SQLZOO记录 2:窗口函数
SQL 窗口函数在行的“窗口”上运行——通常是表中某种意义上相邻的行。了解和学习可以看这篇文章:通俗易懂SQL窗口函数
9- Window functions
- Show the lastName, party and votes for the constituency 'S14000024' in 2017.
SELECT lastName, party, votes
FROM ge
WHERE constituency = 'S14000024' AND yr = 2017
ORDER BY votes DESC
- You can use the RANK function to see the order of the candidates. If you RANK using (ORDER BY votes DESC) then the candidate with the most votes has rank 1.
Show the party and RANK for constituency S14000024 in 2017. List the output by party
学习 RANK() 用法
SELECT party, votes,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY votes DESC) AS posn
FROM ge
WHERE constituency = 'S14000024' AND yr = 2017
ORDER BY party
结果显示系统错误???
- The 2015 election is a different PARTITION to the 2017 election. We only care about the order of votes for each year.
Use PARTITION to show the ranking of each party in S14000021 in each year. Include yr, party, votes and ranking (the party with the most votes is 1).
SELECT yr, party, votes,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY yr ORDER BY votes DESC) AS posn
FROM ge
WHERE constituency = 'S14000021'
ORDER BY party, yr
- Edinburgh constituencies are numbered S14000021 to S14000026.
Use PARTITION BY constituency to show the ranking of each party in Edinburgh in 2017. Order your results so the winners are shown first, then ordered by constituency.
SELECT constituency, party, votes, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY constituency ORDER BY votes DESC) AS posn
FROM ge
WHERE constituency BETWEEN 'S14000021' AND 'S14000026'
AND yr = 2017
ORDER BY posn, constituency
- You can use SELECT within SELECT to pick out only the winners in Edinburgh.
Show the parties that won for each Edinburgh constituency in 2017.
SELECT constituency, party
FROM (SELECT constituency, party, votes, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY constituency ORDER BY votes DESC) AS posn
FROM ge
WHERE constituency BETWEEN 'S14000021' AND 'S14000026'
AND yr = 2017) AS x
WHERE x.posn = 1
- Show how many seats for each party in Scotland in 2017.
You can use COUNT and GROUP BY to see how each party did in Scotland. Scottish constituencies start with 'S'
SELECT party, COUNT(*)
FROM (SELECT constituency, party, votes,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY constituency ORDER BY votes DESC) AS posn
FROM ge
WHERE constituency LIKE 'S%'
AND yr = 2017) AS x
WHERE x.posn = 1
GROUP BY x.party
或
SELECT party, COUNT(*)
FROM ge x
WHERE constituency LIKE 'S%'
AND yr = 2017
AND votes = (SELECT MAX(votes)
FROM ge y
WHERE y.constituency = x.constituency
AND yr = 2017)
GROUP BY party
9+ Window LAG - COVID 19
- The example uses a WHERE clause to show the cases in 'Italy' in March 2020.
Modify the query to show data from Spain
SELECT name, DAY(whn), confirmed, deaths, recovered
FROM covid
WHERE name = 'Spain'
AND MONTH(whn) = 3 AND YEAR(whn) = 2020
ORDER BY whn
- The LAG function is used to show data from the preceding row or the table. When lining up rows the data is partitioned by country name and ordered by the data whn. That means that only data from Italy is considered.
Modify the query to show confirmed for the day before.
SELECT name, DAY(whn), confirmed, LAG(confirmed, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY name ORDER BY whn) AS dbf
FROM covid
WHERE name = 'Italy'
AND MONTH(whn) = 3
AND YEAR(whn) = 2020
ORDER BY whn
从结果中了解 dbf 列中的值如何与左上方对角线上方的行的值匹配
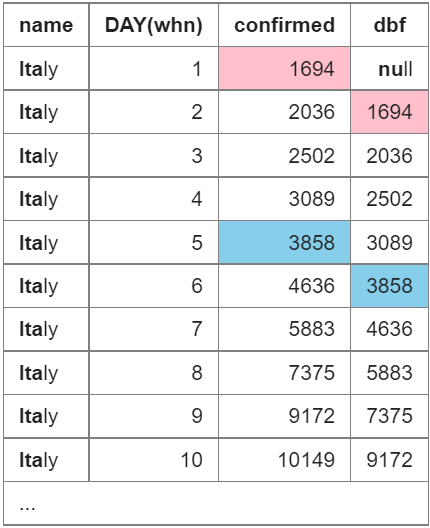
- The number of confirmed case is cumulative - but we can use LAG to recover the number of new cases reported for each day.
Show the number of new cases for each day, for Italy, for March.
SELECT name, DAY(whn), (confirmed - LAG(confirmed, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY name ORDER BY whn)) AS new
FROM covid
WHERE name = 'Italy'
AND MONTH(whn) = 3
AND YEAR(whn) = 2020
ORDER BY whn
- The data gathered are necessarily estimates and are inaccurate. However by taking a longer time span we can mitigate some of the effects.
You can filter the data to view only Monday's figures WHERE WEEKDAY(whn) = 0.
Show the number of new cases in Italy for each week in 2020 - show Monday only.
SELECT name, DATE_FORMAT(whn,'%Y-%m-%d'), (confirmed - LAG(confirmed, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY name ORDER BY whn)) AS newThisWeek
FROM covid
WHERE name = 'Italy'
AND WEEKDAY(whn) = 0
AND YEAR(whn) = 2020
ORDER BY whn
- You can JOIN a table using DATE arithmetic. This will give different results if data is missing.
Show the number of new cases in Italy for each week - show Monday only.
In the sample query we JOIN this week tw with last week lw using the DATE_ADD function.
SELECT tw.name, DATE_FORMAT(tw.whn,'%Y-%m-%d'), tw.confirmed - lw.confirmed
FROM covid tw LEFT JOIN covid lw ON (DATE_ADD(lw.whn, INTERVAL 1 WEEK) = tw.whn)
AND (tw.name = lw.name)
WHERE tw.name = 'Italy'
AND WEEKDAY(tw.whn) = 0
ORDER BY tw.whn
- The query shown shows the number of confirmed cases together with the world ranking for cases.
United States has the highest number, Spain is number 2...
Notice that while Spain has the second highest confirmed cases, Italy has the second highest number of deaths due to the virus.
Include the ranking for the number of deaths in the table.
SELECT name, confirmed, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY confirmed DESC) rc, deaths, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY deaths DESC) rc
FROM covid
WHERE whn = '2020-04-20'
ORDER BY confirmed DESC
- The query shown includes a JOIN t the world table so we can access the total population of each country and calculate infection rates (in cases per 100,000).
Show the infect rate ranking for each country. Only include countries with a population of at least 10 million.
有结果但错误
SELECT world.name, ROUND(100000 * confirmed / population) AS infectionRate, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY confirmed / population DESC) rk
FROM covid JOIN world ON (covid.name = world.name)
WHERE whn = '2020-04-20'
AND population >= 10000000
ORDER BY rk
没有给出正确输出
- For each country that has had at last 1000 new cases in a single day, show the date of the peak number of new cases.
结果和答案一样但错误
WITH temp1 AS (
SELECT *, (confirmed - LAG(confirmed, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY name ORDER BY whn)) day_count
FROM covid
),
temp2 AS (
SELECT name, MAX(day_count) peak_cases
FROM temp1
GROUP BY name
HAVING peak_cases > 1000
)
SELECT temp2.name, DATE_FORMAT(whn, '%Y-%m-%d') date_, peak_cases
FROM temp2 LEFT JOIN temp1 ON (temp2.name = temp1.name) AND (temp2.peak_cases = temp1.day_count)
ORDER BY date

