SpringBoot连接多个不同数据源
连接多个数据库其实也很简单,只是在连接一个数据库的基础上,添加多一个访问的数据源而已,详情请往下看,这里以连接两个数据库为例,更多的连接,请阅览后参考写法继续添加即可!
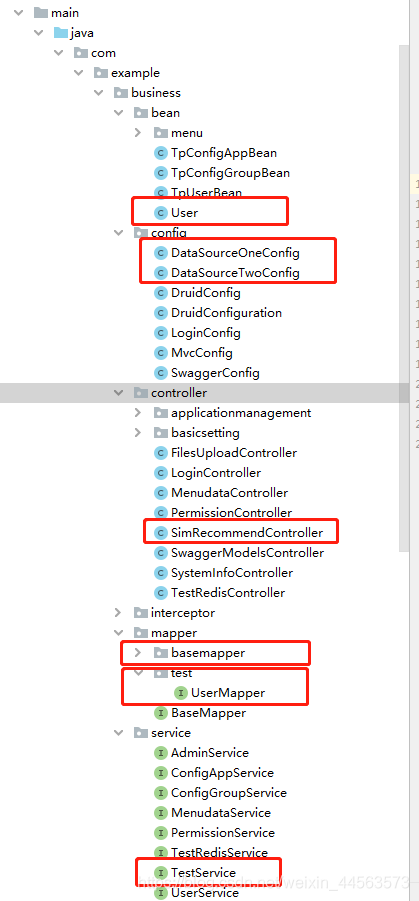
PS:项目目录结构图:
一:更改application.yml
spring:
datasource:
配置多个数据源
one:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
username: root
password: root
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/business?useSSL=true&userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #数据库链接驱动
two:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
username: root
password: root
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=true&userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #数据库链接驱动
需要注意:
连接多个数据库时,url要更改为jdbc-url,否则会报错。
报错内容:
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: jdbcUrl is required with driverClassName
二:添加两个配置类
(1)DataSourceOneConfig
package com.example.business.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.business.mapper.basemapper", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "db1SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSourceOneConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.one")
@Primary
public DataSource db1DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory db1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mapper/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSourceTransactionManager db1TransactionManager(@Qualifier("db1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate db1SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
(2)DataSourceTwoConfig
package com.example.business.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.business.mapper.test", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "db2SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSourceTwoConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.two")
public DataSource db2DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory db2SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mapper/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager db2TransactionManager(@Qualifier("db2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionTemplate db2SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
需要注意:
(1) basePackages
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.business.mapper.test", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "db2SqlSessionTemplate")
basePackages 里面是你的mapper存放的位置,由于这里连接的是两个数据库,所有这里两个值不能一样,即第一个和第二个数据库的mapper应该放在两个不同的目录下。否则启动会报找不到表的错误。
(2)如果启动类添加了@MapperScan,需要去掉。
package com.example.business;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class BusinessApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BusinessApplication.class, args);
}
}
三:测试连接效果
(1)新建Bean
package com.example.business.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Data
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
@Id//主键
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)//自动生成主键
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "password")
private String password;
}
(2)新建Mapper
package com.example.business.service;
import com.example.business.bean.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface TestService {
public List<User> selectUserAll();
}
(3)新建Service
package com.example.business.service;
import com.example.business.bean.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface TestService {
public List<User> selectUserAll();
}
(4)新建ServiceImpl
package com.example.business.serviceImpl;
import com.example.business.bean.User;
import com.example.business.mapper.test.UserMapper;
import com.example.business.service.TestService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public List<User> selectUserAll() {
return userMapper.selectAll();
}
}
(5)新建Controller
package com.example.business.controller;
import com.example.business.service.TestService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/SimRecommendController")
public class SimRecommendController {
private Object result;
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/selectUserAll")
public Object selectUserAll() {
result = testService.selectUserAll();
return result;
}
}
经过访问,完美连接!
PS:项目目录结构图:

目录结构并没有强制限制,按照你自己的项目目录来就可以了,只要注意mapper要区分两个数据库的mapper,要放在不同目录下就可以!
JourneyFlower/springboot: 🌿 springboot 分析与学习 & 入门示例 & 图文教程,本 Spring Boot 系列文章基于 Spring Boot 版本 v2.x 进行学习分析。 (github.com)
学习参考
原文链接:(26条消息) Spring Boot实现优雅地连接多个数据库_程序yang的博客-CSDN博客_springboot连接多个数据库
本文作者:Journey&Flower
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/JourneyOfFlower/p/16211718.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
2020-04-30 [VS2008] [.NET 3.5] 如何解决 The imported project "C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v3.5\Microsoft.CompactFramework.CSharp.targets" was not found