23暑假友谊赛
23暑假友谊赛(牛客小白月赛23)
A-马猴烧酒
注意到他给的行是一个比较小的数,所以我们可以去对行进行一个搜索,每次去搜索将某些行消灭后再去找列里边有哪些需要单独消灭的,这里我们可以将需要消灭的列存入一个set里边,这样即使每次碰到重复的列也不用担心了,如果set的size小于给定的b次的话,说明那就可以在规定次数内全歼,\(num\)就是代表的是当前消灭了多少行
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
int n,m,a,b;
cin >> n >> m >> a >> b;
vector<string> g(n);
for(auto &i : g) cin >> i;
bitset<21> vis(0);
bool ok = false;
auto dfs = [&](auto self,int hang,int num){
if(hang > n || num > a || ok)
return ;
set<int> lie;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++){
if(vis[i]) continue;
for(int j = 0;j < m;j ++){
if(g[i][j] == '*') lie.insert(j);
}
}
if(lie.size() <= b){
ok = true;
return ;
}
vis[hang] = 1;
self(self, hang + 1, num + 1);
vis[hang] = 0;
self(self,hang + 1, num);
};
dfs(dfs,0,0);
cout << (ok ? "yes" : "no") << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B-阶乘 (质因子分解 + 二分)
判断一个\(n!\)是否是\(p\)的倍数,就看\(n!\)的阶乘里是否出现了\(p\)的全部质因子,比如60可以拆解为\(2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 5\),所以当一个\(n!\)的阶乘包含了这些质因子的话就可以是\(p\)的倍数,比如\(5!\),\(1 \times 2 \times 3 \times 4 \times 5\)里面,2和4提供了3个2,3提供了3,5提供了5,即提供了60的全部质因子,而大于5的数的阶乘也一定满足,但是只有5是满足条件的最小值.
所以我们可以先把\(p\)的质因子数记录下来,然后二分答案,找到一个满足全部质因子数的最小即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
#define int long long
int v[N];
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
int p,n,m;
cin >> p;
n = p;
memset(v,0,sizeof v);
for(int i = 2;i * i<= n;i ++){
while(p % i == 0){
p /= i;
v[i]++;
}
}
auto check = [&](int x,int i){
int res = 0;
while(x){
res += x / i;
x /= i;
}
return res >= v[i];
};
int ans = p;
for(int i = 2;i * i<= n;i ++){
if(n % i == 0 && v[i]){
int l = 0, r = 1e9;
while(l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(check(mid,i))
r = mid - 1;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
ans = max(ans, l);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C-完全图(二分 + 贪心)
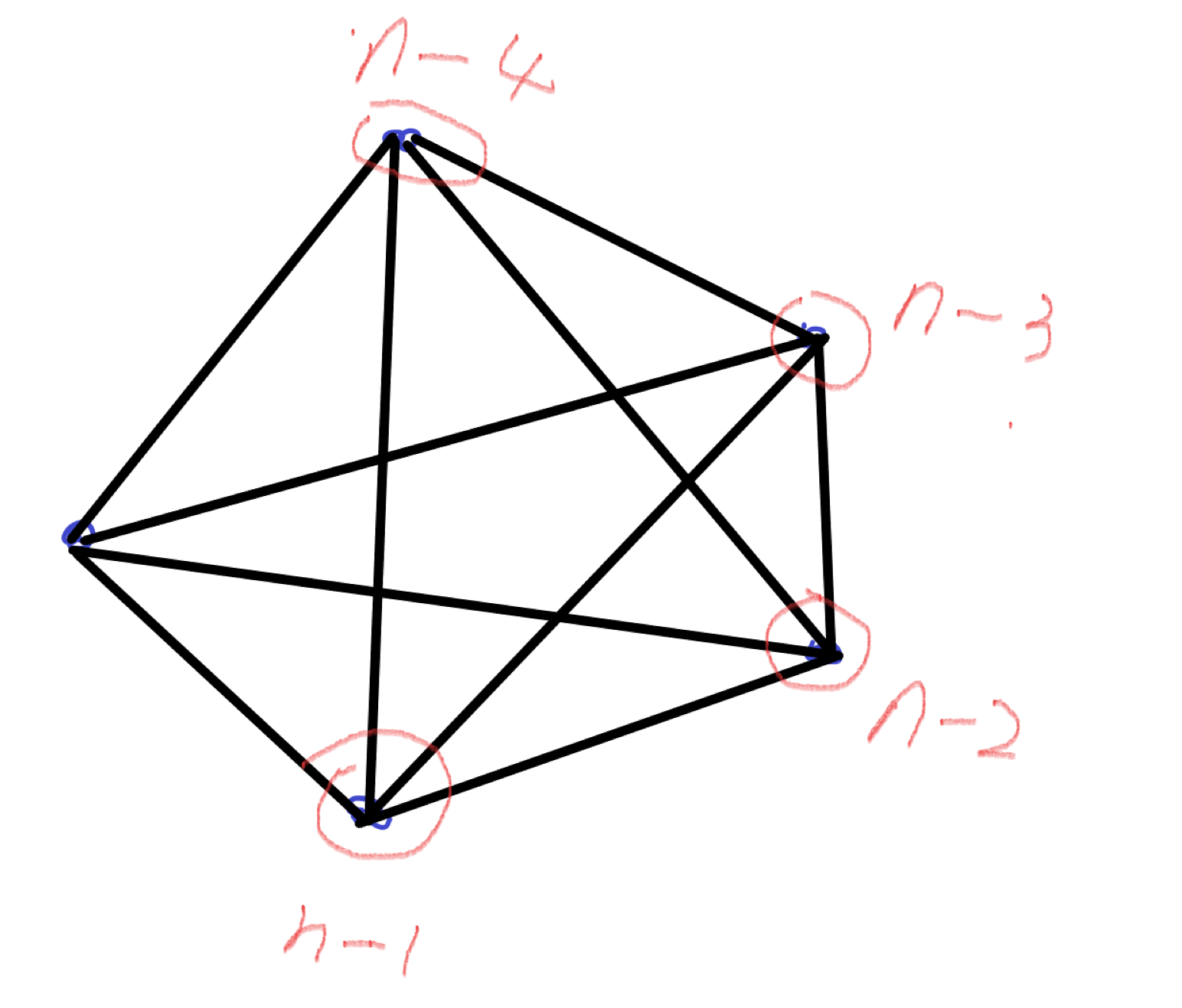
每次贪心的一个点挨着一个点的删,第一个点需要删\((n - 1)\)条边,第二个点需要\((n -2)\)条边\(...\)第\(x\)个点就需要删\((n - x)\)条边,总共删了\(n \cdot x - \frac{x \cdot (x + 1)}{2}\),且答案很大,达到了\(1e18\),乘的时候会爆\(long long\),需要开一下__int28,每次去二分答案找一个小于m的最大值即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m;
auto check = [&](int x){
return (__int128)2 * n * x - x * (x + 1) <= 2 * m;
};
int l = 1, r = n - 1;
while(l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(check(mid))
l = mid + 1;
else
r = mid - 1;
}
cout << l << endl;
}
return 0;
}
E-A+B问题
这题说是挺坑的,咱也WA了一发,涉及到整形溢出,哎,不懂,可以看看下面这篇博客
牛客小白月赛23----A+B问题之整型溢出_长整型 问题 a: a+b_0522Skylar的博客-CSDN博客
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << 4294967296 << endl;
return 0;
}
G-树上求和
我们只需要计算出每条边被访问了多少次,然后将访问次数排序,访问最多的赋值最小的,访问少的赋值最大的就行
访问次数 = 这条边的左端点数\(\times\)这条边的右端点数,即\(size[u] \times (n - size[u])\)
如图
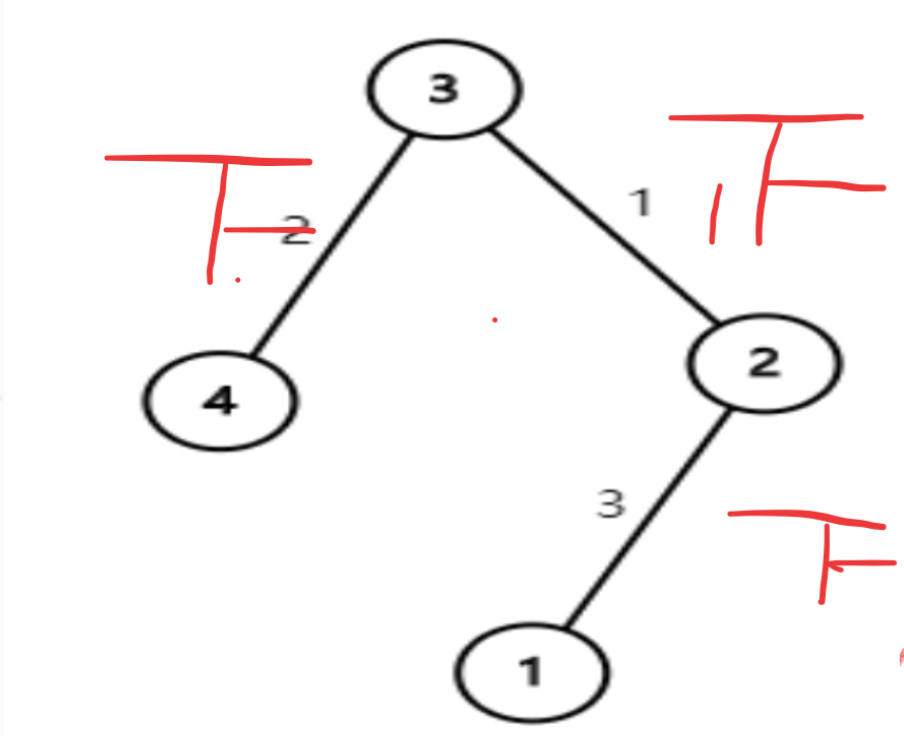
\(<2,3>\)边被访问了4次,其他边被访问了3次,所以让\(<2,3 >\)边赋值1即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);
int n ;
cin >> n;
vector<int> e[n + 1];
for(int i = 1 ,x ,y;i < n;i ++){
cin >> x >> y;
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
vector<int> ans,w(n + 1,1);
function<void(int,int)> dfs = [&](int u, int fa)->void {
for(auto i : e[u]){
if(i == fa) continue;
dfs(i, u);
w[u] += w[i];
}
ans.push_back(1ll * w[u] * (n - w[u]));
};
dfs(1,0);
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < n;i ++){
res += (n - i) * ans[i];
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
H-奇怪的背包问题增加了
这题我是模拟过去的,把每个数的个数记录一下,然后从29开始找,起初需要一个30,如果29个数大于了二倍need,则说明满足条件,否则就往后找,同时need也会变为原来的二倍,直到找到符合条件为止,如果最后need还是不等于0的话,则说明不能组成30,输出impossible,否则就看每个数与原来记录的数相比是不是少了,少了则说明这个被用掉了,输出1,然后这个数记录+1,否则输出0
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> k(n),a(31);
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++){
cin >> k[i];
a[k[i]]++;
}
auto b = a;
int need = 1;
for(int i = 29;i >= 0;i--){
if(b[i] / 2 >= need){
b[i] -= 2 * need;
need = 0;
break;
}else {
need = 2 * need - b[i];
b[i] = 0;
}
}
if(need){
cout << "impossible" << endl;
}else{
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++){
if(a[k[i]] > b[k[i]]){
cout << 1 ;
b[k[i]]++;
}else
cout << 0;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
I-寻找子串
需要注意的是前缀都相同的字符串,长度更长的那个字典序更大,比如aaaaa字典序是大于aaa的,知道了这一点那这题就好做了,直接无脑把每个下标到最后的这段字符串存起来,然后排个序,输出最大值就好了
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);
string s;
cin >> s;
vector<string> as;
for(int i = 0;i < s.size();i ++){
as.push_back(s.substr(i));
}
sort(as.begin(),as.end());
cout << as.back() << endl;
return 0;
}
J-最大的差
排个序,然后用最大值减去最小即可,当然你也可以输入的时候就去记录最大最小值
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for(auto &i : a) cin >> i;
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
cout << a.back() - a.front() << endl;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号