[LeetCode] 173. Binary Search Tree Iterator_Medium_tag: Binary Search Tree
2019-11-17 00:47 Johnson_强生仔仔 阅读(176) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报mplement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
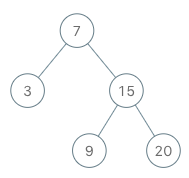
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root); iterator.next(); // return 3 iterator.next(); // return 7 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 9 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 15 iterator.hasNext(); // return true iterator.next(); // return 20 iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
因为是Binary Search Tree, 所以要用inorder travesal,所以可以在初始化的时候将tree 转变为stack,并且用一个指针来指向现在的node所在的位置,如果超过stack,那么就没有next。
T: O(n), S: O(n)
Code:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class BSTIterator(object): def inOrder(self, root): if not root: return self.inOrder(root.left) self.stack.append(root.val) self.inOrder(root.right) def __init__(self, root): """ :type root: TreeNode """ self.stack = [] self.point = 0 self.inOrder(root) def next(self): """ @return the next smallest number :rtype: int """ if self.hasNext(): nextNum = self.stack[self.point] self.point += 1 return nextNum def hasNext(self): """ @return whether we have a next smallest number :rtype: bool """ if not self.stack or self.point >= len(self.stack): return False return True # Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = BSTIterator(root) # param_1 = obj.next() # param_2 = obj.hasNext()


