Codeforces Round #671 (Div. 2)
比赛链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1419
A. Digit Game
题意
给出一个 $n$ 位数,游戏规则如下:
- 1-indexed
- Raze标记奇数位
- Breach标记偶数位
- 如果最后剩下的一位未标记位上的数字为奇数,Raze胜,为偶数,Breach胜
问Raze先手能否胜利。
题解
根据 $n$ 的奇偶性可得最后的未标记位的奇偶性,然后判断该奇偶性的位置上是否存在奇数或偶数即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { int n; cin >> n; string s; cin >> s; bool Raze = true; if (s.size() & 1) { Raze = false; for (int i = 0; i < int(s.size()); i += 2) { if ((s[i] - '0') & 1) Raze = true; } } else { Raze = true; for (int i = 1; i < int(s.size()); i += 2) { if ((s[i] - '0') % 2 == 0) Raze = false; } } cout << (Raze ? 1 : 2) << "\n"; } return 0; }
B. Stairs
题意
共有 $n$ 个边长为 $1$ 的小正方形可用,问能拼成多少个不同的可以被完美覆盖的阶梯。
边长为1、3、7的阶梯都可以被完美覆盖,方式如下:
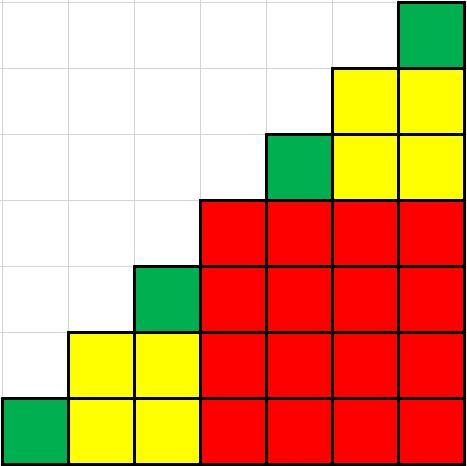
题解
完美阶梯的边长是以 $2$ 的幂次递增的,当前阶梯所用小正方形块数 = 上一个所用块数 X 2 + 递增步长2。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { long long x; cin >> x; int ans = 0; long long pre = 0, now = 0; for (long long i = 1; true; i *= 2) { now = 2 * pre + i * i; x -= now; pre = now; if (x >= 0) { ++ans; } else { cout << ans << "\n"; break; } } } return 0; }
C. Killjoy
题意
有一个初始时感染的账号,Rating为 $x$,感染规则如下:
- Rating相同的账号相互感染
- 可以举办比赛任意加减Rating,但应保证总的变化之和为零,即比赛前后总Rating和不变
- 初始账号不能参加比赛
给出 $n$ 个账号的Rating,计算感染完所有账号至少要举办多少场比赛。
题解
如果总Rating之和为 $x$ 的倍数:
- 如果均为 $x$,无需举办
- 否则举办一场将总Rating均分即可
如果总Rating之和不为 $x$ 的倍数:
- 如果有 $x$,感染 $x$ 后举办一场比赛将其他账号都变为 $x$
- 否则需要先举办一场得到一个 $x$,之后同上
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { int n, x; cin >> n >> x; vector<int> a(n); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; sum += a[i]; } if (sum % n == 0 and sum / n == x) { if (all_of(a.begin(), a.end(), [&](int y) { return y == x; })) cout << 0 << "\n"; else cout << 1 << "\n"; } else { if (any_of(a.begin(), a.end(), [&](int y) { return y == x; })) cout << 1 << "\n"; else cout << 2 << "\n"; } } return 0; }
D2. Sage's Birthday (hard version)
题意
给出 $n$ 个数,试重新排列使得相邻两个数比自己大的数的个数最多。
题解一
先将较小的一半放在中间,然后upper_bound查找每个数左边相邻的数,剩下的数依次填补空位即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i]; sort(a.begin(), a.end()); multiset<int> st(a.begin(), a.end()); vector<int> v(n); for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < n; i += 2) { v[i] = a[j]; st.erase(st.find(a[j])); ++j; } for (int i = 1; i < n; i += 2) { auto it = st.upper_bound(v[i]); if (it != st.end()) { v[i - 1] = *it; st.erase(it); } } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (v[i] == 0) { v[i] = *st.begin(); st.erase(st.begin()); } } int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i + 1 < n; i += 2) { if (v[i - 1] > v[i] and v[i + 1] > v[i]) ++ans; } cout << ans << "\n"; for (auto i : v) cout << i << ' '; return 0; }
题解二
先将较小的一半放在中间,然后将较大的一半放在两边。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i]; sort(a.begin(), a.end()); vector<int> v(n); int cur = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i += 2) { v[i] = a[cur++]; } for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2) { v[i] = a[cur++]; } int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i + 1 < n; i += 2) { if (v[i - 1] > v[i] and v[i] < v[i + 1]) ++ans; } cout << ans << "\n"; for (auto i : v) cout << i << ' '; return 0; }
E. Decryption
题意
将一个合数所有大于 $1$ 的因子围成一个环,使得相邻互质的数最少。
题解
质因子分解和DFS,将DFS过程中最高位不为 $0$ 的质因子作为 $gcd$ 分组。
例如:
$30 = 2^1 \times 3^1 \times 5^1$
DFS过程如下:
一组($gcd = 5$):
$5 = 2^0 \times 3^0 \times 5^1$
二组($gcd = 3$):
$3 = 2^0 \times 3^1 \times 5^0$
$15 = 2^0 \times 3^1 \times 5^1$
三组($gcd = 2$):
$2 = 2^1 \times 3^0 \times 5^0$
$10 = 2^1 \times 3^0 \times 5^1$
$6 = 2^1 \times 3^1 \times 5^0$
$30 = 2^1 \times 3^1 \times 5^1$
发现不同组之间首尾互质(当然了),可以根据DFS的性质:后一组的最大数一定会覆盖前一组的任意一个数将每组反转,得到:
5
15 3
30 6 10 2
此时只有 $5$ 和 $2$ 互质,再根据DFS的性质将最后一组末尾两个数交换,最终得到:
5 15 3 30 6 2 10
此时也可以发现相邻互质的数的对数最少为 $0$ 或 $1$,之后模拟上述过程即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int t; cin >> t; while (t--) { int n; cin >> n; //质因子分解 vector<int> p, e; for (int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) { if (n % i == 0) { p.push_back(i); e.push_back(0); while (n % i == 0) { ++e.back(); n /= i; } } } if (n > 1) { p.push_back(n); e.push_back(1); } //num低位至高位代表从小到大的质因子 vector<int> num(100); function<int(void)> cal_num = [&]() { int res = 1; for (int i = 0; i < int(p.size()); i++) { int mul = 1; for (int j = 0; j < num[i]; j++) { mul *= p[i]; } res *= mul; } return res; }; //对质因子的指数进行dfs map<int, vector<int>> mp; vector<int> order; function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int dep, int top_dep) { if (dep == int(p.size())) { int x = cal_num(); if (x > 1) { if (int(order.size()) == 0 or top_dep != order.back()) { order.push_back(top_dep); } mp[order.back()].push_back(x); } return; } for (int i = 0; i <= e[dep]; i++) { num[dep] = i; if (i >= 1 and top_dep == -1) dfs(dep + 1, dep); else dfs(dep + 1, top_dep); } }; dfs(0, -1); //反转每组因子 vector<int> ans; for (int i = 0; i < int(order.size()); i++) { reverse(mp[order[i]].begin(), mp[order[i]].end()); for (auto j : mp[order[i]]) ans.push_back(j); } //交换最后一组的后两个元素 swap(ans.back(), ans[int(ans.size()) - 2]); for (int i = 0; i < int(ans.size()); i++) { cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == int(ans.size()) - 1]; } //最多有一对因子互质,即只有两个素因子的情况,也可以逐对判断 cout << (__gcd(ans[0], ans[1]) == 1) << "\n"; } return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号