一、Linux指令语法结构
[tyang3@localhost Desktop]$ command [-options] [arguments]
指令 选项 参数
command 命令:表示命令的名称,如 ls、cd、cp等
options 选项:定义命令的执行特性,中刮号[]并不存在亍实际的指令中,而加入选项设定时,通常选项前会带 - 号或--号,有两种长短选项
短选项:用-引导,后面跟单个字符,如 -a、-l、-h等
多个短选项可以组合使用,效果和几个短选项一样,如-a –l -h===-alh
长选项:用--引导,后面跟完整的单词,如—help
arguments 参数:表示命令的作用对象,可以有多个参数,通常情况可以是文件名、目录、或用户名。
说明一:指令中第一个输入的部分绝对是『指令(command)』或者是『可执行文件案』
说明二:命令, 选项, 参数等这几个咚咚中间以空格来区分,不论空几格 shell 都规为一格
[tyang3@localhost Desktop]$ ls -al /etc
[tyang3@localhost Desktop]$ ls -al /etc
[tyang3@localhost Desktop]$ ls -a -l /etc
这三个命令效果完全一样
说明三:指令太长的时候,可以使用反斜杠 (\) 来跳脱[Enter]符号,使指令连续到下一行。 注意!反斜杠后就立刻接特殊字符,才能跳脱!
说明四:在Linux系统中,严格区分英文字母大小写,如cd和CD并不同
二、帮助命令
1. whatis <command>:显示简短功能描述
[tyang3@localhost Desktop]$ whatis ls
ls (1) - list directory contents
ls (1p) - list directory contents
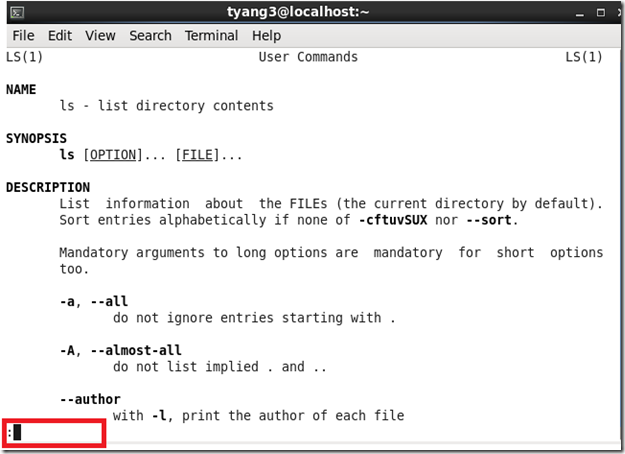
2. <command> --help:显示使用摘要和参数列表(可以查看大多数命令的用法)
[tyang3@localhost Desktop]$ ls --help
Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default).
Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, --all do not ignore entries starting with .
-A, --almost-all do not list implied . and ..
--author with -l, print the author of each file
3. Man [<chapter>] <command>:查看命令描述或手册页(Manual)
[tyang3@localhost Desktop]$ man ls
在man命令下底行模式:输入
/<text> 查找关键字
n/N 下一个/上一个
q 离开
man -k <keyword> 列出包含keyword关键字的手册页
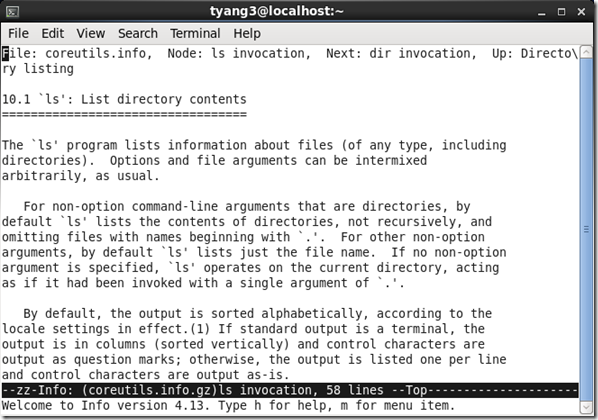
4. Info <command>:查看命令更详细的说明文件
[tyang3@localhost ~]$ info ls
注:info查看的是比man更详细的说明,也就是把man的页再划分为更小的章节,同时这个命令还可以链接到相似主题
info命令底行模式:
pageUp.pageDown 翻页
Tab 跳往下一个链接(有*的地方)
Enter 进入链接
n/p/u 跳往下一个(上一个)小节,上一层章节
s[<text>] 查找关键字
q 离开
在查看命令帮助时,会出现[],<>,|等符号,它们的含义如下:
[] 表示是可选的;
<> 表示是可变化的;
x|y|z 表示只能选择一个;
-abc 表示三个参数(或任何二个)的混合使用
usr/share/doc/ 说明文件目录
http://www.redhat.com/docs/ 在线说明文件
5. Linux下查阅历史记录命令
在Linux下,我们有时希望知道最近执行的命令,history会帮上大忙
- #history 5 显示最近使用的5个命令
- #history | more 显示使用过的所有命令
- #!5 执行历史编号为5的命令
- #!ls 执行最后一次以ls开头的命令
参考资料 http://www.cnblogs.com/CGDeveloper/archive/2011/05/27/2060009.html