Java异步编程CompletableFuture
1. 基本概念
1.1. 是什么
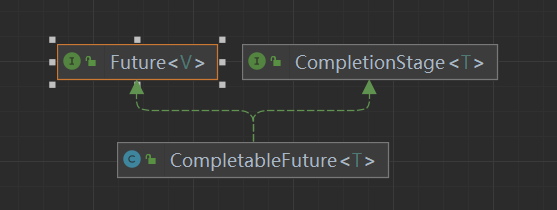
- Java8引入的异步编程工具、支持非阻塞、链式调用、组合异步任务
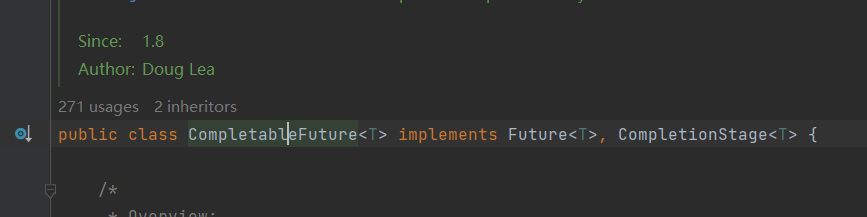
- 继承自Future,扩展CompletionStage接口
1.2. 解决什么问题
- 传统的Future的局限性(阻塞获取结果、无法手动完成、组合能力差)
- 简化异步编程,避免回调地狱
1.3. 核心接口
- CompletiongStage:异步的某个节点,可以与其他阶段组合
2.实用总结
2.1.创建
- 1.创建 CompletableFuture对象
//异步运行一个任务使用CompletableFuture.runAsync方法 没有返回值 CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { System.out.println("Hello CompletableFuture!"); }); //2.获取结果 CompletableFuture<String> futureWithStringResult = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 异步运行一个任务并返回结果使用CompletableFuture.supplyAsync方法 return "Hello CompletableFuture!"; }); try { System.out.println("result from futureWithStringResult: " + futureWithStringResult.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }

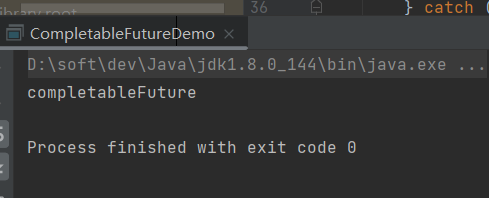
- 2.同步运行一个任务 CompletableFuture.completedFuture
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("completableFuture"); try { System.out.println(completableFuture.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }
-
3.链式调用
- thenApply():当CompletableFuture完成时,应用一个函数到结果上
CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello").thenApply(result -> result + " World"); try { System.out.println(stringCompletableFuture.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } 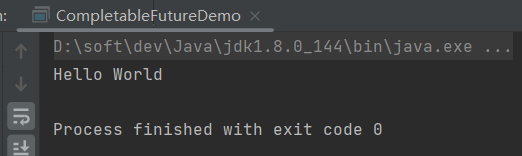
- thenAccept():当CompletableFuture完成时,消费结果
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->"Hello").thenAccept(System.out::println); 
- thenRun():当CompletableFuture完成时,运行一个动作
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello").thenRun(() -> System.out.println("Completed!")); 
-
3.组合CompletableFuture
- thenCombine():组合两个CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello"); CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Word"); future1.thenCombine(future2, (s1, s2) -> s1 + " " + s2).thenAccept(System.out::println); //future1.thenCombineAsync(future2, (s1, s2) -> s1 + " " + s2).thenAccept(System.out::println); 
- threComose():组合两个CompletableFuture,当第一个完成时,是用其结果来创建第二个CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello").thenCompose(result -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> result + " World by thenCompose")).thenAccept(System.out::println); //CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello").thenComposeAsync(result -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> result + " World by thenCompose")).thenAccept(System.out::println); 
-
4.异常处理
- exceptionally():当CompletableFuture完成时,如果内部放生异常,提供一个备用的结果
CompletableFuture<String> exceptionally = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("Something went wrong!"); } return "Hello"; }).exceptionally(e -> "Error" + e.getMessage()); try { System.out.println(exceptionally.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } 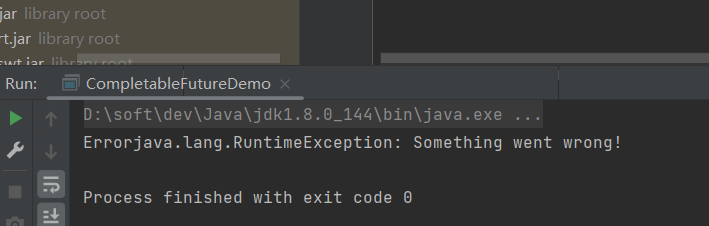
- handle():当CompletableFuture完成时,无论是否发生异常,都应用一个函数到结果或者异常上
CompletableFuture<String> handle = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { if (true) { throw new RuntimeException("Something went wrong!"); } return "Hello"; }).handle((result, e) -> { if (e != null) { return "Handle Error" + e.getMessage(); } return result; }); try { System.out.println(handle.get()); } catch (ExecutionException | InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } 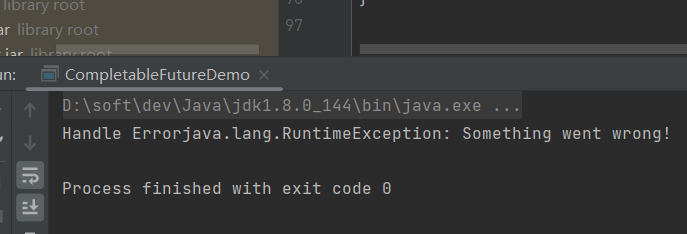
-
5.等待完成
- join()阻塞当前想成,直到CompletableFuture完成,并返回结果,如果发生异常,则抛出CompletionException异常
//单个join String join = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello").join(); System.out.println(join); //多个join System.out.println("multiple join"); List<CompletableFuture<String>> completableFutures = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { final int index = i; completableFutures.add(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 业务处理 return "Hello " + index; })); } completableFutures.stream().map(CompletableFuture::join).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println("completed!"); 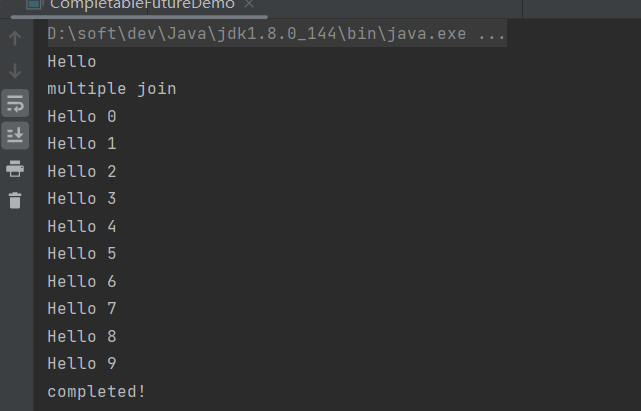
- get():与join类似,但会抛出InterruptedException和ExecuteException
System.out.println("single get"); try { String s = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello").get(); System.out.println(s); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("multiple get"); List<CompletableFuture<String>> completableFutures = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { final int index = i; completableFutures.add(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello " + index)); } completableFutures.stream().map(item-> { try { return item.get(); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println("completed!"); 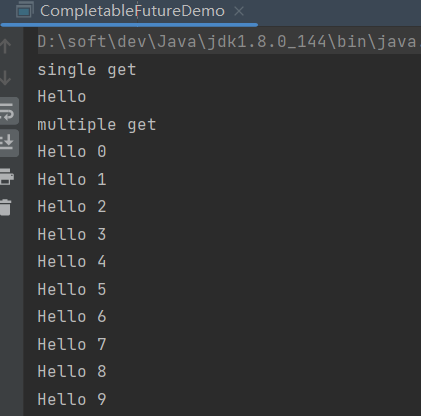
-
取消任务
- cancel():尝试取消任务的执行
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { // 模拟业务操作 Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return "Hello"; }); future.handle((result,e)->{ if(e!=null){ e.printStackTrace(); } return result; }); boolean canceled = future.cancel(true); System.out.println(canceled); try { Thread.sleep(10*1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } 
以上就是CompleteFuture常用的一些方法






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)