MyBatis二级缓存配置
正如大多数持久层框架一样,MyBatis 同样提供了一级缓存和二级缓存的支持
Mybatis二级缓存是SessionFactory,如果两次查询基于同一个SessionFactory,那么就从二级缓存中取数据,而不用到数据库里去取了。
1. 一级缓存: 基于PerpetualCache 的 HashMap本地缓存,其存储作用域为 Session,当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该Session中的所有 Cache 就将清空。
2. 二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用 PerpetualCache,HashMap存储,不同在于其存储作用域为 Mapper(Namespace),并且可自定义存储源,如 Ehcache。
启动二级缓存:
1.mybatis-config.xml添加
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/><!-- 二级缓存 --> </settings> <typeAliases> <package name="pojo"/> </typeAliases> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lol?characterEncoding=UTF-8"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <mapper resource="pojo/Product.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
2.在Product.xml(数据库关系映射)中增加 <cache/>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="pojo"> <cache/> <insert id="addProduct" parameterType="Product" > insert into product (name, price) values (#{name}, #{price}) </insert> <select id="listProduct" resultType="Product"> select * from product </select> <delete id="deleteProduct" parameterType="Product" > delete from product where id= #{id} </delete> <select id="getProduct" parameterType="_int" resultType="Product"> select * from product where id=#{id} </select> <select id="listProductByIdAndName" resultType="Product"> <bind name="likename" value="'%' + name + '%'" /> select * from product <where> <if test="name!=null"> and name like #{likename} <if test="price!=null"> and price > #{price} </if> </if> </where> </select> </mapper>
3.序列化Product.java(pojo类)
通常来说,二级缓存的机制里会有一个: 当缓存的个数达到某个数量的时候,把缓存对象保存在硬盘上。 如果要把对象保存在硬盘上,就必须实现序列化接口。
序列化相关知识:http://blog.csdn.net/wangloveall/article/details/7992448/
package pojo; import java.io.Serializable; public class Product implements Serializable{ private int id; private String name; private float price; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public float getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(float price) { this.price = price; } }
4.测试类
package controller; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import pojo.Product; public class TestMybatis { public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException{ String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); Product p = session.selectOne("getProduct", 1); session.commit(); session.close(); SqlSession session1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();//二级缓存测试 Product p2 = session1.selectOne("getProduct", 1); session1.commit(); session1.close(); } }
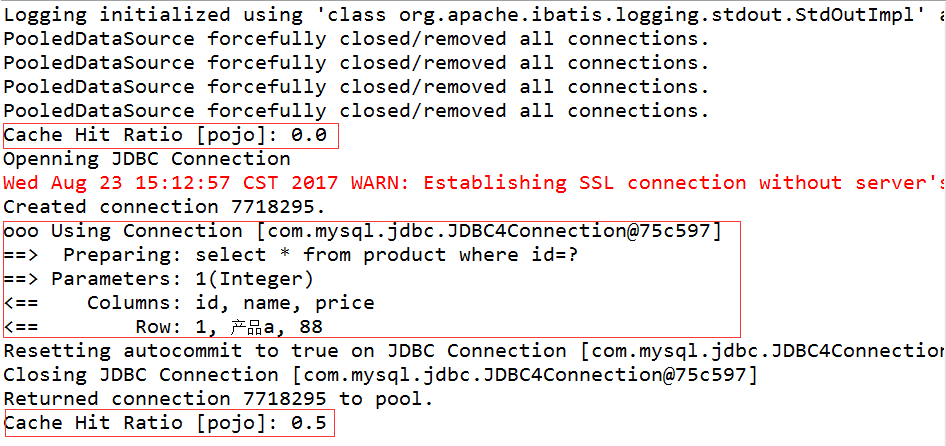
5.结果



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号