Python Rapid GUI Programming 第二篇。 30行写一个更奇葩的计算器。Python 基础教程
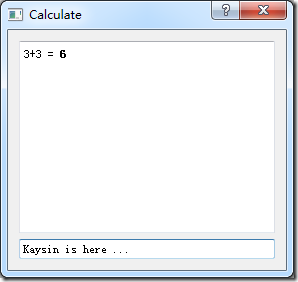
接上一篇GUI编程的日志,现在我们来写一个正常点程序。先让我们看一下程序的样子。
看似正常多了。我们有了一个框框,一个X。而且不需要命令行输入了!
根据上一篇日志所述,我们需要载入模块。
先载入QT4所用的模块以及计算所用的math模块。
from __future__ import division #精确除法 import sys from math import * from PyQt4.QtCore import * from PyQt4.QtGui import *
根据截图,这个应用程序用了两个widgets ,一个是QTextBrowser这是一个只读的文本或者HTML查看器, 另一个是QLineEdit 是一个单行的可写的文本查看器。
根据QT的规则,所有的字符都为Uni编码。
def __init__(self, parent=None): super(Form, self).__init__(parent) self.browser = QTextBrowser() self.lineedit = QLineEdit("Type an expression and press Enter") self.lineedit.selectAll() layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.browser) layout.addWidget(self.lineedit) self.setLayout(layout) self.lineedit.setFocus() self.connect(self.lineedit, SIGNAL("returnPressed()"), self.updateUi) self.setWindowTitle("Calculate coding by Kaysin")
这样就完成了初始画面的定义。
QVBoxLayout() 就是一个可以放置widget的页面。
而下面的addWidget方法,就是将所创建的widget添加进新的页面。
下面有触发信号,按下回车。
载入函数 upadteUi
def updateUi(self): try: text = unicode(self.lineedit.text()) self.browser.append("%s = <b>%s</b>" % (text, eval(text))) except: self.browser.append( "<font color=red>%s is invalid!</font>" % text)
这个很好理解,就是判断输入是否合法,出现异常则输出不合法。
我们看下源程序。
from __future__ import division import sys from math import * from PyQt4.QtCore import * from PyQt4.QtGui import * class Form(QDialog): def __init__(self, parent=None): super(Form, self).__init__(parent) self.browser = QTextBrowser() self.lineedit = QLineEdit("Type an expression and press Enter") self.lineedit.selectAll() layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.browser) layout.addWidget(self.lineedit) self.setLayout(layout) self.lineedit.setFocus() self.connect(self.lineedit, SIGNAL("returnPressed()"), self.updateUi) self.setWindowTitle("Calculate coding by Kaysin") def updateUi(self): try: text = unicode(self.lineedit.text()) self.browser.append("%s = <b>%s</b>" % (text, eval(text))) except: self.browser.append( "<font color=red>%s is invalid!</font>" % text) app = QApplication(sys.argv) form = Form() form.show() app.exec_()






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库