md4算法实现原理深剖
一、基本介绍
MD系列算法是信息摘要三大算法中的一种,全称:Message Digest算法,按照规范版本分为MD2、MD4、MD5三种算法,目前最常用的是MD5版本算法。本文介绍MD4算法的实现原理。
1990 年,罗纳德·李维斯特教授开发出较之 MD2 算法有着更高安全性的 MD4 算法。在这个算法中,我们仍需对信息进行数据补位。不同的是,这种补位使其信息的字节长度加上 448 个字节后能成为 512 的倍数(信息字节长度 mod 512 = 448)。此外,关于 MD4 算法的处理与 MD2 算法又有很大差别。但最终仍旧是会获得一个 128 位的散列值。MD4 算法对后续消息摘要算法起到了推动作用,许多比较有名的消息摘要算法都是在 MD4 算法的基础上发展而来的,如 MD5、SHA-1、RIPE-MD 和 HAVAL 算法等。
二、实现原理
有关 MD4 算法详情请参见 RFC 1320 http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc1320.txt,RFC 1320 是MD4算法的官方文档,其实现原理共分为5步:
第1步:字节填充(Append Padding Bytes)
数据先补上1个1比特,再补上k个0比特,使得补位后的数据比特数(n+1+k)满足(n+1+k) mod 512 = 448,k取最小正整数。
第2步:追加长度信息(Append Length)
数据比特位的数据长度追加到最后8字节中。
第3步:初始化MD Buffer(Initialize MD Buffer)
这一步最简单了,定义ABCD四个4字节数组,分别赋初值即可。
uint32_t A = 0x67452301; // [ 0x01, 0x23, 0x45, 0x67 ] uint32_t B = 0xEFCDAB89; // [ 0x89, 0xAB, 0xCD, 0xEF ] uint32_t C = 0x98BADCFE; // [ 0xFE, 0xDC, 0xBA, 0x98 ] uint32_t D = 0x10325476; // [ 0x76, 0x54, 0x32, 0x10 ]
第4步:处理消息块(Process Message in 16-Byte Blocks)
这个是MD4算法最核心的部分了,对第2步组装数据进行分块依次处理。
Process each 16-word block. */
For i = 0 to N/16-1 do
/* Copy block i into X. */
For j = 0 to 15 do
Set X[j] to M[i*16+j].
end /* of loop on j */
/* Save A as AA, B as BB, C as CC, and D as DD. */
AA = A
BB = B
CC = C
DD = D
/* Round 1. */
/* Let [abcd k s] denote the operation
a = (a + F(b,c,d) + X[k]) <<< s. */
/* Do the following 16 operations. */
[ABCD 0 3] [DABC 1 7] [CDAB 2 11] [BCDA 3 19]
[ABCD 4 3] [DABC 5 7] [CDAB 6 11] [BCDA 7 19]
[ABCD 8 3] [DABC 9 7] [CDAB 10 11] [BCDA 11 19]
[ABCD 12 3] [DABC 13 7] [CDAB 14 11] [BCDA 15 19]
/* Round 2. */
/* Let [abcd k s] denote the operation
a = (a + G(b,c,d) + X[k] + 5A827999) <<< s. */
/* Do the following 16 operations. */
[ABCD 0 3] [DABC 4 5] [CDAB 8 9] [BCDA 12 13]
[ABCD 1 3] [DABC 5 5] [CDAB 9 9] [BCDA 13 13]
[ABCD 2 3] [DABC 6 5] [CDAB 10 9] [BCDA 14 13]
[ABCD 3 3] [DABC 7 5] [CDAB 11 9] [BCDA 15 13]
/* Round 3. */
/* Let [abcd k s] denote the operation
a = (a + H(b,c,d) + X[k] + 6ED9EBA1) <<< s. */
/* Do the following 16 operations. */
[ABCD 0 3] [DABC 8 9] [CDAB 4 11] [BCDA 12 15]
[ABCD 2 3] [DABC 10 9] [CDAB 6 11] [BCDA 14 15]
[ABCD 1 3] [DABC 9 9] [CDAB 5 11] [BCDA 13 15]
[ABCD 3 3] [DABC 11 9] [CDAB 7 11] [BCDA 15 15]
/* Then perform the following additions. (That is, increment each
of the four registers by the value it had before this block
was started.) */
A = A + AA
B = B + BB
C = C + CC
D = D + DD
end /* of loop on i */
第5步:输出(Output)
这一步也非常简单,只需要将计算后的A、B、C、D进行拼接输出即可。
三、示例讲解
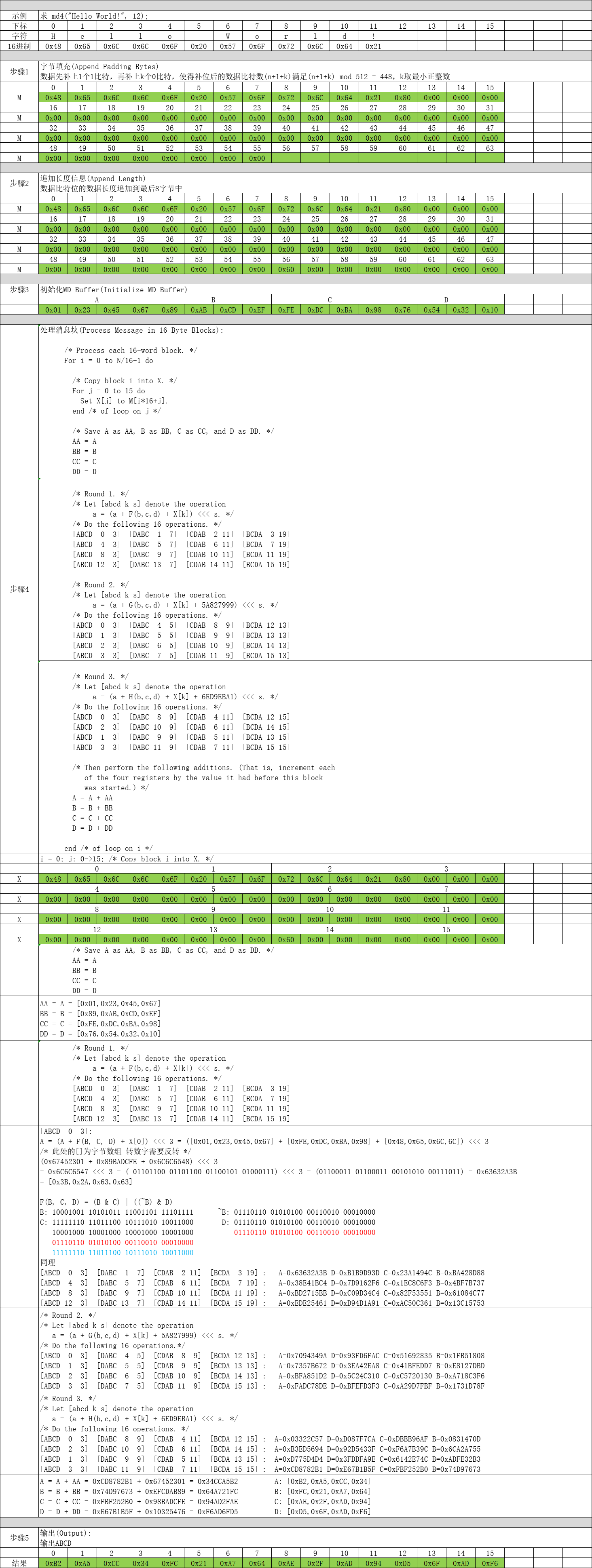
四、代码实现
以下为C/C++代码实现:
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define HASH_BLOCK_SIZE 64 /* 512 bits = 64 bytes */
#define HASH_LEN_SIZE 8 /* 64 bits = 8 bytes */
#define HASH_LEN_OFFSET 56 /* 64 bytes - 8 bytes */
#define HASH_DIGEST_SIZE 16 /* 128 bits = 16 bytes */
#define HASH_ROUND_NUM 64
typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
typedef unsigned short int uint16_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
typedef unsigned long long uint64_t;
static uint32_t F(uint32_t X, uint32_t Y, uint32_t Z)
{
return (X & Y) | ((~X) & Z);
}
static uint32_t G(uint32_t X, uint32_t Y, uint32_t Z)
{
return (X & Y) | (X & Z) | (Y & Z);
}
static uint32_t H(uint32_t X, uint32_t Y, uint32_t Z)
{
return X ^ Y ^ Z;
}
/* 循环向左移动offset个单位 */
static uint32_t MoveLeft(uint32_t X, uint8_t offset)
{
return (X << offset) | (X >> (32 - offset));
}
static uint32_t Round1(uint32_t A, uint32_t B, uint32_t C, uint32_t D, uint32_t M, uint32_t N)
{
return MoveLeft(A + F(B, C, D) + M, N);
}
static uint32_t Round2(uint32_t A, uint32_t B, uint32_t C, uint32_t D, uint32_t M, uint32_t N)
{
return MoveLeft(A + G(B, C, D) + M + 0x5A827999, N);
}
static uint32_t Round3(uint32_t A, uint32_t B, uint32_t C, uint32_t D, uint32_t M, uint32_t N)
{
return MoveLeft(A + H(B, C, D) + M + 0x6ED9EBA1, N);
}
#define ASSERT_RETURN_INT(x, d) if(!(x)) { return d; }
int md4(unsigned char *out, const unsigned char* in, const int inlen)
{
ASSERT_RETURN_INT(out && in && (inlen > 0), 1);
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
unsigned char L = 0, t = 0;
// step 1: 字节填充(Append Padding Bytes)
// 数据先补上1个1比特,再补上k个0比特,使得补位后的数据比特数(n+1+k)满足(n+1+k) mod 512 = 448,k取最小正整数
int iX = inlen / HASH_BLOCK_SIZE;
int iY = inlen % HASH_BLOCK_SIZE;
iX = (iY < HASH_LEN_OFFSET) ? iX : (iX + 1);
int iLen = (iX + 1) * HASH_BLOCK_SIZE;
unsigned char* M = malloc(iLen);
memcpy(M, in, inlen);
// 先补上1个1比特+7个0比特
M[inlen] = 0x80;
// 再补上(k-7)个0比特
for (i = inlen + 1; i < (iX * HASH_BLOCK_SIZE + HASH_LEN_OFFSET); i++)
{
M[i] = 0;
}
// step 2: 追加长度信息(Append Length)
uint64_t *pLen = (uint64_t*)(M + (iX * HASH_BLOCK_SIZE + HASH_LEN_OFFSET));
*pLen = inlen << 3;
// Step 3. 初始化MD Buffer(Initialize MD Buffer)
uint32_t A = 0x67452301; // [ 0x01, 0x23, 0x45, 0x67 ]
uint32_t B = 0xEFCDAB89; // [ 0x89, 0xAB, 0xCD, 0xEF ]
uint32_t C = 0x98BADCFE; // [ 0xFE, 0xDC, 0xBA, 0x98 ]
uint32_t D = 0x10325476; // [ 0x76, 0x54, 0x32, 0x10 ]
uint32_t X[HASH_BLOCK_SIZE / 4] = { 0 };
// step 4: 处理消息块(Process Message in 64-Byte Blocks)
for (i = 0; i < iLen / HASH_BLOCK_SIZE; i++)
{
/* Copy block i into X. */
for (j = 0; j < HASH_BLOCK_SIZE; j = j + 4)
{
uint32_t* temp = &M[i * HASH_BLOCK_SIZE + j];
X[j/4] = *temp;
}
/* Save A as AA, B as BB, C as CC, and D as DD. */
uint32_t AA = A;
uint32_t BB = B;
uint32_t CC = C;
uint32_t DD = D;
/* Round 1. */
/* Let [abcd k s] denote the operation
a = (a + F(b,c,d) + X[k]) <<< s. */
/* Do the following 16 operations.
[ABCD 0 3][DABC 1 7][CDAB 2 11][BCDA 3 19]
[ABCD 4 3][DABC 5 7][CDAB 6 11][BCDA 7 19]
[ABCD 8 3][DABC 9 7][CDAB 10 11][BCDA 11 19]
[ABCD 12 3][DABC 13 7][CDAB 14 11][BCDA 15 19]
*/
A = Round1(A, B, C, D, X[0], 3); D = Round1(D, A, B, C, X[1], 7); C = Round1(C, D, A, B, X[2], 11); B = Round1(B, C, D, A, X[3], 19);
A = Round1(A, B, C, D, X[4], 3); D = Round1(D, A, B, C, X[5], 7); C = Round1(C, D, A, B, X[6], 11); B = Round1(B, C, D, A, X[7], 19);
A = Round1(A, B, C, D, X[8], 3); D = Round1(D, A, B, C, X[9], 7); C = Round1(C, D, A, B, X[10], 11); B = Round1(B, C, D, A, X[11], 19);
A = Round1(A, B, C, D, X[12], 3); D = Round1(D, A, B, C, X[13], 7); C = Round1(C, D, A, B, X[14], 11); B = Round1(B, C, D, A, X[15], 19);
/* Round 2. */
/* Let [abcd k s] denote the operation
a = (a + G(b,c,d) + X[k] + 5A827999) <<< s. */
/* Do the following 16 operations.
[ABCD 0 3][DABC 4 5][CDAB 8 9][BCDA 12 13]
[ABCD 1 3][DABC 5 5][CDAB 9 9][BCDA 13 13]
[ABCD 2 3][DABC 6 5][CDAB 10 9][BCDA 14 13]
[ABCD 3 3][DABC 7 5][CDAB 11 9][BCDA 15 13]
*/
A = Round2(A, B, C, D, X[0], 3); D = Round2(D, A, B, C, X[4], 5); C = Round2(C, D, A, B, X[8], 9); B = Round2(B, C, D, A, X[12], 13);
A = Round2(A, B, C, D, X[1], 3); D = Round2(D, A, B, C, X[5], 5); C = Round2(C, D, A, B, X[9], 9); B = Round2(B, C, D, A, X[13], 13);
A = Round2(A, B, C, D, X[2], 3); D = Round2(D, A, B, C, X[6], 5); C = Round2(C, D, A, B, X[10], 9); B = Round2(B, C, D, A, X[14], 13);
A = Round2(A, B, C, D, X[3], 3); D = Round2(D, A, B, C, X[7], 5); C = Round2(C, D, A, B, X[11], 9); B = Round2(B, C, D, A, X[15], 13);
/* Round 3. */
/* Let [abcd k s] denote the operation
a = (a + H(b,c,d) + X[k] + 6ED9EBA1) <<< s. */
/* Do the following 16 operations.
[ABCD 0 3][DABC 8 9][CDAB 4 11][BCDA 12 15]
[ABCD 2 3][DABC 10 9][CDAB 6 11][BCDA 14 15]
[ABCD 1 3][DABC 9 9][CDAB 5 11][BCDA 13 15]
[ABCD 3 3][DABC 11 9][CDAB 7 11][BCDA 15 15]
*/
A = Round3(A, B, C, D, X[0], 3); D = Round3(D, A, B, C, X[8], 9); C = Round3(C, D, A, B, X[4], 11); B = Round3(B, C, D, A, X[12], 15);
A = Round3(A, B, C, D, X[2], 3); D = Round3(D, A, B, C, X[10], 9); C = Round3(C, D, A, B, X[6], 11); B = Round3(B, C, D, A, X[14], 15);
A = Round3(A, B, C, D, X[1], 3); D = Round3(D, A, B, C, X[9], 9); C = Round3(C, D, A, B, X[5], 11); B = Round3(B, C, D, A, X[13], 15);
A = Round3(A, B, C, D, X[3], 3); D = Round3(D, A, B, C, X[11], 9); C = Round3(C, D, A, B, X[7], 11); B = Round3(B, C, D, A, X[15], 15);
/* Then perform the following additions. (That is, increment each
of the four registers by the value it had before this block
was started.) */
A = A + AA;
B = B + BB;
C = C + CC;
D = D + DD;
}
// step 5: 输出ABCD
memcpy(out + 0, &A, 4);
memcpy(out + 4, &B, 4);
memcpy(out + 8, &C, 4);
memcpy(out + 12, &D, 4);
free(M);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
unsigned char digest[16] = { 0 };
md4(digest, "Hello World!", strlen("Hello World!"));
return 0;
}



