【c++】string详解
参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/this-543273659/archive/2011/07/21/2113172.html 感谢博主
我能不用char*就不用,而使用C++标准程序库中的string类。string不必担心内存、字符长度等等的问题,并且string作为一个类,它的操作函数能够基本满足我的需要。string使用起来非常简单,我们用=赋值,用==比较是否相同,用+合并字符等等。
使用之前需要包含头文件 #include<string>
1.声明字符,调用构造函数初始化字符串
a.将strA赋值为空字符。
string strA;
b.复制字符串赋初值,将“B"赋值给strB,将strB赋值给strA。
1 string strB("B"); 2 string strA(strB);
c.截取字符串,赋初值
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 string strA("ABCDEF"); 7 string strB(strA, 1);//从1开始截取到最后 8 cout << strB << endl; 9 string strC(strA, 1, 2);//从1开始截取2位 10 cout << strC << endl; 11 string strD(strA, 1, 20000);//从1开始截取到最后 12 cout << strD << endl; 13 // string strE(strA, 10000, 2);//错误 14 // cout << strE << endl; 15 cin.get(); 16 return 0; 17 }

d.将C字符串作为strA的初值???没搞懂CString?
string strA(cstr); //将CString作为s的初值
e.将C字符串前chars_len个字符作为字符串strA的初值。???没搞懂CString?
string strA(chars,chars_len);
f. string s(num,c) //生成一个字符串,包含num个c字符
g. string s(beg,end) //以区间beg;end(不包含end)内的字符作为字符串s的初值
h. s.~string() //销毁所有字符,释放内存
2.字符串操作函数
a. 赋新值=,assign()
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 string strA; 7 8 strA = "A"; 9 cout << strA << endl; 10 11 strA.assign("B"); 12 cout << strA << endl; 13 14 cin.get(); 15 return 0; 16 }
b. 交换两个字符串的内容swap()
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 string strA("A"); 7 string strB("B"); 8 cout << strA << endl; 9 cout << strB << endl; 10 11 strA.swap(strB); 12 cout << strA << endl; 13 cout << strB << endl; 14 cin.get(); 15 return 0; 16 }
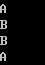
c. 在尾部添加字符+=,append(),push_back()
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 string strA("A"); 7 string strB("B"); 8 9 strA += strB;//AB 10 strA += "C"; //ABC 11 strA += "DD"; //ABCD 12 cout << strA << endl; 13 14 strA.append("E");//ABCDE 15 strA.append("F");//ABCDEF 16 strA.append("GG");//ABCDEFGG 17 cout << strA << endl; 18 19 strA.push_back('H');//添加元素 ABCDEFGGH 20 strA.push_back('I');//ABCDEFGGHI 21 strA.push_back('J');//ABCDEFGGHIJ 22 strA.push_back('J');//ABCDEFGGHIJJ 23 cout << strA << endl; 24 25 cin.get(); 26 return 0; 27 }

d. 插入字符 insert()
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 string strA = "ABCDE"; 8 9 strA.insert(1, "插入"); //在A后面插入 10 cout << strA << endl; 11 12 strA.insert(0, "头部"); //在头部插入 13 cout << strA << endl; 14 15 strA.insert(strA.size(), "尾部"); //在尾部插入 16 cout << strA << endl; 17 18 cin.get(); 19 }

e. 删除字符erase()、clear()
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 string strA = "ABCD"; 8 strA.erase(1, 2); //从索引1开始 删除2个字符 即删除了BC 9 cout << strA << endl; 10 strA.erase(0,strA.size()); //全部清空 11 strA.clear(); //全部清空 12 cin.get(); 13 }
f. 删除字符replace()
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 string strA = "ABCDEFG"; 8 strA.replace(2, 3, "王牌飞行员"); //从索引2开始3个字节的字符全替换成"王牌飞行员" 9 //strA.replace(2, 0, "王牌飞行员");//replace()相当于insert() 10 //strA.replace(2, 0, ""); //replace()相当于erase() 11 //strA.replace(0, strA.size(), "");//replace()相当于clear() 12 cout << strA << endl; 13 cin.get(); 14 }
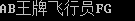
g. 合并字符串 +
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 string strA = "A"; 8 string strB = "B"; 9 strA = strA + strB + "合并"; 10 cout << strA << endl; 11 cin.get(); 12 }
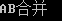
h. 比较字符串==,!=,<,<=,>,>=,compare()
根据“当前字符特性”将字符按字典顺序进行逐一得比较。字典排序靠前的字符小,比较的顺序是从前向后比较,遇到不相等的字符就按这个位置上的两个字符的比较结果确定两个字符串的大小。
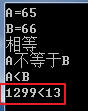
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 cout << "ascii,A" << int('A') << endl; 8 cout << "ascii,B" << int('B') << endl; 9 10 string strA = "A"; 11 if (strA == "A") cout << "相等" << endl; 12 if (strA != "B") cout << "A不等于B" << endl; 13 if ("A" < "B") cout << "A<B" << endl; 14 if ("1299" < "13") cout << "1299<13" << endl;// 第一位相同 第二位2<3 比较结束 15 16 cin.get(); 17 }
i. 返回字符数量 size(),length(),两者没有区别
1 #include <string> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 string strA = "A汉123"; 8 cout << strA.size() << endl;//6 9 cin.get(); 10 }


