2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营3
2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营3
智乃的博弈游戏
思路
当石子数 n 为奇数时,先手每次取 11 个石子,剩余偶数个石子。对方被迫取与偶数互质的奇数,剩余奇数个石子。循环此过程,最终先手在石子数为 11 时获胜。若 n 为偶数,后手将采用相同策略获胜。因此,判断 n 的奇偶性即可,奇数输出 Yes,偶数输出 No。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); i64 n; cin >> n; cout << (n % 2 == 0 ? "No" : "Yes") << "\n"; return 0; }
智乃的Notepad(Easy version)
思路
为了在记事本上显示所有单词,可以利用单词之间的共同前缀来减少按键次数。通过构建一个字典树(Trie),我们可以统计所有单词的共同前缀。假设字典树有 \(n\) 个节点,每个节点代表一个字符,那么总的按键次数为 \((n - 1) \times 2\),其中 \(n - 1\) 是边的数量,乘以 2 表示输入和退格操作。减去最长的单词长度 \(\text{mx}\),因为最长的单词不需要额外的退格操作。最终,最少按键次数为 \((n - 1) \times 2 - \text{mx}\)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; struct trie { int n; vector<array<int, 26>> trans; vector<int> cnt; trie() : n(0) { new_node(); } int new_node() { trans.push_back({}); trans.back().fill(0); cnt.push_back(0); return n++; } int insert(const string &s) { int now = 0; for (char c : s) { int i = c - 'a'; if (!trans[now][i]) { trans[now][i] = new_node(); } now = trans[now][i]; cnt[now]++; } return now; } }; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; trie tr; vector<string> s(n); int mx = 0; for (auto &i : s) { cin >> i; tr.insert(i); mx = max<int>(mx, i.size()); } while (m--) { int l, r; cin >> l >> r; } cout << (tr.n - 1) * 2 - mx << "\n"; return 0; }
智乃的小球
思路
要解决这个问题,我们需要确定在给定的 \(n\) 个小球中,第 \(k\) 对碰撞发生的时间。由于小球的质量相同,碰撞后它们会交换速度。我们可以将问题转化为寻找在时间 \(t\) 内发生的碰撞次数。
首先,我们将小球分为向右移动的集合 \(R\) 和向左移动的集合 \(L\),并分别对它们的位置进行排序。对于每个向右移动的小球 \(x \in R\),我们计算在时间 \(t\) 内有多少个向左移动的小球 \(y \in L\) 满足 \(x < y \leq x + 2t\)。这个条件确保了在时间 \(t\) 内,这两个小球会发生碰撞。
我们使用二分搜索来确定最小的时间 \(t\),使得在时间 \(t\) 内发生的碰撞次数至少为 \(k\)。具体来说,我们定义一个检查函数 \(check(mid)\),它计算在时间 \(mid\) 内发生的碰撞次数。如果这个次数大于或等于 \(k\),我们调整搜索范围以找到更小的时间。
最终,我们输出找到的最小时间 \(t\),确保在第 \(k\) 对碰撞发生时的时间精度达到 \(10^{-7}\)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, k; cin >> n >> k; vector<int> L, R; for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; if (y == 1) { R.emplace_back(x); } else { L.emplace_back(x); } } ranges::sort(R); ranges::sort(L); int Mi = 0; for (auto x : R) { auto t = upper_bound(L.begin(), L.end(), x); Mi += L.end() - t; } if (R.empty() || L.empty() || R.front() > L.back() || Mi < k) { cout << "No\n"; return 0; } cout << "Yes\n"; constexpr double eps = 1e-7; auto check = [&](double mid)->bool{ int res = 0; for (auto x : R) { auto a = upper_bound(L.begin(), L.end(), x); auto b = upper_bound(L.begin(), L.end(), x + 2 * mid); res += b - a; } return res >= k; }; double l = 0, r = (L.back() - R.front()); while (r - l > eps) { double mid = (l + r) / 2; if (check(mid)) { r = mid; } else { l = mid; } } cout << fixed << setprecision(6) << l << "\n"; return 0; }
智乃的捉迷藏
思路
问方程组是否存在非负整数解
等式左右两边求和得 \(2(x_1 + x_3 + x_5) + (x_2 + x_4 + x_6) = A + B + C\),令 \(X = x_1 + x_3 + x_5\),\(Y = x_2 + x_4 + x_6\),得
解得
题目要求 \(X, Y\) 同时为非负整数
则整理后得 \(N \leq A + B + C \leq 2N\) 时,符合条件
时间复杂度 \(O(1)\)
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; void solve() { int n, a, b, c; cin >> n >> a >> b >> c; if (a + b + c >= n && a + b + c <= 2 * n) { cout << "Yes\n"; } else { cout << "No\n"; } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { solve(); } return 0; }
智乃与模数
思路
首先,我们观察到余数的分布具有一定的规律性。对于每个区间 \([l, r]\),其中 \(r = \left\lfloor \frac{n}{\left\lfloor \frac{n}{l} \right\rfloor} \right\rfloor\),余数的值 \(a = n \mod i\) 会随着 \(i\) 的增加而递减。我们可以利用这一性质,通过二分搜索找到第 \(k\) 大的余数值 \(val\),并统计所有大于等于 \(val\) 的余数的个数及其总和。
具体实现中,我们使用二分搜索确定 \(val\),并通过分段计算每个区间内满足条件的余数的个数和总和。最终,我们将这些结果累加,得到前 \(k\) 项余数的和。时间复杂度为 \(O(\sqrt{n} \log n)\)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int N, K; cin >> N >> K; int L = 1, R = N; int val = 0, vtot = 0; while (L <= R) { int mid = (L + R) / 2; int tot = 0; for (int l = 1, r; l <= N; l = r + 1) { r = N / (N / l); int a = N - N / l * l; int k = (N / l); if (a < mid)continue; tot += min((a - mid) / k + 1, r - l + 1); } if (tot >= K) { L = mid + 1; } else { vtot = tot; val = mid; R = mid - 1; } } i64 ans = 1LL * (K - vtot) * (val - 1); for (int l = 1, r; l <= N; l = r + 1) { r = N / (N / l); int a = N - N / l * l; int k = (N / l); if (a < val) continue; int len = min((a - val) / k + 1, r - l + 1); ans += 1LL * (a * 2 - k * (len - 1)) * len / 2; } cout << ans << "\n"; return 0; }
智乃的逆序数
思路
首先,我们将所有“紧密”序列按照起始元素从小到大排序,并将它们的元素合并为一个序列 \(a\),同时记录每个元素所属的原始序列编号。
接下来,我们计算当前序列 \(a\) 的逆序数。如果当前逆序数已经大于 \(k\),则无法满足条件,输出“No”。否则,我们通过交换不同序列的元素来增加逆序数,直到逆序数恰好为 \(k\)。具体来说,我们从左到右遍历序列,如果发现相邻的两个元素属于不同序列且前一个元素小于后一个元素,则交换它们,并减少 \(k\) 的值。
最终,如果能够通过上述操作使逆序数恰好为 \(k\),则输出“Yes”并输出构造的序列;否则,输出“No”。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, k; cin >> n >> k; vector v(n, vector<int>()); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int l; cin >> l; for (int j = 0; j < l; ++j) { int x; cin >> x; v[i].push_back(x); } } sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](auto & x, auto & y) { return x[0] < y[0]; }); vector<pair<int, int>> a; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (auto &j : v[i]) { a.emplace_back(i, j); } } auto calc = [&]()->int{ int ret = 0; for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < a.size(); ++j) { if (a[i] > a[j])++ret; } } return ret; }; k -= calc(); if (k < 0) { cout << "No\n"; return 0; } auto bsort = [&]()->void{ for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i) { for (int j = 0; j + 1 < a.size(); ++j) { if (a[j].first == a[j + 1].first) continue; if (k > 0 && a[j].second < a[j + 1].second) { swap(a[j], a[j + 1]); --k; } } } }; bsort(); if (k > 0) { cout << "No\n"; return 0; } cout << "Yes\n"; for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i) { cout << a[i].second << " \n"[i == a.size() - 1]; } return 0; }
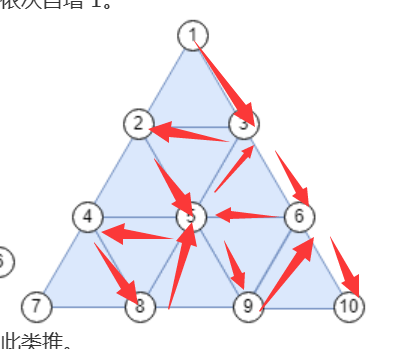
智乃的三角遍历
思路
按照如图方向勾画即可,最后从右下角节点一笔画到最左边然后上来回到第一个节点。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n; cin >> n; cout << "Yes\n"; n ++; vector a(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1)); int cnt = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++) { a[i][j] = ++cnt; } } for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) { cout << a[i - 1][i - 1] << " "; for (int j = i; j < n; j ++) { cout << a[j][i] << " " << a[j][i - 1] << " "; } for (int j = n; j > i; j --) { cout << a[j][i] << " "; } } int x = n * (n + 1) / 2; for (int j = 0; j < n; x--, j++) { cout << x << " "; } for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i --) { x -= i; cout << x + 1 << " "; } return 0; }
智乃的牛题
思路
题中已将字母按 \(Ascii\) 码排序,所以我们将给的字符串排序后比较即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); string s; cin >> s; string p = "cdenoorw"; sort(s.begin(), s.end()); if (s == p) { cout << "happy new year\n"; } else { cout << "I AK IOI\n"; } return 0; }
本文作者:Ke_scholar
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Kescholar/p/18706443
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步