蒟蒻成长记录
排列数
算是记录一个求全排列的方法吧,()
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> #include <cstdio> #include <utility> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define endl '\n' #define int long long using namespace std; const int N = 1e5+10; //typedef long long ll; int n,m,t,a[N]; bool vis[N]; void dfs(int x){ //if(x > n) return; if(x > n){ for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cout << a[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; return ; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { if(!vis[i]){ vis[i] = 1; a[x] = i; dfs(x + 1); vis[i] = 0; a[x] = 0; } } } signed main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); cin >> n; dfs(1); return 0; }

以后可以不用一直想着那个next_permutation那个了(又难记又不好控制)
该方法应用P1088 [NOIP2004 普及组] 火星人 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
还可以从任意给定的顺序进行全排列
如何控制可以看看该题题解:
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> #include <cstdio> #include <utility> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define endl '\n' #define int long long using namespace std; const int N = 1e5+10, M = 20; //typedef long long ll; int n,m,mars[N],ans; bool return0, vis[N] ; int a[N]; void dfs(int x) { if(return0) return ; if(x > n) { ans++; if(ans == m + 1){ return0 = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << a[i] << ' '; } return ; } for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i++ ) { if(!ans){ i = mars[x];//从给定的顺序进行排列 } if(!vis[i]){ vis[i] = 1; a[x] = i; dfs(x + 1); a[x] = 0; vis[i] = 0; } } } signed main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> m; for(int i = 1; i <= n ;i ++) { cin >> mars[i]; } dfs(1); return 0; }
组合数
C(5,3)
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> #include <cstdio> #include <utility> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define endl '\n' #define int long long using namespace std; const int N = 1e5+10, M = 20; //typedef long long ll; int n,m,arr[N],ans = 1e9 ,A,B; bool return0, vis[N] ; void dfs(int x, int y) { if(x > m) { for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cout << arr[i] << ' '; cout << endl; return ; } for(int i = y;i <= n; i++) { if(!vis[i]) { vis[i] = 1; arr[x] = i; dfs(x + 1, i + 1); vis[i] = 0; arr[x] = 0; } } } signed main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> m; dfs(1,1); return 0; }
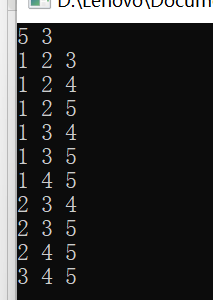
例题
本文作者:Ke_scholar
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Kescholar/p/17289075.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步