多元线性回归的梯度下降
通过房子的大小,卧室数量,层数,房龄预测价格
| Size (sqft) | Number of Bedrooms | Number of floors | Age of Home | Price (1000s dollars) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2104 | 5 | 1 | 45 | 460 |
| 1416 | 3 | 2 | 40 | 232 |
| 852 | 2 | 1 | 35 | 178 |
预测(带入)
"""
single predict using linear regression
Args:
x (ndarray): Shape (n,) example with multiple features
w (ndarray): Shape (n,) model parameters
b (scalar): model parameter
Returns:
p (scalar): prediction
"""
def predict(x, w, b):
p = np.dot(x, w) + b
return p
代价函数
"""
compute cost
Args:
X (ndarray (m,n)): Data, m examples with n features
y (ndarray (m,)) : target values
w (ndarray (n,)) : model parameters
b (scalar) : model parameter
Returns:
cost (scalar): cost
"""
def compute_cost(X, y, w, b):
m = X.shape[0]
cost = 0.0
for i in range(m):
f_wb_i = np.dot(X[i], w) + b
cost += (f_wb_i - y[i])**2
cost /= 2*m
return cost
X_train = np.array([[2104, 5, 1, 45], [1416, 3, 2, 40], [852, 2, 1, 35]])
y_train = np.array([460, 232, 178])
b_init = 785.1811367994083
w_init = np.array([ 0.39133535, 18.75376741, -53.36032453, -26.42131618])
cost = compute_cost(X_train, y_train, w_init, b_init)
print(f'Cost at optimal w : {cost}')
Cost at optimal w : 1.5578904330213735e-12
多变量梯度下降
重复, 直到收敛
n: 特征数量, m: 训练集的个数
计算梯度
"""
Computes the gradient for linear regression
Args:
X (ndarray (m,n)): Data, m examples with n features
y (ndarray (m,)) : target values
w (ndarray (n,)) : model parameters
b (scalar) : model parameter
Returns:
dj_dw (ndarray (n,)): The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameters w.
dj_db (scalar): The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameter b.
"""
def compute_gradient(X, y, w, b):
m, n = X.shape #(m:number of examples, n:number of features)
dj_dw = np.zeros((n,))
dj_db = 0.
for i in range(m):
dif = np.dot(X[i], w) + b - y[i]
for j in range(n):
dj_dw[j] = dj_dw[j] + dif * X[i, j]
dj_db = dj_db + dif
dj_dw /= m
dj_db /= m
return dj_db, dj_dw
tmp_dj_db, tmp_dj_dw = compute_gradient(X_train, y_train, w_init, b_init)
print(f'dj_db at initial w,b: {tmp_dj_db}')
print(f'dj_dw at initial w,b: \n {tmp_dj_dw}')
dj_db at initial w,b: -1.6739251122999121e-06
dj_dw at initial w,b:
[-2.73e-03 -6.27e-06 -2.22e-06 -6.92e-05]
梯度下降
"""
Performs batch gradient descent to learn theta. Updates theta by taking
num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha
Args:
X (ndarray (m,n)) : Data, m examples with n features
y (ndarray (m,)) : target values
w_in (ndarray (n,)) : initial model parameters
b_in (scalar) : initial model parameter
cost_function : function to compute cost
gradient_function : function to compute the gradient
alpha (float) : Learning rate
num_iters (int) : number of iterations to run gradient descent
Returns:
w (ndarray (n,)) : Updated values of parameters
b (scalar) : Updated value of parameter
"""
def gradient_descent(X, y, w_in, b_in, cost_function, gradient_function, alpha, num_iters):
# An array to store cost J and w's at each iteration primarily for graphing later
J_history = []
w = copy.deepcopy(w_in) #avoid modifying global w within function
b = b_in
for i in range(num_iters):
# Calculate the gradient and update the parameters
dj_db,dj_dw = gradient_function(X, y, w, b)
# Update Parameters using w, b, alpha and gradient
w = w - alpha * dj_dw
b = b - alpha * dj_db
# Save cost J at each iteration
if i<100000: # prevent resource exhaustion
J_history.append( cost_function(X, y, w, b))
# Print cost every at intervals 10 times or as many iterations if < 10
if i% math.ceil(num_iters / 10) == 0:
print(f"Iteration {i:4d}: Cost {J_history[-1]:8.2f} ")
return w, b, J_history
测试
# initialize parameters
initial_w = np.zeros_like(w_init)
initial_b = 0.
# some gradient descent settings
iterations = 1000
alpha = 5.0e-7
# run gradient descent
w_final, b_final, J_hist = gradient_descent(X_train, y_train, initial_w, initial_b,
compute_cost, compute_gradient,
alpha, iterations)
print(f"b,w found by gradient descent: {b_final:0.2f},{w_final} ")
m,_ = X_train.shape
for i in range(m):
print(f"prediction: {np.dot(X_train[i], w_final) + b_final:0.2f}, target value: {y_train[i]}")
Iteration 0: Cost 2529.46
Iteration 100: Cost 695.99
Iteration 200: Cost 694.92
Iteration 300: Cost 693.86
Iteration 400: Cost 692.81
Iteration 500: Cost 691.77
Iteration 600: Cost 690.73
Iteration 700: Cost 689.71
Iteration 800: Cost 688.70
Iteration 900: Cost 687.69
b,w found by gradient descent: -0.00,[ 0.2 0. -0.01 -0.07]
prediction: 426.19, target value: 460
prediction: 286.17, target value: 232
prediction: 171.47, target value: 178
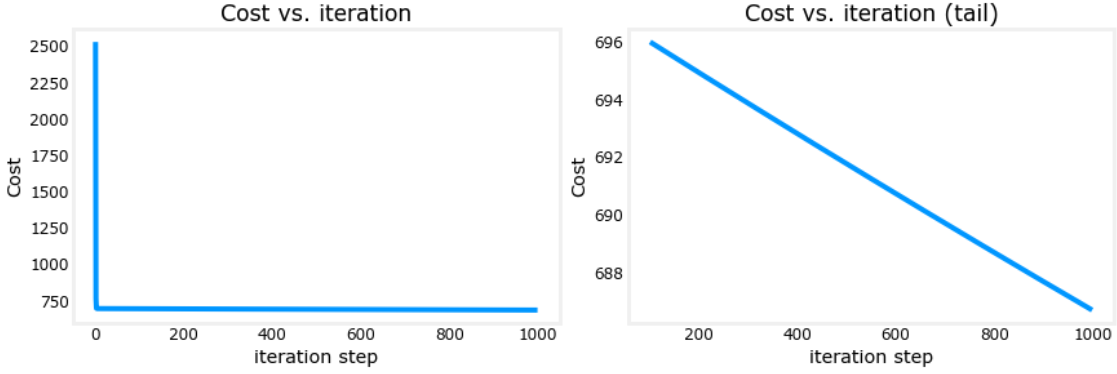
绘制cost-iteration图像
# plot cost versus iteration
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, constrained_layout=True, figsize=(12, 4))
ax1.plot(J_hist)
ax2.plot(100 + np.arange(len(J_hist[100:])), J_hist[100:])
ax1.set_title("Cost vs. iteration"); ax2.set_title("Cost vs. iteration (tail)")
ax1.set_ylabel('Cost') ; ax2.set_ylabel('Cost')
ax1.set_xlabel('iteration step') ; ax2.set_xlabel('iteration step')
plt.show()
本文来自博客园,作者:泥烟,CSDN同名, 转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Knight02/articles/16828580.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号