Android学习笔记(三) UI布局
每一个布局都有其适合的方式,另外,这几个布局元素可以相互嵌套应用,做出美观的界面。
一、线性布局(LinearLayout)
线性布局,这个东西,从外框上可以理解为一个div,他首先是一个一个从上往下罗列在屏幕上。每一个LinearLayout里面又可分为垂直布局(android:orientation="vertical")和水平布局(android:orientation="horizontal" )。当垂直布局时,每一行就只有一个元素,多个元素依次垂直往下;水平布局时,只有一行,每一个元素依次向右排列。
linearLayout中有一个重要的属性 android:layout_weight="1",这个weight在垂直布局时,代表行距;水平的时候代表列宽;weight值越大就越大。
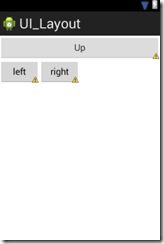
在XML文件中修改
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <Button android:text="Up" android:id="@+id/Button03" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button> <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <Button android:text="left" android:id="@+id/Button01" android:width="120px" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button> <Button android:text="right" android:id="@+id/Button02" android:width="120px" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
效果如下:
二、相对布局(RelativeLayout)
相对布局可以理解为某一个元素为参照物,来定位的布局方式。
android:layout_方向 = id 表示 在这个id对应的控件的方向上(上|下)
android:layout_align方向 = id 表示和这个控件的(上下左右)对齐
android: layout_to方向Of = id 表示在这个控件的左或者右
eg:
android:layout_below="@id/la1"/> 将当前控件放置于id为la1 的控件下方。
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" 使当前控件的右端和父控件的右端对齐。这里属性值只能为true或false,默认false。
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip" 使当前控件左边空出相应的空间。
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/true" 使当前控件置于id为true的控件的左边。
android:layout_alignTop="@id/ok" 使当前控件与id为ok的控件上端对齐。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:text="请输入信息" android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/editText1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_below="@+id/textView2" android:ems="10" > <requestFocus /> </EditText> <Button android:id="@+id/button2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_below="@+id/editText1" android:text="取消" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/button2" android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/button2" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/button2" android:text="确定" /> </RelativeLayout>
三、使用表格布局(TableLayout)来布局屏幕
三、表格布局(TableLayout)
表格布局类似Html里面的Table。每一个TableLayout里面有表格行TableRow,TableRow里面可以具体定义每一个元素。每个TableRow 都会定义一个 row (事实上,你可以定义其它的子对象,这在下面会解释到)。TableLayout 容器不会显示row 、cloumns 或cell 的边框线。每个 row 拥有0个或多个的cell ;每个cell 拥有一个View 对象。表格由列和行组成许多的单元格。表格允许单元格为空。单元格不能跨列,这与HTML 中的不一样。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/TableLayout01" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TableRow android:gravity="center" > <Button android:id="@+id/Button01" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button01" > </Button> </TableRow> <TableRow> <Button android:id="@+id/Button2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Button2" > </Button> </TableRow> <TableRow> <Button android:id="@+id/Button3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="1" android:text="Button3" > </Button> <Button android:id="@+id/Button4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="1" android:text="Button4" > </Button> </TableRow> <TableRow> <Button android:id="@+id/Button5" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="2" android:text="Button5" > </Button> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
四、层布局(FrameLayout)
层布局是最简单的一种布局方法,它在屏幕上设置一个空白备用区域。不能为FrameLayout中的一个子元素制定一个位置,后一个子元素将会直接在前一个子元素之上进行覆盖填充,把他们部分或全部挡住。
在FrameLayout布局里,定义任何空间的位置相关的属性都毫无意义。控件自动的堆放在左上角,根本不听你的控制。所以一般比较少用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="50sp" android:textColor="#000000" android:text="第一层"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="40sp" android:textColor="#ffff00" android:text="第二层"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="30sp" android:textColor="#ff00ff" android:text="第三层"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="20sp" android:textColor="#00ffff" android:text="第四层"/> </FrameLayout>
效果图