Class.forName 和 .loadClass 方法的区别
Java反射 Class.forName 和 loadClass 方法的区别
java中Class.forName()和ClassLoader都可以对类进行加载。
ClassLoader就是遵循双亲委派模型最终调用启动类加载器的类加载器,实现的功能是“通过一个类的全限定名来获取描述此类的二进制字节流”,获取到二进制流后放到JVM中。Class.forName()方法实际上也是调用的CLassLoader来实现的。
区别:
a).Class.forName除了将类的.class文件加载到jvm中之外,还会对类进行解释,执行类中的static块。
b).而classloader只干一件事情,就是将.class文件加载到jvm中,不会执行static中的内容,只有在newInstance才会去执行static块。
c).Class.forName(name,initialize,loader)带参数也可控制是否加载static块。并且只有调用了newInstance()方法采用调用构造函数,创建类的对象
源码对比
Class.forName(className)方法,内部实际调用的方法是 Class.forName(className,true,classloader);
第2个boolean参数表示类是否需要初始化, Class.forName(className)默认是需要初始化。
一旦初始化,就会触发目标对象的 static块代码执行,static参数也也会被再次初始化。
ClassLoader.loadClass(className)方法,内部实际调用的方法是 ClassLoader.loadClass(className,false);
第2个 boolean参数,表示目标对象是否进行链接,false表示不进行链接,由上面介绍可以,
不进行链接意味着不进行包括初始化等一些列步骤,那么静态块和静态对象就不会得到执行
Class.forName(String className);
用例
Person emp2 = (Person) Class.forName("org.pro.com.Person").newInstance();
源码:
@CallerSensitive public static Class<?> forName(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); return forName0(className, true, ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller), caller); }
最后调用的方法是forName0这个方法,在这个forName0方法中的第二个参数被默认设置为了true,这个参数代表是否对加载的类进行初始化,设置为true时会类进行初始化,代表会执行类中的静态代码块,以及对静态变量的赋值等操作。
也可以调用Class.forName(String name, boolean initialize,ClassLoader loader)方法来手动选择在加载类的时候是否要对类进行初始化。Class.forName(String name, boolean initialize,ClassLoader loader)的源码如下:
/* @param name fully qualified name of the desired class * @param initialize if {@code true} the class will be initialized. * See Section 12.4 of <em>The Java Language Specification</em>. * @param loader class loader from which the class must be loaded * @return class object representing the desired class * * @exception LinkageError if the linkage fails * @exception ExceptionInInitializerError if the initialization provoked * by this method fails * @exception ClassNotFoundException if the class cannot be located by * the specified class loader * * @see java.lang.Class#forName(String) * @see java.lang.ClassLoader * @since 1.2 */ @CallerSensitive public static Class<?> forName(String name, boolean initialize, ClassLoader loader) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> caller = null; SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { // Reflective call to get caller class is only needed if a security manager // is present. Avoid the overhead of making this call otherwise. caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); if (sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(loader)) { ClassLoader ccl = ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller); if (!sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(ccl)) { sm.checkPermission( SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION); } } } return forName0(name, initialize, loader, caller); }
源码中的注释只摘取了一部分,其中对参数initialize的描述是:if {@code true} the class will be initialized.意思就是说:如果参数为true,则加载的类将会被初始化
ClassLoader.loadClass
用例
ClassLoader cl; // 如何获得ClassLoader参考1.6
Class cls = cl.loadClass("com.rain.B"); // 使用第一步得到的ClassLoader来载入B
B b = (B)cls.newInstance(); // 有B的类得到一个B的实例
ClassLoader.loadClass()源码
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException { return loadClass(name, false); } ... ... /** * @param resolve * If <tt>true</tt> then resolve the class */ protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException { // First, check if the class has already been loaded Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name); if (c == null) { try { if (parent != null) { c = parent.loadClass(name, false); } else { c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found // from the non-null parent class loader } if (c == null) { // If still not found, then invoke findClass in order // to find the class. c = findClass(name); } } return c; }
loadClass(String name)方法调用了loadClass(String name, boolean resolve),resolve为false,即为通过ClassLoader.loadClass加载的类不进行解析操作,不进行解析操作就意味着初始化也不会进行,那么其类的静态参数就不会初始化,静态代码块也不会被执行。
再来看看代码:
测试对比打印调用静态代码用例
测试类
public class TestBean {
public static String param1 = "testBean";
static {
System.out.println("====TestBean====");
}
}
使用Class.forName(String className);
try {
Class.forName("com.jm.loaderTest.TestBean");
System.out.println("#########-------------结束符------------##########");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
打印结果,打印了静态代码
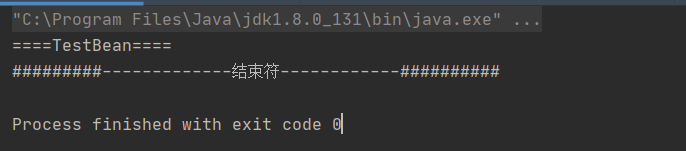
使用 ClassLoader.loadClass()源码
try {
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass("com.jm.loaderTest.TestBean");
System.out.println("#########-------------结束符------------##########");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
打印结果,没有打印静态代码
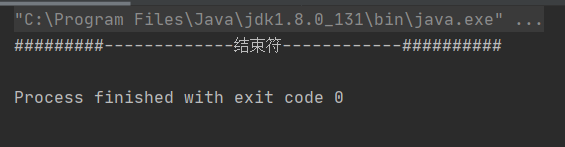
可以看到 forName 执行静态代码, loadClass 没有
根据运行结果得出Class.forName加载类时将类进了初始化,而ClassLoader的loadClass并没有对类进行初始化,只是把类加载到了虚拟机中。
应用场景
ClassLoader: Spring框架中的IOC的实现就是使用的ClassLoader。
Class.forName():JDBC时通常是使用Class.forName()方法来加载数据库连接驱动。
这是因为在JDBC规范中明确要求Driver(数据库驱动)类必须向DriverManager注册自己。
具体:https://www.cnblogs.com/jimoer/p/9185662.html
面试
SPI是怎么破坏双亲委派模型: 就是Class.forName()在加载数据库驱动的这个方式,其实是一种破坏了双亲委派模型的使用,通过Application ClassLoader来加载了一个第三方类,而并没有使用父级的Bootstrap ClassLoader加载器。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[1] https://www.cnblogs.com/jimoer/p/9185662.html
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/zhangshuny/article/details/106898286
[3] https://blog.csdn.net/wt520it/article/details/83014038



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号