排序算法复习笔记
最近在复习排序算法,看了很多大佬的博客,整理如下:
先是排序中常用的swap()函数:
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) { int tmp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = tmp; }
冒泡排序:
/** * 冒泡排序:每次循环,将最后一个位置排序好 * 算法改进:加一个标志位,记录每趟排序最后一个进行交换的位置,下一次只需扫描到pos */ public void bubbleSort(int[] a) { if (a == null) { return; } int right = a.length - 1; while (right > 0) { int pos = 0; for (int start = 0; start < right; start++) { if (a[start] > a[start + 1]) { swap(a, start, start + 1); pos = start; } } right = pos; } }
直接插入排序:
/* 将一个记录插入到已排序好的有序表中,从而得到一个新,记录数增1的有序表。即:先将序列的第1个记录看成是一个有序的子序列,然后从第2个记录逐个进行插入,直至整个序列有序为止。 */ public void insertSort(int[] a) { for (int right = 1; right < a.length; right++) { if (a[right] < a[right - 1]) { int tmp = a[right]; // 保存临时变量 int left = right - 1; a[right] = a[right - 1]; // 先后移一个位置 for (; left >= 0 && tmp < a[left]; left--) { a[left + 1] = a[left]; } a[left + 1] = tmp;// 插入到正确位置 } } }
简单选择排序 :
- 选出最小的元素,与数组第一个位置交换
- 选出第i小的元素,与数组第i个位置交换
- 直到第n-1个元素,与第n个元素比较为止
/** * 选择排序-简单选择排序 * 基本思想:在一组要排序的数中,选取最小的与第一个位置交换 */ public void selectSort(int[] a) { for(int start = 0; start < a.length; start++) { int key = selectMinKey(a, start); swap(a, key, start); } } private int selectMinKey(int[] a, int start) { int key = start; for(int i = start; i < a.length; i++) { key = a[key] > a[i] ? i : key; } return key; }
快速排序:
public void quickSort(int[] a) { quickSort0(a, 0, a.length - 1); } private void quickSort0(int[] a, int low, int high) { if (low < high) { int pos = partition(a, low, high); quickSort0(a, low, pos - 1); quickSort0(a, pos + 1, high); } } private int partition(int[] a, int low, int high) { int privotKey = a[low]; while (low < high) { while (low < high && a[high] >= privotKey) { high--; } swap(a, low, high); while (low < high && a[low] <= privotKey) { low++; } swap(a, low, high); } return low; }
归并排序:
public void mergeSort(int[] a) { mergeSort0(a, 0, a.length - 1); } private void mergeSort0(int[] a, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; mergeSort0(a, left, mid); mergeSort0(a, mid + 1, right); merge(a, left, mid, right); } } private void merge(int[] a, int start1, int mid, int right) { int[] tmp = new int[a.length]; int k = start1; // tmp的初始下标 int start = start1; // 记录初始位置 int start2 = mid + 1; // 第2个数组的起始位置 for(; start1 <= mid && start2 <= right; k++) { tmp[k] = a[start1] < a[start2] ? a[start1++] : a[start2++]; } // 左边剩余的合并 while (start1 <= mid) { tmp[k++] = a[start1++]; } // 右边剩余的合并 while (start2 <= right) { tmp[k++] = a[start2++]; } // 复制数组 while (start <= right) { a[start] = tmp[start]; start++; } }
堆排序:
public void heapSort(int[] a) { buildingHeap(a, a.length); for (int i = a.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { swap(a, i, 0); adjustHeap(a, 0, i); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } } /** * 选择排序-堆排序 * * 若以一维数组存储一个堆,则堆对应一个完全二叉树,且所有非叶结点的值,不大于其子女的值 * 堆顶元素是最小的(小顶堆) * * * 已知a[s...m]除了a[s]外均满足堆的定义 调整a[s],使之成为大顶堆,将第s个结点为根的子树筛选 * * a:待调整的堆数组 s:待调整的数组元素的位置 length:数组长度 */ private void adjustHeap(int[] a, int s, int length) { int tmp = a[s]; int child = 2 * s + 1; // 左孩子结点位置 while (child < length) { // 如果有右孩子,同时右孩子值 > 左孩子值 if (child + 1 < length && a[child] < a[child + 1]) child++; if (a[s] < a[child]) { // 较大的子结点>父节点 a[s] = a[child]; // 替换父节点 s = child; // 重新设置,待调整的下一个结点位置 child = 2 * s + 1; } else break; a[s] = tmp; // 交换 } } /** * 初始堆进行调整 将a[0...length-1]建成堆 * 调整完后,第一个元素是序列最小的元素 */ private void buildingHeap(int[] a, int length) { // 最有一个有孩子结点的位置是 i = (length - 1) / 2 for (int i = (length - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { adjustHeap(a, i, length); } } //测试用例 public void testHeapSort() { int[] a = new int[] { 4, 11, 5, 8, 1, 9, 2 }; heapSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); }
以下是图解:
选择、冒泡、直接插入排序:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6103002.html
堆排序:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6129630.html
希尔排序:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6104371.html
归并排序:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6194356.html
快速排序:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6262208.html
HashMap实现原理:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6059914.html#t1
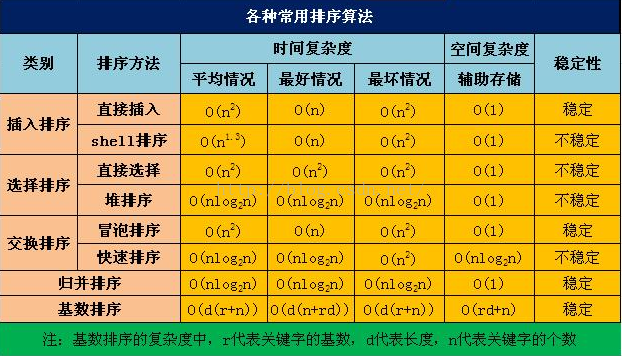
另外推荐一个数据结构网站:http://data.biancheng.net/view/117.html



