2023 ICPC网络赛第一场(A,D,J,L)
2023 ICPC网络赛第一场(A,D,J,L)
A Qualifiers Ranking Rules
先把两场比赛的学校排名处理出来,然后两场比赛的同位次进行合并即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector<string> str1, str2,ans; map<string, bool> vis1, vis2, vis; string s; for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { cin >> s; if (vis1[s]) continue; str1.emplace_back(s); vis1[s] = true; } for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) { cin >> s; if (vis2[s]) continue; str2.emplace_back(s); vis2[s] = true; } n = str1.size(), m = str2.size(); for (int i = 0; i < max(n,m); i ++) { if (i < n && !vis[str1[i]]) { ans.emplace_back(str1[i]); vis[str1[i]] = true; } if (i < m && !vis[str2[i]]) { ans.emplace_back(str2[i]); vis[str2[i]] = true; } } for (auto i : ans) cout << i << '\n'; return 0; }
D Transitivity
如果题目给的所有的团都是完全图,那么就要合并两个最小的团,答案就是这两个团的点数的乘积,否则就要把所有的团都补成完全图,bfs或者并查集即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug(a) cout<<#a<<"="<<a<<'\n'; using namespace std; using i64 = long long; typedef pair<i64, i64> PII; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector g(n + 1, vector<int>()); for (int i = 0, x, y; i < m; i ++) { cin >> x >> y; g[x].push_back(y); g[y].push_back(x); } vector<bool> vis(n + 1); vector<i64> ans; auto bfs = [&](int i) -> pair<i64, i64> { queue<int> Q; Q.push(i); int edge = 0, node = 0; while (Q.size()) { auto v = Q.front(); Q.pop(); if(vis[v]) continue; vis[v] = true; node ++; for (auto i : g[v]) { if (vis[i]) continue; Q.push(i); edge ++; } } return {node, edge}; }; bool is_Tuan = true; i64 res = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { if (vis[i]) continue; auto [num, Edge] = bfs(i); if (Edge != num * (num - 1) / 2) { is_Tuan = false; res += num * (num - 1) / 2 - Edge; } ans.push_back(num); } if (!is_Tuan) { cout << res << '\n'; } else { sort(ans.begin(), ans.end()); cout << ans[0] * ans[1] << '\n'; } return 0; }
J Minimum Manhattan Distance
题意是求在\(C_2\)上取一点到\(C_1\)任意一点的最小期望曼哈顿距离.
由于题目要求是最小期望曼哈顿距离,所以可以等价于看做就到\(C_1\)圆心,为了方便计算,可以把\(C_2\)的圆心看成坐标轴原点,\(C_1\)的圆心通过对称变换到第一象限,设\(\{x_0,y_0\}\)为答案点,则有\(\begin{cases} x_0 = x_2 + r_2\cos\theta \\ y_0 = y_2+r_2\sin \theta\end{cases}\),答案为\(|x_1-x_0|+|y_1-y_0|\),
且题目规定\(\forall x_i \in C_1 \neq \forall x_j \in C_2,\forall y_i \in C_1 \neq \forall y_j\in C_2,\),所以当\(C_1\)在第一象限时,总有\(x_1>x_0,y_1>y_0\),所以绝对值可拆,然后用三角函数计算一下,可得出当\(\theta = \frac{\pi}{4}\)时有最小值\(x+y-\sqrt{2}\times r_2\).
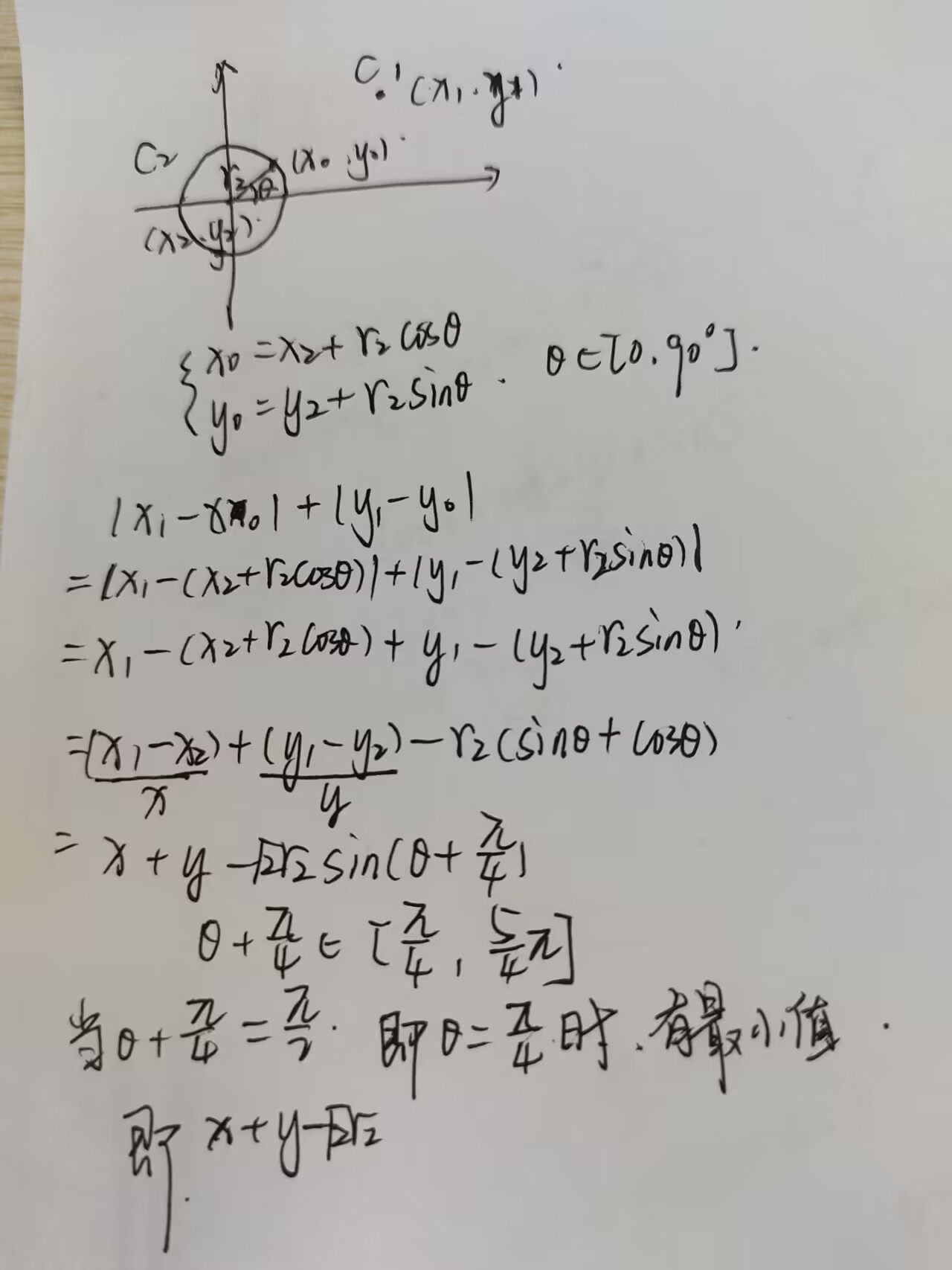
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using i64 = long long; using namespace std; typedef pair<i64, i64> PII; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); auto get = [&](double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ return sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2)); }; int T; cin >> T; while(T--){ double xa,ya,xb,yb,xc,yc,xd,yd; cin >> xa >> ya >> xb >> yb >> xc >> yc >> xd >> yd; double r2 = get(xc,yc,xd,yd) / 2; double x1 = (xa + xb) / 2, y1 = (ya + yb) / 2; double x2 = (xc + xd) / 2, y2 = (yc + yd) / 2; double ans = fabs(x1 - x2) + fabs(y1 - y2) - r2 * sqrt(2) ; printf("%.10lf\n",ans); } return 0; }
L KaChang!
签到题,题目规定了\(k\geq 2\),所以答案为\(\max(2,\lceil\frac{T}{\max\limits_{i=1}^{n}a_i}\rceil)\)
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug(a) cout<<#a<<"="<<a<<'\n'; using namespace std; using i64 = long long; typedef pair<i64, i64> PII; int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); i64 n, k; cin >> n >> k; i64 ma = 0, x; for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++){ cin >> x; ma = max(ma, x); } cout << max(2ll, (k + ma - 1) / k) << '\n'; return 0; }
本文作者:Ke_scholar
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Kescholar/p/17722627.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步