复排列,n种球中选择k个。
证明:
1 假设选择了x种。
2 ans=sigma(C(n,x)*C(k-x+x-1,x-1)) (1<=x<=n)//隔板法
3 =sigma(C(n,x)*C(k-1,k-1))
4 =C(n+k-1,k)
这题中k很大。。然后我们就转化成C(n+k-1,n-1).
然后直接容斥定理做,假设某几个一定爆掉了。
第二次容斥定理。。哭。。QAQ。。
1 #include<cstdio>
2 #include<cstdlib>
3 #include<cstring>
4 #include<iostream>
5 #include<algorithm>
6 #include<queue>
7 using namespace std;
8
9 typedef long long LL;
10 const LL N=25,S=5000100,mod=998244353;
11 LL n,K,a[N],ny[N];
12
13 LL quickpow(LL x,LL y)
14 {
15 LL ans=1;
16 while(y)
17 {
18 if(y&1) ans=ans*x%mod;
19 x=x*x%mod;
20 y/=2;
21 }
22 return ans;
23 }
24
25 LL find_c(LL k)
26 {
27 LL ans=1;
28 for(LL i=0;i<n-1;i++) ans=ans*(n+k-1-i)%mod;
29 for(LL i=0;i<n-1;i++) ans=ans*ny[n-1-i]%mod;
30 return ans;
31 }
32
33 int main()
34 {
35 freopen("b.in","r",stdin);
36 freopen("b.out","w",stdout);
37 scanf("%I64d%I64d",&n,&K);
38 for(LL i=1;i<=n;i++)
39 {
40 ny[i]=quickpow(i,mod-2);
41 }
42 for(LL i=0;i<n;i++)
43 {
44 scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
45 }
46 LL ans=0;
47 for(LL s=0;s<(1<<n);s++)
48 {
49 LL cnt=0,sum=0,now=0;
50 for(LL i=0;i<n;i++)
51 {
52 if(s&(1<<i)) cnt++,sum+=(a[i]+1);
53 }
54 if(K-sum>=0)
55 {
56 now=find_c(K-sum);
57 if(!(cnt&1)) ans=(ans+now)%mod;
58 else ans=((ans-now)%mod+mod)%mod;
59 }
60 }
61 printf("%I64d\n",ans);
62 return 0;
63 }



跪%YC。。打整体二分。。
这题我打的是线段树,就是题解上说的这个:

1 #include<cstdio>
2 #include<cstdlib>
3 #include<cstring>
4 #include<iostream>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 const int N=100010,INF=(int)1e9;
8 int n,m,tl,a[N],ans[N];
9 struct trnode{
10 int l,r,lc,rc,lazy,mn,d;
11 }t[2*N];
12
13 int minn(int x,int y){return x<y ? x:y;}
14
15 int bt(int l,int r)
16 {
17 int x=++tl;
18 t[x].l=l;t[x].r=r;
19 t[x].lc=t[x].rc=0;
20 t[x].lazy=0;t[x].mn=INF;
21 if(l<r)
22 {
23 int mid=(l+r)/2;
24 t[x].lc=bt(l,mid);
25 t[x].rc=bt(mid+1,r);
26 int lc=t[x].lc,rc=t[x].rc;
27 t[x].mn=minn(t[lc].mn,t[rc].mn);
28 }
29 else
30 {
31 t[x].mn=a[l];
32 if(a[l]<=0) {ans[l]=0;t[x].mn=INF;}
33 }
34 return x;
35 }
36
37 void pd(int x)
38 {
39 if(t[x].lazy==0) return;
40 int d=t[x].lazy,lc=t[x].lc,rc=t[x].rc;
41 t[x].lazy=0;
42 if(t[x].mn<INF) t[x].mn-=d;
43 if(lc) t[lc].lazy+=d;
44 if(rc) t[rc].lazy+=d;
45 }
46
47 void upd(int x)
48 {
49 int lc=t[x].lc,rc=t[x].rc;
50 pd(lc);pd(rc);
51 t[x].mn=minn(t[lc].mn,t[rc].mn);
52 }
53
54 void fd(int x,int d,int id)
55 {
56 pd(x);
57 if(t[x].l==t[x].r)
58 {
59 t[x].d-=d;
60 t[x].mn=INF;
61 ans[t[x].l]=id;
62 return;
63 }
64 int lc=t[x].lc,rc=t[x].rc;
65 pd(lc);pd(rc);
66 if(t[lc].mn-d<=0) fd(lc,d,id);
67 else t[lc].lazy+=d;
68 if(t[rc].mn-d<=0) fd(rc,d,id);
69 else t[rc].lazy+=d;
70 upd(x);
71 }
72
73 void change(int x,int l,int r,int d,int id)
74 {
75 pd(x);
76 if(t[x].l==l && t[x].r==r)
77 {
78 if(t[x].mn-d<=0) fd(x,d,id);
79 else t[x].lazy+=d,pd(x);
80 return ;
81 }
82 int lc=t[x].lc,rc=t[x].rc,mid=(t[x].l+t[x].r)/2;
83 if(r<=mid) change(lc,l,r,d,id);
84 else if(l>mid) change(rc,l,r,d,id);
85 else
86 {
87 change(lc,l,mid,d,id);
88 change(rc,mid+1,r,d,id);
89 }
90 upd(x);
91 }
92
93 void output(int x)
94 {
95 printf("x = %d l = %d r = %d mn = %d lazy = %d\n",x,t[x].l,t[x].r,t[x].mn,t[x].lazy);
96 if(t[x].lc) output(t[x].lc);
97 if(t[x].rc) output(t[x].rc);
98 }
99
100 int main()
101 {
102 // freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
103 // freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
104 freopen("c.in","r",stdin);
105 freopen("c.out","w",stdout);
106 int k,x,l,r,d;
107 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
108 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
109 {
110 scanf("%d",&a[i]);
111 }
112 tl=0;bt(1,n);
113 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) ans[i]=-1;
114 // memset(ans,-1,sizeof(ans));
115 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
116 {
117 scanf("%d%d%d",&l,&r,&d);
118 if(l<=r) change(1,l,r,d,i);
119 else
120 {
121 change(1,l,n,d,i);
122 change(1,1,r,d,i);
123 }
124 // output(1);
125 // printf("\n");
126 }
127 scanf("%d",&k);
128 for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
129 {
130 scanf("%d",&x);
131 if(ans[x]==-1) printf("So sad\n");
132 else printf("%d\n",ans[x]);
133 }
134 return 0;
135 }

