2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2
2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2
A-一起奏响历史之音!_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
按题意模拟即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int x; for (int i = 0; i < 7; i ++) { cin >> x; if (x != 1 && x != 2 && x != 3 && x != 5 && x != 6) { cout << "NO\n"; return 0; } } cout << "YES\n"; return 0; }
B-能去你家蹭口饭吃吗_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
排序后找中位数,然后 \(-1\) 即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); for (auto &i : a) { cin >> i; } sort(a.begin(), a.end()); cout << a[n / 2] - 1 << "\n"; return 0; }
C-字符串外串_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
参考出题人题解 1

代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; signed main() { int Task = 1; for (cin >> Task; Task; Task--) { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; if (n == m || n - m > 26) { cout << "NO\n"; continue; } cout << "YES\n"; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cout << (char)('a' + i % (n - m)); } cout << "\n"; } }
D-字符串里串_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
找到每个字符的最后一个位置,然后从前遍历,如果当前字母的位置不是它的最后一个位置,则说明后面一定存在一个相同字符使得它能被构造出来;相同地,前面也可以,所以可以将字符串反转后再来一次,取最大值即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n; cin >> n; string s; cin >> s; auto check = [](string & s)->int{ vector<int> pos(26); for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++) { pos[s[i] - 'a'] = i; } int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++) { if (pos[s[i] - 'a'] != i) { res = i + 1; } } return res; }; int ans = 0; ans = max(ans, check(s)); reverse(s.begin(), s.end()); ans = max(ans, check(s)); cout << ans << "\n"; return 0; }
E-一起走很长的路!_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
参考出题人题解1
考虑每个减法是局部的负贡献,而加法是局部的正贡献,若想将每一步的加法变为全局正贡献,只需要把加法操作使用在 \(i = l\),便可以对 \(i \in [l, r]\) 起正贡献。
对于每个询问 \([l, r]\) 可以发现本质上是求对于任意的 \(\max_{i=l+1}^{r}(0, a_i - \sum_{j=l}^{i-1} a_j)\),那么就可以考虑用前缀和、\(ST\) 表或者线段树维护区间最大值即可,特别的由于 \(i\) 是手推,不需要贡献,所以特别 \(l\) 时不需要操作的情况。
时间 \(O(n \times \log n + q)\)。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; template<typename T> struct RMQ { int n; vector<T>a; RMQ(vector<T>_a, int _n): a(_a), n(_n) { stmin.resize(n + 5); for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { stmin[i].resize(21, 0); } solve(); } vector<vector<T>> stmin; void solve() { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { stmin[i][0] = a[i]; } for (int i = 1; (1 << i) <= n; i++) { int len = (1 << i); for (int j = 1; j + len - 1 <= n; j++) { stmin[j][i] = min(stmin[j][i - 1], stmin[j + (1 << (i - 1))][i - 1]); } } } T askmin(int l, int r) { int len = log2(r - l + 1); return min(stmin[l][len], stmin[r - (1 << len) + 1][len]); } }; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); int n, q; cin >> n >> q; vector<i64>a(n + 1), s(n + 2); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i]; } vector<i64>cz(n + 2); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cz[i] = s[i - 1] - a[i]; } RMQ<i64> T(cz, n); while (q--) { int l, r; cin >> l >> r; if (l == r) { cout << 0 << "\n"; continue; } i64 ts = s[l - 1]; cout << abs(min(0LL, T.askmin(l + 1, r) - ts)) << "\n"; } return 0; }
F-一起找神秘的数!_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
赛时打表猜的,出题人有严谨证明,这里给出出题人题解。
对于任意两个数 \(x\) 和 \(y\),我们可以从二进制的角度来看,对于第 \(i\) 位,记为 \(\bar{x}\) 和 \(\bar{y}\),有以下四种情况:
- 当 \(\bar{x} = 0, \bar{y} = 0\) 时:\((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) = 0, \, (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = 0, \, \bar{x} + \bar{y} = 0\)。所以 \((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) + (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = \bar{x} + \bar{y}\);
- 当 \(\bar{x} = 0, \bar{y} = 1\) 时:\((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) = 0, \, (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = 1, \, \bar{x} + \bar{y} = 1\)。所以 \((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) + (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = \bar{x} + \bar{y}\);
- 当 \(\bar{x} = 1, \bar{y} = 0\) 时:\((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) = 0, \, (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = 1, \, \bar{x} + \bar{y} = 1\)。所以 \((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) + (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = \bar{x} + \bar{y}\);
- 当 \(\bar{x} = 1, \bar{y} = 1\) 时:\((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) = 1, \, (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = 1, \, \bar{x} + \bar{y} = 2\)。所以 \((\bar{x} \text{ and } \bar{y}) + (\bar{x} \text{ or } \bar{y}) = \bar{x} + \bar{y}\)。
综上,我们证明了 \((x \text{ and } y) + (x \text{ or } y) = x + y\)。
故题意转化为求 \(x \text{ or } y = 0\) 的对数,根据异或性质可得,当且仅当 \(x = y\) 时等式成立,故答案为区间长度,即 \(r - l + 1\)。
时间 \(O(T)\)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; void solve() { i64 l, r; cin >> l >> r; cout << r - l + 1 << "\n"; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { solve(); } return 0; }
G-一起铸最好的剑!_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
由于幂的增长性很快,直接暴力枚举即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; void solve() { i64 n, m; cin >> n >> m; int ans = 1,k = m; while (abs(m * k - n) < abs(n - m)) { m *= k; ans ++; } cout << ans << "\n"; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { solve(); } return 0; }
H-一起画很大的圆!_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
想复杂了,参考出题人题解1。
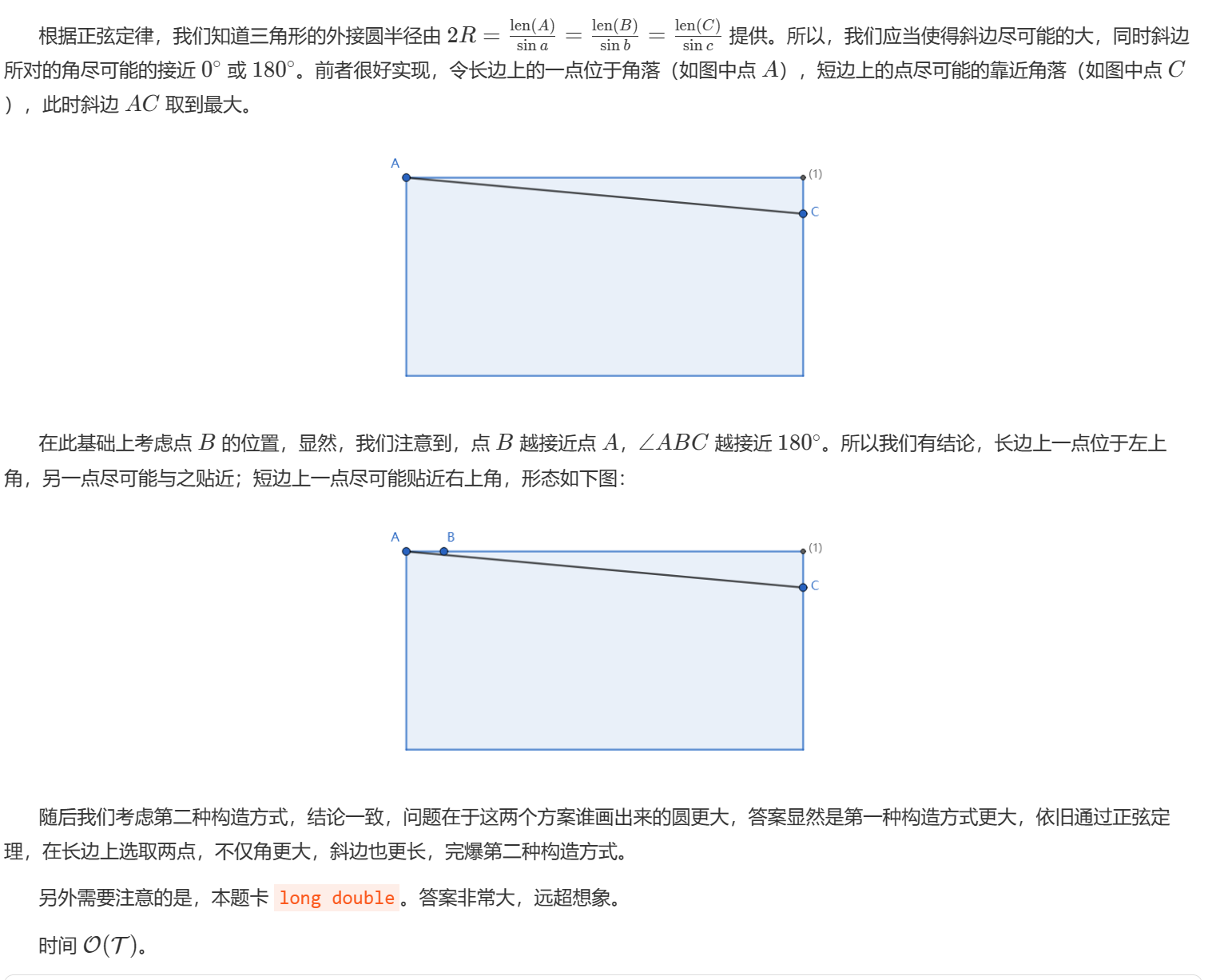
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; signed main() { int T; cin >> T; while (T--) { int a, b, c, d; cin >> a >> b >> c >> d; if (b - a < d - c) { cout << a << " " << c << "\n"; cout << a << " " << c + 1 << "\n"; cout << a + 1 << " " << d << "\n"; } else { cout << a << " " << d << "\n"; cout << a + 1 << " " << d << "\n"; cout << b << " " << d - 1 << "\n"; } } }
J-数据时间?_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
模拟。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, h, m; cin >> n >> h >> m; vector<set<string>> ans(3); for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { string user, date, Time; cin >> user >> date >> Time; int y = stoi(date.substr(0, 4)); int mo = stoi(date.substr(5, 2)); if (y != h || mo != m) { continue; } int hh = stoi(Time.substr(0, 2)); int mm = stoi(Time.substr(3, 2)); int ss = stoi(Time.substr(6, 2)); int t = hh * 3600 + mm * 60 + ss; if ((t >= 7 * 3600 && t <= 9 * 3600) || (t >= 18 * 3600 && t <= 20 * 3600)) { ans[0].insert(user); } else if (t >= 11 * 3600 && t <= 13 * 3600) { ans[1].insert(user); } else if (t >= 22 * 3600 || t <= 3600) { ans[2].insert(user); } } for (int i = 0; i < 3; i ++) { cout << ans[i].size() << " "; } return 0; }
K-可以分开吗?_2025牛客寒假算法基础集训营2 (nowcoder.com)
思路
找联通块,然后对其用 \(BFS\) 把周围的白块记录一下,最后取所有记录的最小值即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; const int u[] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, v[] = {0, 0, 1, -1}; bool vis[502][502]; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector<string> s(n); for (auto &i : s) { cin >> i; } int ans = n * m, cnt = 0; vector last(n, vector(m, 0)); for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++) { if (vis[i][j] || s[i][j] != '1') continue; int res = 0; cnt ++; queue<pair<int, int>> Q; Q.emplace(i, j); vis[i][j] = 1; while (Q.size()) { auto [nx, ny] = Q.front(); Q.pop(); for (int k = 0; k < 4; k ++) { int dx = nx + u[k], dy = ny + v[k]; if (dx < 0 || dx >= n || dy < 0 || dy >= m) continue; if (s[dx][dy] == '1' && !vis[dx][dy]) { Q.emplace(dx, dy); vis[dx][dy] = 1; } else if (s[dx][dy] == '0') { if (last[dx][dy] != cnt) { res ++; last[dx][dy] = cnt; } } } } ans = min(ans, res); } } cout << ans << "\n"; return 0; }
参考文献
本文作者:Ke_scholar
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Kescholar/p/18692176
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步