常见的五种服务限流算法及其实现
常见的五种限流算法可简单概括为“两窗两漏一令牌”,下面将进行详细介绍:
1. 固定窗口算法
| 介绍 |
固定时间周期划分时间为多个时间窗口,如:每10秒为一个时间窗口。 在每个时间窗口内,每有一个请求,计数器加一。 当计数器超过限制,丢弃本窗口之后的所有请求。 当下一时间窗口开始,重置计数器。 |
| 优点 |
原理简单,固定窗口计数。 |
| 缺点 | 无法处理前后密集型请求,例如每秒限制100次,前最后一秒的10ms请求100次,后最后一秒的前10ms请求100次,相当于200次/0.02s。 |
| 图例 | 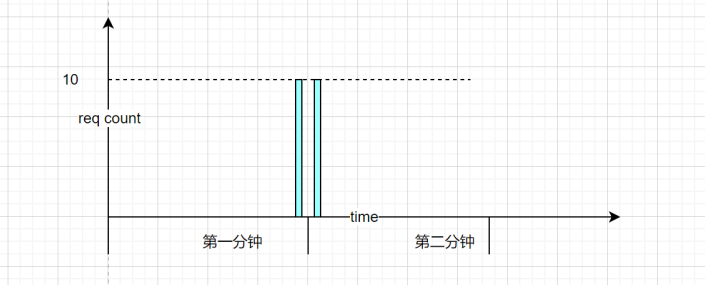 |
| 示例 | 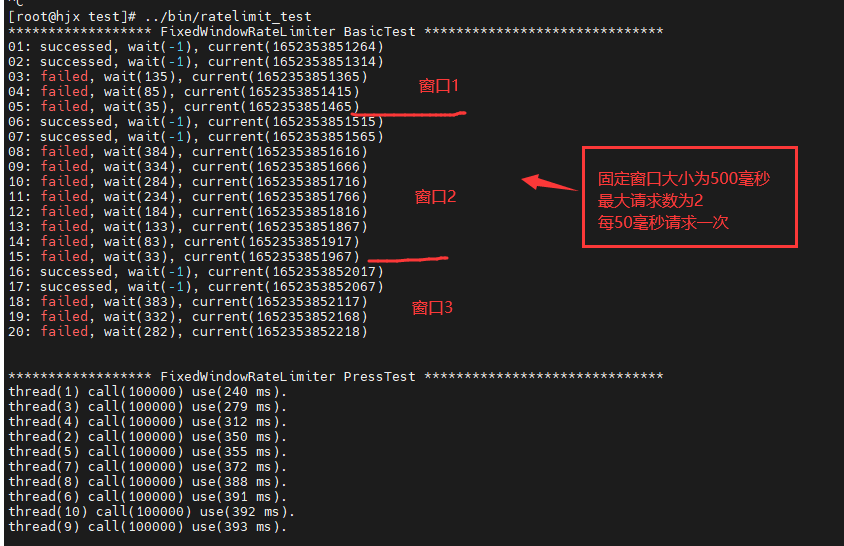 |
| 实现 |

struct FixedWindow { int64_t lLastNo; // 上一次No(记录不同固定窗口区间标识); int64_t lRemainReq; // 剩余req }; typedef std::map<std::string, FixedWindow> FixedWindowMap; class FixedWindowManager { private: FixedWindowManager() {} virtual ~FixedWindowManager() {} FixedWindowManager(const FixedWindowManager&) = delete; FixedWindowManager& operator = (const FixedWindowManager&) = delete; using MutexLockUnique = std::unique_lock<std::mutex>; public: static FixedWindowManager* GetInstance() { static FixedWindowManager manager; return &manager; } bool tryAcquire(const std::string& strKey, int32_t& lMilSec, const uint64_t lReqNum, const uint32_t lFixedMs, const uint64_t lMaxReq) { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutexFixedWindow); lMilSec = -1; uint64_t lCurrentMilSec = AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec(); uint64_t lFixedWindowsNo = lCurrentMilSec / lFixedMs; FixedWindowMap::iterator it = m_mapFixedWindow.find(strKey); if (it == m_mapFixedWindow.end()) { FixedWindow FixedWindow; FixedWindow.lLastNo = lFixedWindowsNo; FixedWindow.lRemainReq = lMaxReq - lReqNum; m_mapFixedWindow[strKey] = FixedWindow; return true; } #if 0 printf("CurrentMs[%lld], CurrentNo[%lld], LastNo[%lld], RemainReq[%lld] \n", lCurrentMilSec, lFixedWindowsNo, it->second.lLastNo, it->second.lRemainReq); #endif if (lFixedWindowsNo == it->second.lLastNo) { // 在一个固定窗口内 if (it->second.lRemainReq >= lReqNum) { it->second.lRemainReq -= lReqNum; return true; } else { // 计算下一个最近窗口的时间间隔; lMilSec = (lFixedWindowsNo + 1) * lFixedMs - lCurrentMilSec; return false; } } it->second.lLastNo = lFixedWindowsNo; it->second.lRemainReq = lMaxReq - lReqNum; return true; } private: FixedWindowMap m_mapFixedWindow; mutable std::mutex m_mutexFixedWindow; }; #define AflGetFixedWindowManager FixedWindowManager::GetInstance |
2. 滑动窗口算法
| 介绍 |
以当前时间为截止时间,往前取一定的时间作为时间窗口,比如:往前取 10s 的时间 当有新的请求进入时,删除时间窗口之外的请求,对时间窗口之内的请求进行计数统计,若未超过限制,则进行放行操作;若超过限制,则拒绝本次服务。 |
| 优点 |
有效处理固定窗口的突发缺点。 |
| 缺点 | 当时间区越长、精度越高,占用的空间资源就越大。 |
| 图例 | 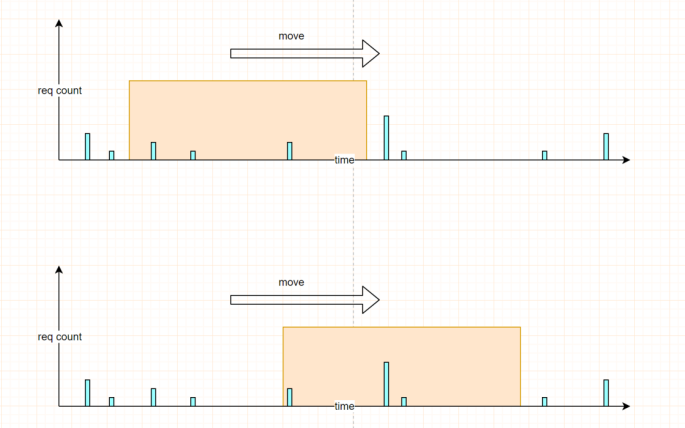 |
| 示例 | 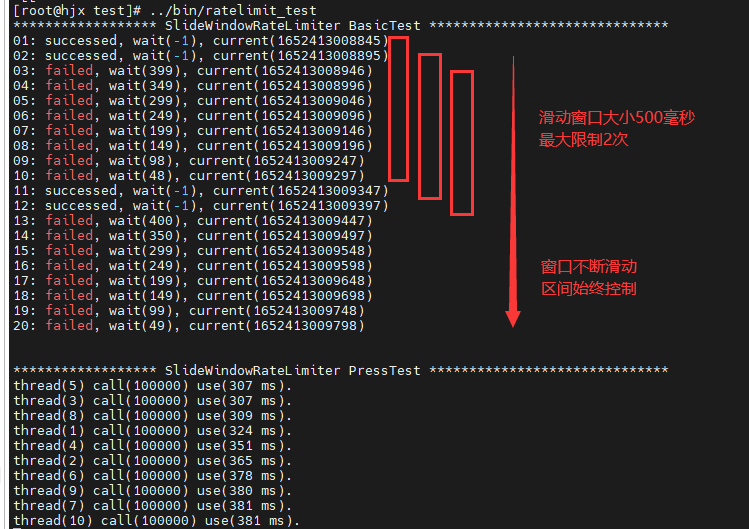 |
| 实现 |

/* key: ms, value: usereq */ typedef std::map<int64_t, int64_t> SlideWindow; typedef std::map<std::string, SlideWindow> SlideWindowMap; class SlideWindowManager { private: SlideWindowManager() {} virtual ~SlideWindowManager() {} SlideWindowManager(const SlideWindowManager&) = delete; SlideWindowManager& operator = (const SlideWindowManager&) = delete; using MutexLockUnique = std::unique_lock<std::mutex>; public: static SlideWindowManager* GetInstance() { static SlideWindowManager manager; return &manager; } bool tryAcquire(const std::string& strKey, int32_t& lMilSec, const uint64_t lReqNum, const uint32_t lSlideMs, const uint64_t lMaxReq) { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutexSlideWindow); lMilSec = -1; uint64_t lCurrentMilSec = AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec(); SlideWindowMap::iterator it = m_mapSlideWindow.find(strKey); if (it == m_mapSlideWindow.end()) { SlideWindow& slide = m_mapSlideWindow[strKey]; slide[lCurrentMilSec] = lReqNum; return true; } SlideWindow& slide = it->second; uint64_t lUseReq = 0; for (SlideWindow::iterator itWin = slide.begin(); itWin != slide.end(); ) { if ((lCurrentMilSec - itWin->first) >= lSlideMs) { // 滑动窗口过期; itWin = slide.erase(itWin); } else { lUseReq += itWin->second; itWin++; } } if ((lMaxReq - lUseReq) >= lReqNum) { SlideWindow::iterator itTemp = slide.find(lCurrentMilSec); if (itTemp == slide.end()) { slide[lCurrentMilSec] = 0; } slide[lCurrentMilSec] += lReqNum; return true; } #if 0 printf("CurrentMs[%lld], UseReq[%lld] \n", lCurrentMilSec, lUseReq); #endif // 未来需要等待释放的请求数; uint64_t lWaitReq = lReqNum - (lMaxReq - lUseReq); for (SlideWindow::iterator itWin = slide.begin(); itWin != slide.end(); ) { lWaitReq -= itWin->second; if (lWaitReq <= 0) { lMilSec = itWin->first + lSlideMs - lCurrentMilSec; break; } } return false; } private: SlideWindowMap m_mapSlideWindow; mutable std::mutex m_mutexSlideWindow; }; #define AflGetSlideWindowManager SlideWindowManager::GetInstance |
3. 漏桶算法
| 介绍 |
将每个请求视为水滴加入漏桶进行存储 漏桶以固定速率匀速出水(处理请求) 若桶满则抛弃请求 |
| 优点 |
限流的绝对平均化。 |
| 缺点 | 不适合突发请求场景、请求延迟高:当短时间内有大量的突发请求时,即便此时服务器没有任何负载,每个请求也都得在队列中等待一段时间才能被响应。 |
| 图例 | 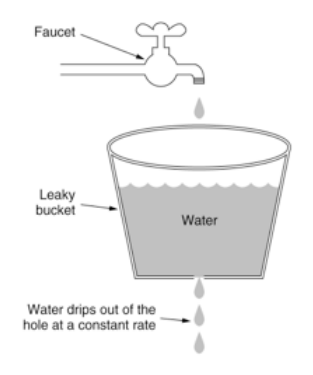 |
| 示例 | 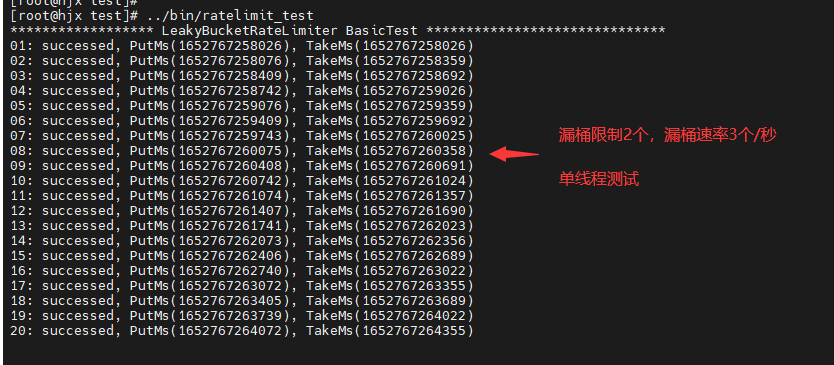 |
| 实现 |

using MutexLockUnique = std::unique_lock<std::mutex>; class LeakyBucket { public: explicit LeakyBucket(uint64_t iMaxSize, uint64_t iTakeMs) : m_lMaxSize(iMaxSize), m_lTakeMs(iTakeMs), m_lLastMs(-1) { } ~LeakyBucket() { } bool put(const uint64_t& x) { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutex); if (m_queue.size() >= m_lMaxSize) { return false; } m_queue.push_back(x); m_notEmpty.notify_one(); return true; } uint64_t take() { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutex); m_notEmpty.wait(lock, [this] { return !(this->m_queue.empty()); }); assert(!m_queue.empty()); int64_t lWaitMs = m_lTakeMs - (AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec() - m_lLastMs); if (lWaitMs > 0) { AbstractRateLimiter::myMSleep(lWaitMs); } m_lLastMs = AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec(); uint64_t front(std::move(m_queue.front())); m_queue.pop_front(); return front; } private: int64_t m_lMaxSize; std::condition_variable m_notEmpty; mutable std::mutex m_mutex; std::deque<uint64_t> m_queue; int64_t m_lLastMs; // 上一次take ms int64_t m_lTakeMs; // take间隔 ms }; typedef std::map<std::string, LeakyBucket*> LeakyBucketMap; class LeakyBucketManager { private: LeakyBucketManager() {} virtual ~LeakyBucketManager() {} LeakyBucketManager(const LeakyBucketManager&) = delete; LeakyBucketManager& operator = (const LeakyBucketManager&) = delete; public: static LeakyBucketManager* GetInstance() { static LeakyBucketManager manager; return &manager; } bool tryAcquire(const std::string& strKey, int32_t& lMilSec, const uint64_t lTokenNum, const uint64_t lCapacityNum, const double dRate) { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutexLeakyBucket); lMilSec = -1; uint64_t lCurrentMilSec = AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec(); LeakyBucketMap::iterator it = m_mapLeakyBucket.find(strKey); if (it == m_mapLeakyBucket.end()) { LeakyBucket* pLeakyBucket = new LeakyBucket(lCapacityNum, (1000 / dRate)); m_mapLeakyBucket[strKey] = pLeakyBucket; it = m_mapLeakyBucket.find(strKey); if (it == m_mapLeakyBucket.end()) { return false; } } if (!it->second->put(1)) { return false; } it->second->take(); return true; } private: LeakyBucketMap m_mapLeakyBucket; mutable std::mutex m_mutexLeakyBucket; }; #define AflGetLeakyBucketManager LeakyBucketManager::GetInstance |
4. 漏斗算法
| 介绍 |
漏斗算法是《Redis深度历险》中提到的一种限流方案。漏斗有一定的容量,并且以一定速率漏水,漏斗的剩余空间即允许请求的空间。 漏斗算法的模型和漏桶算法在模型上是一致的,容器叫法不同,一个叫漏斗,一个叫漏桶,剩余空间直接决定了请求是否可以通过,只不过在漏斗算法中,一旦通过,请求便可以立即访问; 而漏桶算法中,请求通过后,会被暂存在容器中,等待被匀速处理,两者的差别即在于此。 |
| 优点 |
预热限流和平滑限流兼备。 |
| 缺点 | |
| 图例 | 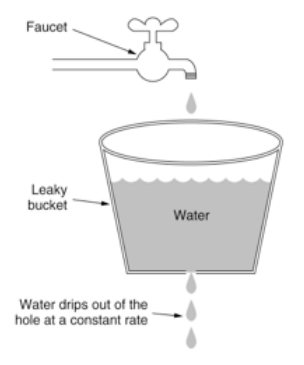 |
| 示例 | 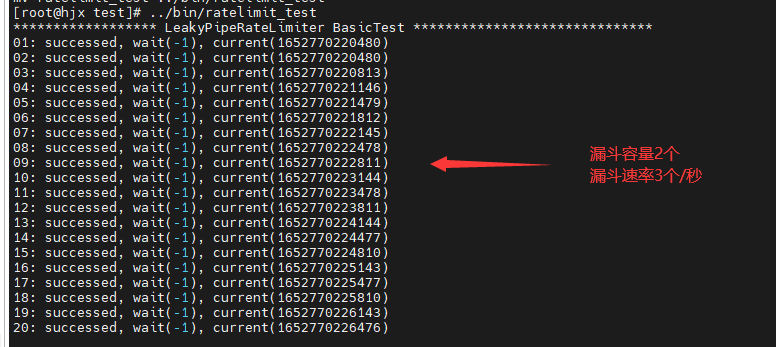 |
| 实现 |

using MutexLockUnique = std::unique_lock<std::mutex>; class LeakyPipe { public: explicit LeakyPipe(uint64_t lCapacity, uint64_t iTakeMs) : m_lCapacity(lCapacity), m_lReamin(lCapacity), m_lTakeMs(iTakeMs), m_lLastMs(-1) { } ~LeakyPipe() { } bool put(const uint64_t& x) { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutex); if (m_queue.size() >= m_lCapacity) { return false; } m_queue.push_back(x); m_notEmpty.notify_one(); return true; } uint64_t take() { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutex); m_notEmpty.wait(lock, [this] { return !(this->m_queue.empty()); }); assert(!m_queue.empty()); // 计算剩余空间; m_lReamin += (AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec() - m_lLastMs) / m_lTakeMs; if (m_lReamin > m_lCapacity) { m_lReamin = m_lCapacity; } if (m_lReamin <= 0) { int64_t lWaitMs = m_lTakeMs - (AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec() - m_lLastMs); if (lWaitMs > 0) { AbstractRateLimiter::myMSleep(lWaitMs); } ++m_lReamin; } --m_lReamin; m_lLastMs = AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec(); uint64_t front(std::move(m_queue.front())); m_queue.pop_front(); return front; } private: std::condition_variable m_notEmpty; mutable std::mutex m_mutex; std::deque<uint64_t> m_queue; int64_t m_lLastMs; // 上一次take ms int64_t m_lTakeMs; // take间隔 ms int64_t m_lCapacity; // 容量; int64_t m_lReamin; // 剩余容量; }; typedef std::map<std::string, LeakyPipe*> LeakyPipeMap; class LeakyPipeManager { private: LeakyPipeManager() {} virtual ~LeakyPipeManager() {} LeakyPipeManager(const LeakyPipeManager&) = delete; LeakyPipeManager& operator = (const LeakyPipeManager&) = delete; public: static LeakyPipeManager* GetInstance() { static LeakyPipeManager manager; return &manager; } bool tryAcquire(const std::string& strKey, int32_t& lMilSec, const uint64_t lTokenNum, const uint64_t lCapacityNum, const double dRate) { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutexLeakyPipe); lMilSec = -1; uint64_t lCurrentMilSec = AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec(); LeakyPipeMap::iterator it = m_mapLeakyPipe.find(strKey); if (it == m_mapLeakyPipe.end()) { LeakyPipe* pLeakyPipe = new LeakyPipe(lCapacityNum, (1000 / dRate)); m_mapLeakyPipe[strKey] = pLeakyPipe; it = m_mapLeakyPipe.find(strKey); if (it == m_mapLeakyPipe.end()) { return false; } } if (!it->second->put(1)) { return false; } it->second->take(); return true; } private: LeakyPipeMap m_mapLeakyPipe; mutable std::mutex m_mutexLeakyPipe; }; #define AflGetLeakyPipeManager LeakyPipeManager::GetInstance |
5. 令牌桶算法
| 介绍 |
以恒定的速度往令牌桶中放入令牌 当有请求过来则从令牌桶中获取令牌进行后续请求 当获取令牌失败后则进行友好处理。 |
| 优点 |
预热限流和平滑限流兼备。 |
| 缺点 | |
| 图例 | 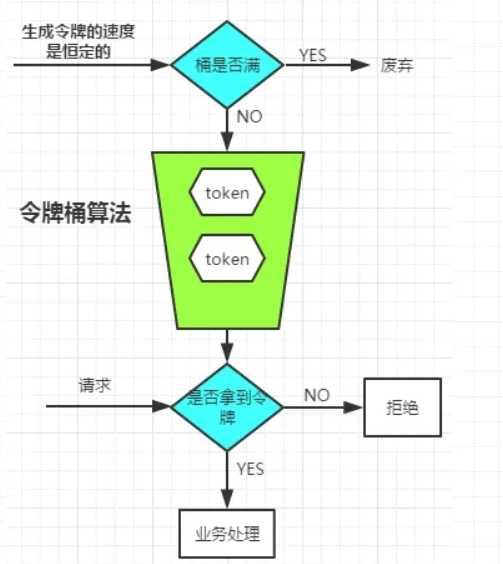 |
| 示例 | 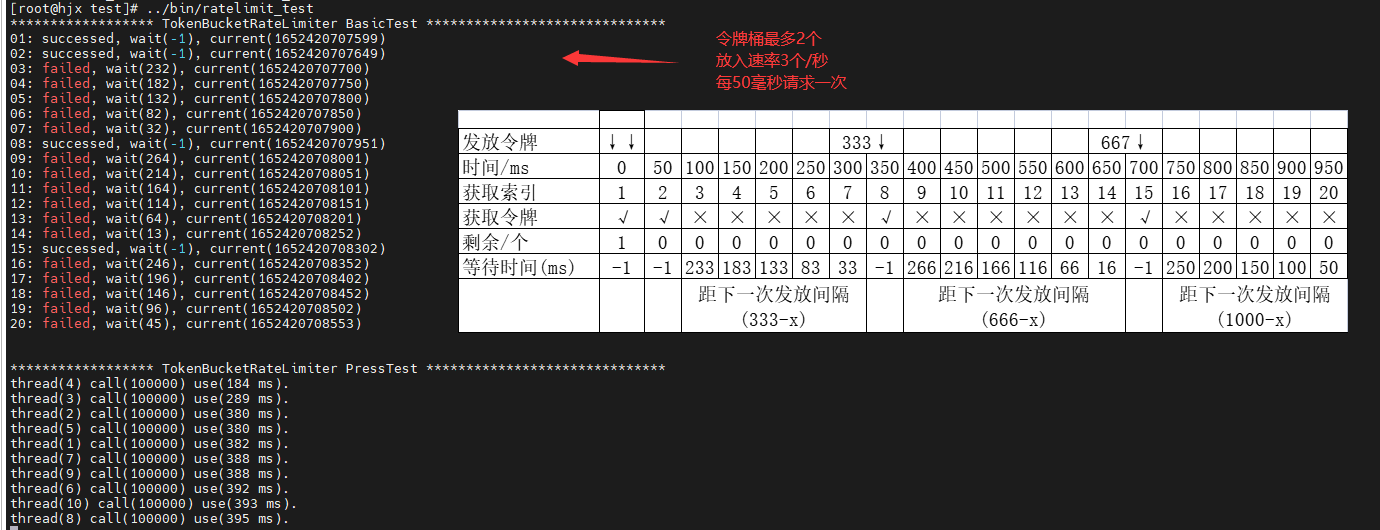 |
| 实现 |

struct TokenBucket { int64_t lLastMs; // 上一次ms; int64_t lRemainToken; // 剩余token }; typedef std::map<std::string, TokenBucket> TokenBucketMap; class TokenBucketManager { private: TokenBucketManager() {} virtual ~TokenBucketManager() {} TokenBucketManager(const TokenBucketManager&) = delete; TokenBucketManager& operator = (const TokenBucketManager&) = delete; using MutexLockUnique = std::unique_lock<std::mutex>; public: static TokenBucketManager* GetInstance() { static TokenBucketManager manager; return &manager; } bool tryAcquire(const std::string& strKey, int32_t& lMilSec, const uint64_t lTokenNum, const uint64_t lMaxTokenNum, const double dSpeed) { MutexLockUnique lock(m_mutexTokenBucket); lMilSec = -1; uint64_t lCurrentMilSec = AbstractRateLimiter::getCurrentMilSec(); TokenBucketMap::iterator it = m_mapTokenBucket.find(strKey); if (it == m_mapTokenBucket.end()) { TokenBucket tokenBucket; tokenBucket.lLastMs = lCurrentMilSec; tokenBucket.lRemainToken = lMaxTokenNum - lTokenNum; m_mapTokenBucket[strKey] = tokenBucket; return true; } #if 0 printf("CurrentMs[%lld], LastMs[%lld], RemainToken[%lld] \n", lCurrentMilSec, it->second.lLastMs, it->second.lRemainToken); #endif uint64_t lDiffTime = lCurrentMilSec - it->second.lLastMs; double dOneTime = 1000.0 / dSpeed; // 一个令牌的填充时间 if (lDiffTime > dOneTime) { // 如果间隔大于了一个令牌的填充时间 则进行填充; uint64_t lNowRemain = it->second.lRemainToken + (lDiffTime / dOneTime); if (lNowRemain >= lMaxTokenNum) { it->second.lLastMs = lCurrentMilSec; it->second.lRemainToken = lMaxTokenNum - lTokenNum; return true; } else { it->second.lLastMs = it->second.lLastMs + (uint64_t(lDiffTime / dOneTime) * dOneTime); it->second.lRemainToken = lNowRemain; } } if (it->second.lRemainToken >= lTokenNum) { it->second.lRemainToken -= lTokenNum; return true; } // 计算下一次满足令牌的时间 uint64_t lNextTime = it->second.lLastMs + (lTokenNum - it->second.lRemainToken) * dOneTime; lMilSec = lNextTime - lCurrentMilSec; return false; } private: TokenBucketMap m_mapTokenBucket; mutable std::mutex m_mutexTokenBucket; }; #define AflGetTokenBucketManager TokenBucketManager::GetInstance |
以上均为单进程的服务限流,主要目的是了解五种常见限流算法及其优缺点,详细参见gitee项目:https://gitee.com/ma_you_sun0821vip/RateLimiter。
后续会补充分布式的服务限流,敬请期待!




