第四期coding_group笔记_用CRF实现分词-词性标注
一、背景知识
1.1 什么是分词?
NLP的基础任务分为三个部分,词法分析、句法分析和语义分析,其中词法分析中有一种方法叫Tokenization,对汉字以字为单位进行处理叫做分词。
Example : 我 去 北 京
S S B E
注:S代表一个单独词,B代表一个词的开始,E表示一个词的结束(北京是一个词)。
1.2 什么是词性标注?
句法分析中有一种方法叫词性标注(pos tagging),词性标注的目标是使用类似PN、VB等的标签对句子(一连串的词或短语)进行打签。
Example : I can open this can .
Pos tagging -> PN MD VV PN NN PU
注:PN代词 MD情态动词 VV 动词 NN名词 PU标点符号
1.3 什么是分词-词性标注?
分词-词性标注就是将分词和词性标注两个任务同时进行,在一个模型里完成,可以减少错误传播。
Example : 我 去 北 京
S-PN S-VV B-NN E-NN
注:如果想理解更多关于nlp基础任务的知识,可参看我整理的张岳老师暑期班的第一天的笔记。
1.4 什么是CRF?
条件随机场(conditional random field)是一种用来标记和切分序列化数据的统计模型。在NLP领域可以用来做序列标注任务。
注:更多关于条件随机场的理论知识,可以参考以下内容:
条件随机场介绍(译)Introduction to Conditional Random Fields
二、CRF序列标注
2.1 模型结构图
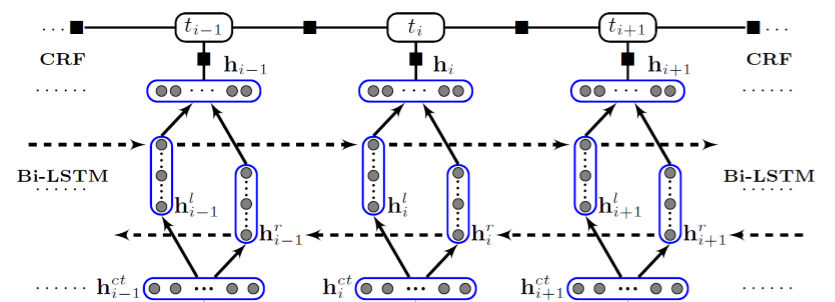
最底下的词向量层,上两层是Bi-LSTM层,最上面一层是CRF层。数据流程是从下层向上层计算。
2.2 CRF部分
2.2.1 理论
Point 1: 在CRF中,每个特征函数以下列信息作为输入,输出是一个实数值。
(1)一个句子s
(2)词在句子中的位置i
(3)当前词的标签
(4)前一个词的标签
注:通过限制特征只依赖于当前与之前词的标签,而不是句子中的任意标签,实际上是建立了一种特殊的线性CRF,而不是广义上的CRF。
Point 2: CRF的训练参数
(1)Input: x = {我,去,北京}
(2)Answer: ygold = {PN, VV, NN}
(3)y'是CRF标注的所有可能值,有3*3*3=27个;
(4)T矩阵存储转移分数,T[yiyi-1]是上个标签是的情况下,下个标签是yi的分数;
(5)hi是向量序列,通过神经网络Bi-LSTM得到,hi[yi]是被标成的发射分数;
(6)score(x,y)是模型对x被标注成y所打出的分数,是一个实数值;
![]()
Example : 我 去 北京
PN VV NN
![]()
(7)P(ygold|x)是模型x对标注出ygold的概率;
![]()
Point 3: CRF的训练目标:训练模型使得变大
Step 1: 对P(ygold|x)进行转化,取对数
![]()
![]()
Step 2: 最终目标函数,使用梯度下降法
![]()
![]()
Step 3: 编程实现
![]()
1 def _forward_alg(self, feats): 2 # do the forward algorithm to compute the partition function 3 init_alphas = torch.Tensor(1, self.labelSize).fill_(0) 4 # Wrap in a variable so that we will get automatic backprop 5 forward_var = autograd.Variable(init_alphas) 6 7 # Iterate through the sentence 8 for idx in range(len(feats)): 9 feat = feats[idx] 10 alphas_t = [] # The forward variables at this timestep 11 for next_tag in range(self.labelSize): 12 # broadcast the emission score: it is the same regardless of the previous tag 13 if idx == 0: 14 alphas_t.append(feat[next_tag].view(1, -1)) 15 else: 16 emit_score = feat[next_tag].view(1, -1).expand(1, self.labelSize) 17 # the ith entry of trans_score is the score of transitioning to next_tag from i 18 trans_score = self.T[next_tag] 19 # The ith entry of next_tag_var is the value for the edge (i -> next_tag) before we do log-sum-exp 20 next_tag_var = forward_var + trans_score + emit_score 21 # The forward variable for this tag is log-sum-exp of all the scores. 22 alphas_t.append(self.log_sum_exp(next_tag_var)) 23 forward_var = torch.cat(alphas_t).view(1, -1) 24 alpha_score = self.log_sum_exp(forward_var) 25 return alpha_score
1 # Compute log sum exp in a numerically stable way for the forward algorithm 2 def log_sum_exp(self, vec): 3 max_score = vec[0, self.argmax(vec)] 4 max_score_broadcast = max_score.view(1, -1).expand(1, vec.size()[1]) 5 return max_score + torch.log(torch.sum(torch.exp(vec - max_score_broadcast)))
![]()
1 def neg_log_likelihood(self, feats, tags): 2 forward_score = self._forward_alg(feats) # calculate denominator 3 gold_score = self._score_sentence(feats, tags) 4 return forward_score - gold_score # calculate loss
train()中的训练部分:
1 for iter in range(self.hyperParams.maxIter): 2 print('###Iteration' + str(iter) + "###") 3 random.shuffle(indexes) 4 for idx in range(len(trainExamples)): 5 # Step 1. Remember that Pytorch accumulates gradients. We need to clear them out before each instance 6 self.model.zero_grad() 7 # Step 2. Get our inputs ready for the network, that is, turn them into Variables of word indices. 8 self.model.LSTMHidden = self.model.init_hidden() 9 exam = trainExamples[indexes[idx]] 10 # Step 3. Run our forward pass. Compute the loss, gradients, and update the parameters by calling optimizer.step() 11 lstm_feats = self.model(exam.feat) 12 loss = self.model.crf.neg_log_likelihood(lstm_feats, exam.labelIndexs) 13 loss.backward() 14 optimizer.step() 15 if (idx + 1) % self.hyperParams.verboseIter == 0: 16 print('current: ', idx + 1, ", cost:", loss.data[0])
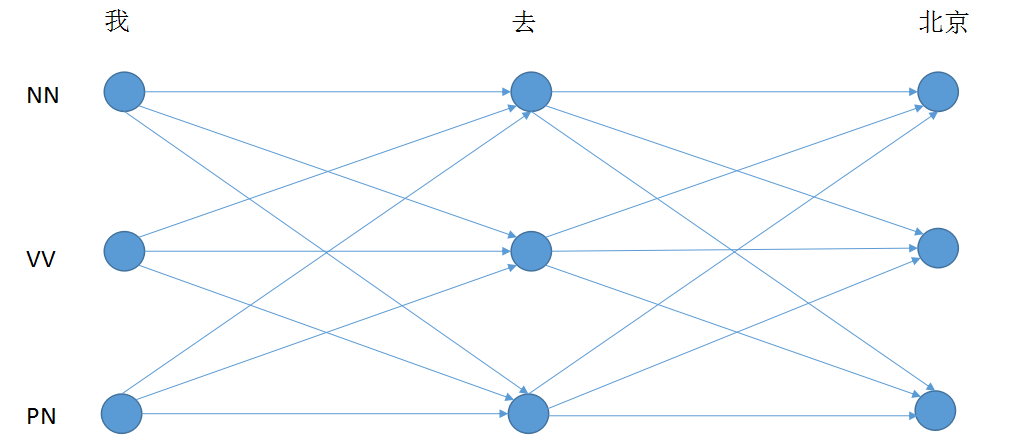
Point 4: 使用模型预测序列
使用维特比解码算法,解决篱笆图中的最短路径问题
step 1: 初始节点没有转移值
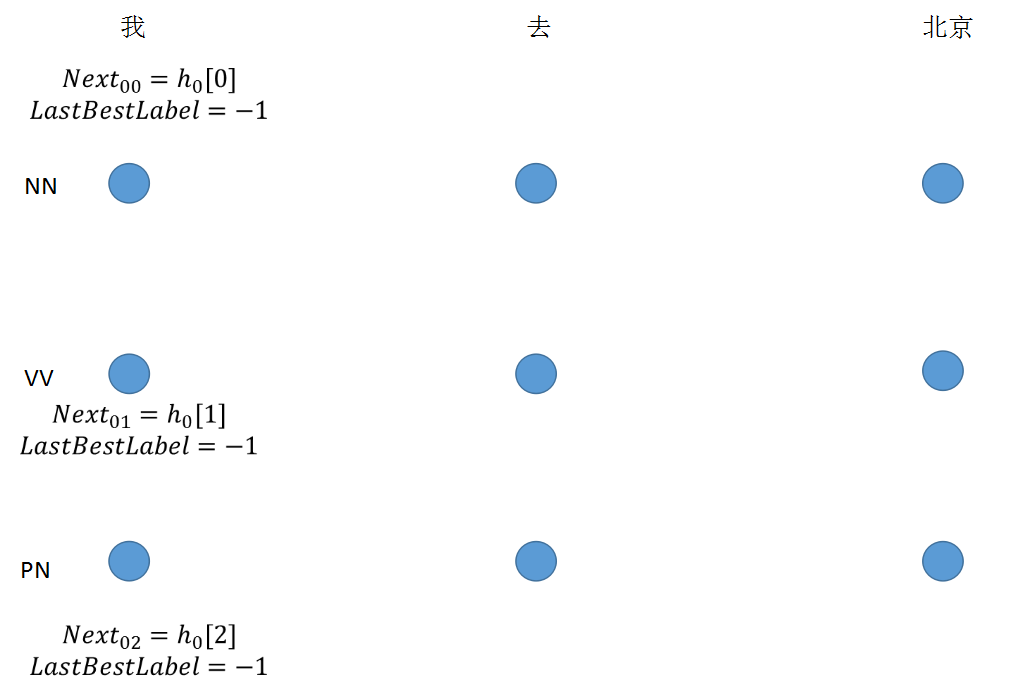
1 if idx == 0: 2 viterbi_var.append(feat[next_tag].view(1, -1))
step 2: 节点值由三部分组成,最后求取最大值,得到lastbestlabel的下标
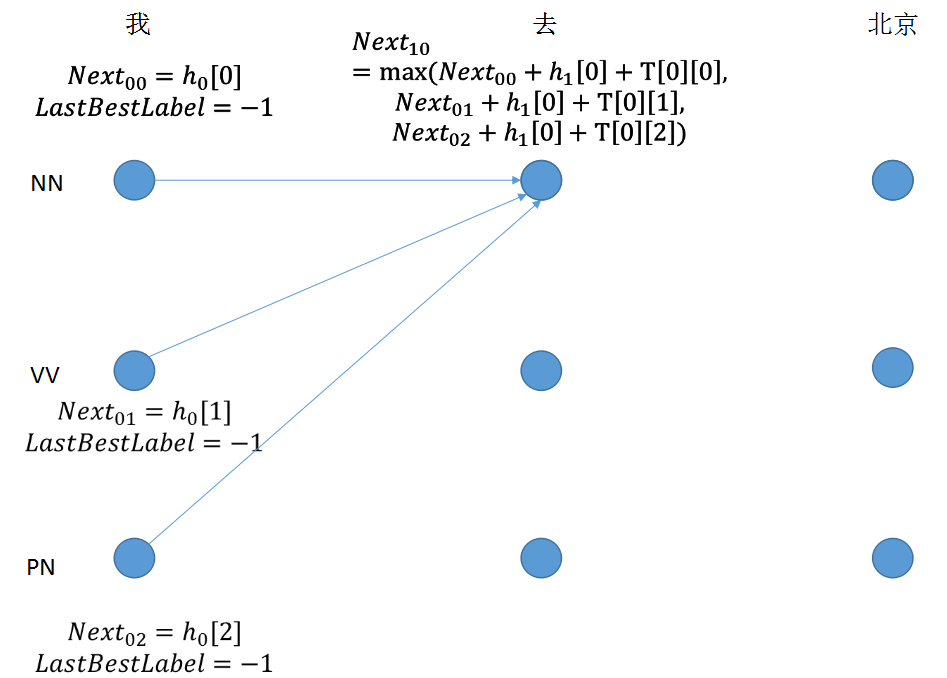
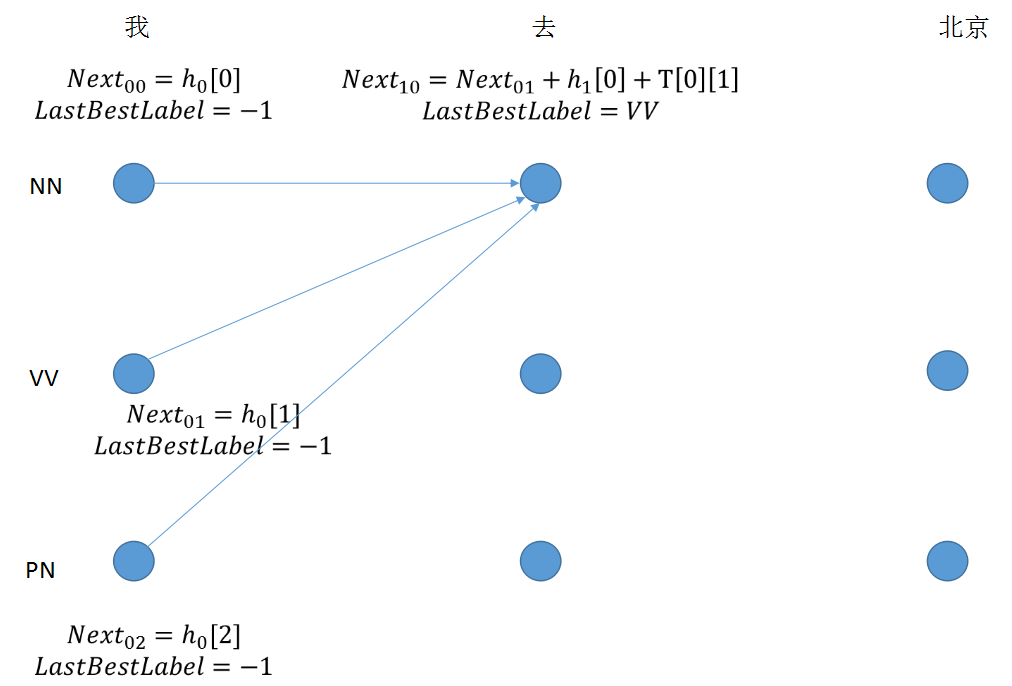
1 for next_tag in range(self.labelSize): 2 if idx == 0: 3 viterbi_var.append(feat[next_tag].view(1, -1)) 4 else: 5 emit_score = feat[next_tag].view(1, -1).expand(1, self.labelSize) 6 trans_score = self.T[next_tag] 7 next_tag_var = forward_var + trans_score + emit_score 8 best_label_id = self.argmax(next_tag_var) 9 bptrs_t.append(best_label_id) 10 viterbi_var.append(next_tag_var[0][best_label_id])
step 3: 计算出所有节点,比较最后一个词的值,求取最大值之后,向前推出最佳序列。
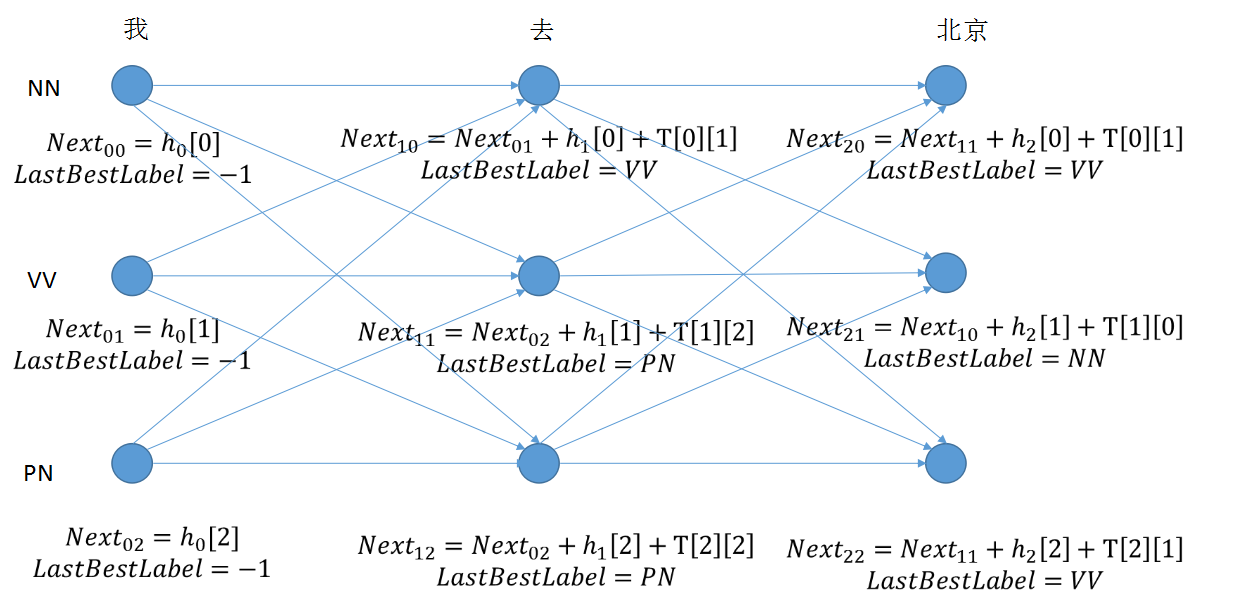

维特比解码算法实现预测序列
1 def _viterbi_decode(self, feats): 2 init_score = torch.Tensor(1, self.labelSize).fill_(0) 3 # forward_var at step i holds the viterbi variables for step i-1 4 forward_var = autograd.Variable(init_score) 5 back = [] 6 for idx in range(len(feats)): 7 feat = feats[idx] 8 bptrs_t = [] # holds the backpointers for this step 9 viterbi_var = [] # holds the viterbi variables for this step 10 for next_tag in range(self.labelSize): 11 # next_tag_var[i] holds the viterbi variable for tag i at the previous step, 12 # plus the score of transitioning from tag i to next_tag. 13 # We don't include the emission scores here because the max does not 14 # depend on them (we add them in below) 15 if idx == 0: 16 viterbi_var.append(feat[next_tag].view(1, -1)) 17 else: 18 emit_score = feat[next_tag].view(1, -1).expand(1, self.labelSize) 19 trans_score = self.T[next_tag] 20 next_tag_var = forward_var + trans_score + emit_score 21 best_label_id = self.argmax(next_tag_var) 22 bptrs_t.append(best_label_id) 23 viterbi_var.append(next_tag_var[0][best_label_id]) 24 # Now add in the emission scores, and assign forward_var to the set of viterbi variables we just computed 25 forward_var = (torch.cat(viterbi_var)).view(1, -1) 26 if idx > 0: 27 back.append(bptrs_t) 28 best_label_id = self.argmax(forward_var) 29 # Follow the back pointers to decode the best path. 30 best_path = [best_label_id] 31 path_score = forward_var[0][best_label_id] 32 for bptrs_t in reversed(back): 33 best_label_id = bptrs_t[best_label_id] 34 best_path.append(best_label_id) 35 best_path.reverse() 36 return path_score, best_path
train()函数中的预测部分
1 # Check predictions after training 2 eval_dev = Eval() 3 for idx in range(len(devExamples)): 4 predictLabels = self.predict(devExamples[idx]) 5 devInsts[idx].evalPRF(predictLabels, eval_dev) 6 print('Dev: ', end="") 7 eval_dev.getFscore() 8 9 eval_test = Eval() 10 for idx in range(len(testExamples)): 11 predictLabels = self.predict(testExamples[idx]) 12 testInsts[idx].evalPRF(predictLabels, eval_test) 13 print('Test: ', end="") 14 eval_test.getFscore()
1 def predict(self, exam): 2 tag_hiddens = self.model(exam.feat) 3 _, best_path = self.model.crf._viterbi_decode(tag_hiddens) 4 predictLabels = [] 5 for idx in range(len(best_path)): 6 predictLabels.append(self.hyperParams.labelAlpha.from_id(best_path[idx])) 7 return predictLabels
Point 5 : 使用F1分数测量精度,最佳值为1,最差为0
![]()
1 def getFscore(self): 2 if self.predict_num == 0: 3 self.precision = 0 4 else: 5 self.precision = self.correct_num / self.predict_num 6 7 if self.gold_num == 0: 8 self.recall = 0 9 else: 10 self.recall = self.correct_num / self.gold_num 11 12 if self.precision + self.recall == 0: 13 self.fscore = 0 14 else: 15 self.fscore = 2 * (self.precision * self.recall) / (self.precision + self.recall) 16 print("precision: ", self.precision, ", recall: ", self.recall, ", fscore: ", self.fscore)
注:全部代码和注释链接
扩展:可将数据中第二列和第一列一起放入Bi-LSTM中提取特征,这次只用到数据的第一列和第三列。





【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步