N数码问题的启发式搜索算法--A*算法python实现
- 一、启发式搜索:A算法
1)评价函数的一般形式 : f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
g(n):从S0到Sn的实际代价(搜索的横向因子)
h(n):从N到目标节点的估计代价,称为启发函数(搜索的纵向因子);
特点: 效率高, 无回溯,
搜索算法
OPEN表 : 存放待扩展的节点.
CLOSED表 : 存放已被扩展过的节点.
2)评价函数 f(x) = g(x) + h(x)
当f(x) = g(x) 时,为宽度优先搜索
当f(x) = 1/g(x)时,为深度优先搜索
当f(x) = h(x) 时,为全局优先搜索
比较f(x)大小,决定节点搜索顺序,即在OPEN表中的顺序
3)Step1: 把初始节点S0放入OPEN表中;
Step2: 若OPEN表为空,则搜索失败,退出.
Step3: 移出OPEN中第一个节点N放入CLOSED表中, 并标以顺序号n;
Step4: 若目标节点Sg=N, 则搜索成功,结束.
Step5: 若N不可扩展, 则转Step2;
Step6: 扩展N, 生成一组子节点, 对这组子节点作如下处理后, 放入 OPEN表, 按f值重新排序OPEN表, 转 Step2;
删除重复节点和修改返回指针处理.
- 二、启发式搜索:A*算法
1)评价函数的一般形式:
f(n) = g(n) + h(n) 且 h(n) <= h*(n)
g(n),h(n):定义同A算法;
h*(n):从N到目标节点的最短路径; 称此时的A算法为A*算法.
2)程序关键点
解的路径的输出:通过目标状态节点向上回溯找其父节点,直至开始状态。
- 三、python代码实现
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Sun Sep 16 14:31:40 2018 4 A*算法解决N数码问题 5 运行程序后如下是输入格式: 6 请输入矩阵的行数 7 8 3 输入对应的N 9 请输入初始矩阵A 10 11 1 0 2 一行行输入,每行数字空格隔开,每行最后一个数字输入完成后直接回车开始输入第二行 12 13 4 5 6 14 15 3 7 8 16 请输入目标矩阵B 17 18 1 2 3 19 20 8 0 4 21 22 7 6 5 23 24 """ 25 import numpy as np 26 import copy 27 import time 28 from operator import itemgetter 29 30 goal = {} 31 32 def get_location(vec, num): #根据num元素获取num在矩阵中的位置 33 row_num = vec.shape[0] #numpy-shape函数获得矩阵的维数 34 line_num = vec.shape[1] 35 36 for i in range(row_num): 37 for j in range(line_num): 38 if num == vec[i][j]: 39 return i, j 40 41 def get_actions(vec): #获取当前位置可以移动的下一个位置,返回移动列表 42 row_num = vec.shape[0] 43 line_num = vec.shape[1] 44 45 (x, y) = get_location(vec, 0) #获取0元素的位置 46 action = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)] 47 48 if x == 0: #如果0在边缘则依据位置情况,减少0的可移动位置 49 action.remove((-1, 0)) 50 if y == 0: 51 action.remove((0, -1)) 52 if x == row_num - 1: 53 action.remove((1, 0)) 54 if y == line_num - 1: 55 action.remove((0, 1)) 56 57 return list(action) 58 59 def result(vec, action): #移动元素,进行矩阵转化 60 (x, y) = get_location(vec, 0) #获取0元素的位置 61 (a, b) = action #获取可移动位置 62 63 n = vec[x+a][y+b] #位置移动,交换元素 64 s = copy.deepcopy(vec) 65 s[x+a][y+b] = 0 66 s[x][y] = n 67 68 return s 69 70 def get_ManhattanDis(vec1, vec2): #计算两个矩阵的曼哈顿距离,vec1为目标矩阵,vec2为当前矩阵 71 row_num = vec1.shape[0] 72 line_num = vec1.shape[1] 73 dis = 0 74 75 for i in range(row_num): 76 for j in range(line_num): 77 if vec1[i][j] != vec2[i][j] and vec2[i][j] != 0: 78 k, m = get_location(vec1, vec2[i][j]) 79 d = abs(i - k) + abs(j - m) 80 dis += d 81 82 return dis 83 84 def expand(p, actions, step): #actions为当前矩阵的可扩展状态列表,p为当前矩阵,step为已走的步数 85 children = [] #children用来保存当前状态的扩展节点 86 for action in actions: 87 child = {} 88 child['parent'] = p 89 child['vec'] = (result(p['vec'], action)) 90 child['dis'] = get_ManhattanDis(goal['vec'], child['vec']) 91 child['step'] = step + 1 #每扩展一次当前已走距离加1 92 child['dis'] = child['dis'] + child['step'] #更新该节点的f值 f=g+h(step+child[dis]) 93 child['action'] = get_actions(child['vec']) 94 children.append(child) 95 96 return children 97 98 def node_sort(nodelist): #按照节点中字典的距离字段对列表进行排序,从大到小 99 return sorted(nodelist, key = itemgetter('dis'), reverse=True) 100 101 def get_input(num): 102 A = [] 103 for i in range(num): 104 temp = [] 105 p = [] 106 s = input() 107 temp = s.split(' ') 108 for t in temp: 109 t = int(t) 110 p.append(t) 111 A.append(p) 112 113 return A 114 115 def get_parent(node): 116 q = {} 117 q = node['parent'] 118 return q 119 120 def test(): 121 openlist = [] #open表 122 close = [] #存储扩展的父节点 123 124 print('请输入矩阵的行数') 125 num = int(input()) 126 127 print("请输入初始矩阵A") 128 A = get_input(num) 129 130 print("请输入目标矩阵B") 131 B = get_input(num) 132 133 print("请输入结果文件名") 134 resultfile = input() 135 136 goal['vec'] = np.array(B) #建立矩阵 137 138 p = {} 139 p['vec'] = np.array(A) 140 p['dis'] = get_ManhattanDis(goal['vec'], p['vec']) 141 p['step'] = 0 142 p['action'] = get_actions(p['vec']) 143 p['parent'] = {} 144 145 if (p['vec'] == goal['vec']).all(): 146 return 147 148 openlist.append(p) 149 150 start_CPU = time.clock() #开始扩展时CPU开始计算 151 152 while openlist: 153 154 children = [] 155 156 node = openlist.pop() #node为字典类型,pop出open表的最后一个元素 157 close.append(node) #将该元素放入close表 158 159 if (node['vec'] == goal['vec']).all(): #比较当前矩阵和目标矩阵是否相同 160 end_CPU = time.clock() #CPU结束计算 161 162 h = open(resultfile,'w',encoding='utf-8',) #将结果写入文件 并在控制台输出 163 h.write('搜索树规模:' + str(len(openlist)+len(close)) + '\n') 164 h.write('close:' + str(len(close)) + '\n') 165 h.write('openlist:' + str(len(openlist)) + '\n') 166 h.write('cpu运行时间:' + str(end_CPU - start_CPU) + '\n') 167 h.write('路径长:' + str(node['dis']) + '\n') 168 169 h.write('解的路径:' + '\n') 170 i = 0 171 way = [] 172 while close: 173 way.append(node['vec']) #从最终状态开始依次向上回溯将其父节点存入way列表中 174 node = get_parent(node) 175 if(node['vec'] == p['vec']).all(): 176 way.append(node['vec']) 177 break 178 while way: 179 i += 1 180 h.write(str(i) + '\n') 181 h.write(str(way.pop()) + '\n') 182 h.close() 183 f = open(resultfile,'r',encoding='utf-8',) 184 print(f.read()) 185 186 return 187 188 children = expand(node, node['action'], node['step']) #如果不是目标矩阵,对当前节点进行扩展,取矩阵的可能转移情况 189 190 for child in children: #如果转移之后的节点,既不在close表也不再open表则插入open表,如果在close表中则舍弃,如果在open表则比较这两个矩阵的f值,留小的在open表 191 f = False 192 flag = False 193 j = 0 194 for i in range(len(openlist)): 195 if (child['vec'] == openlist[i]['vec']).all(): 196 j = i 197 flag = True 198 break 199 for i in range(len(close)): 200 if(child['vec'] == close[i]).all(): 201 f = True 202 break 203 if f == False and flag == False : 204 openlist.append(child) 205 206 elif flag == True: 207 if child['dis'] < openlist[j]['dis']: 208 del openlist[j] 209 openlist.append(child) 210 211 212 openlist = node_sort(openlist) #对open表进行从大到小排序 213 214 test()
- 四、程序运行结果如下图所示
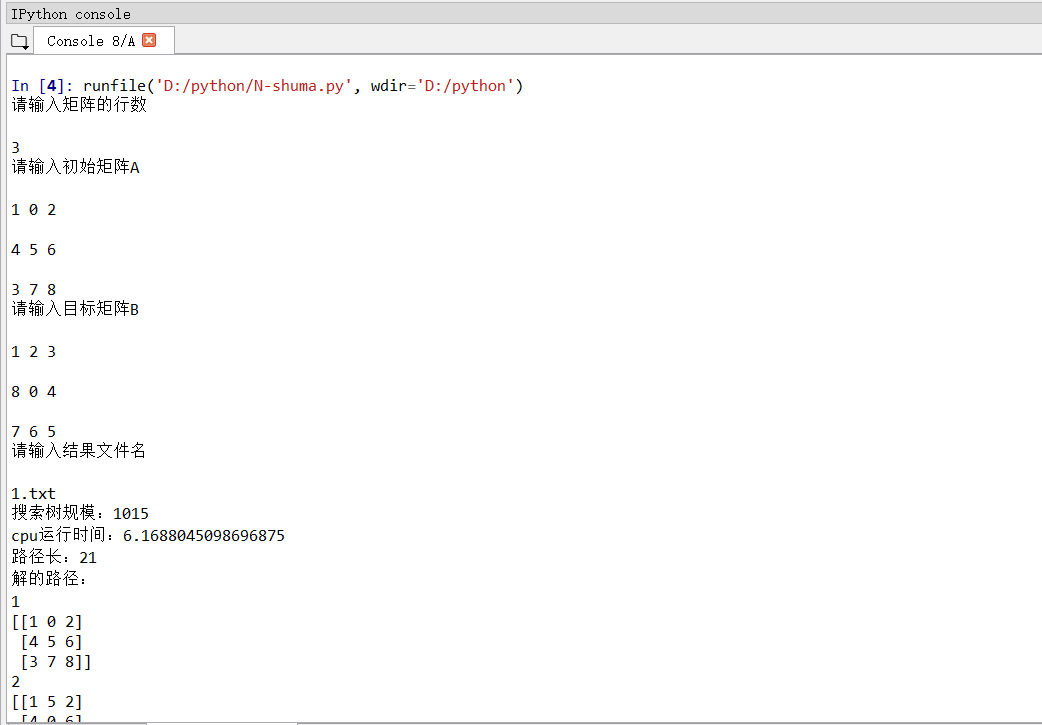
图 1

图 2
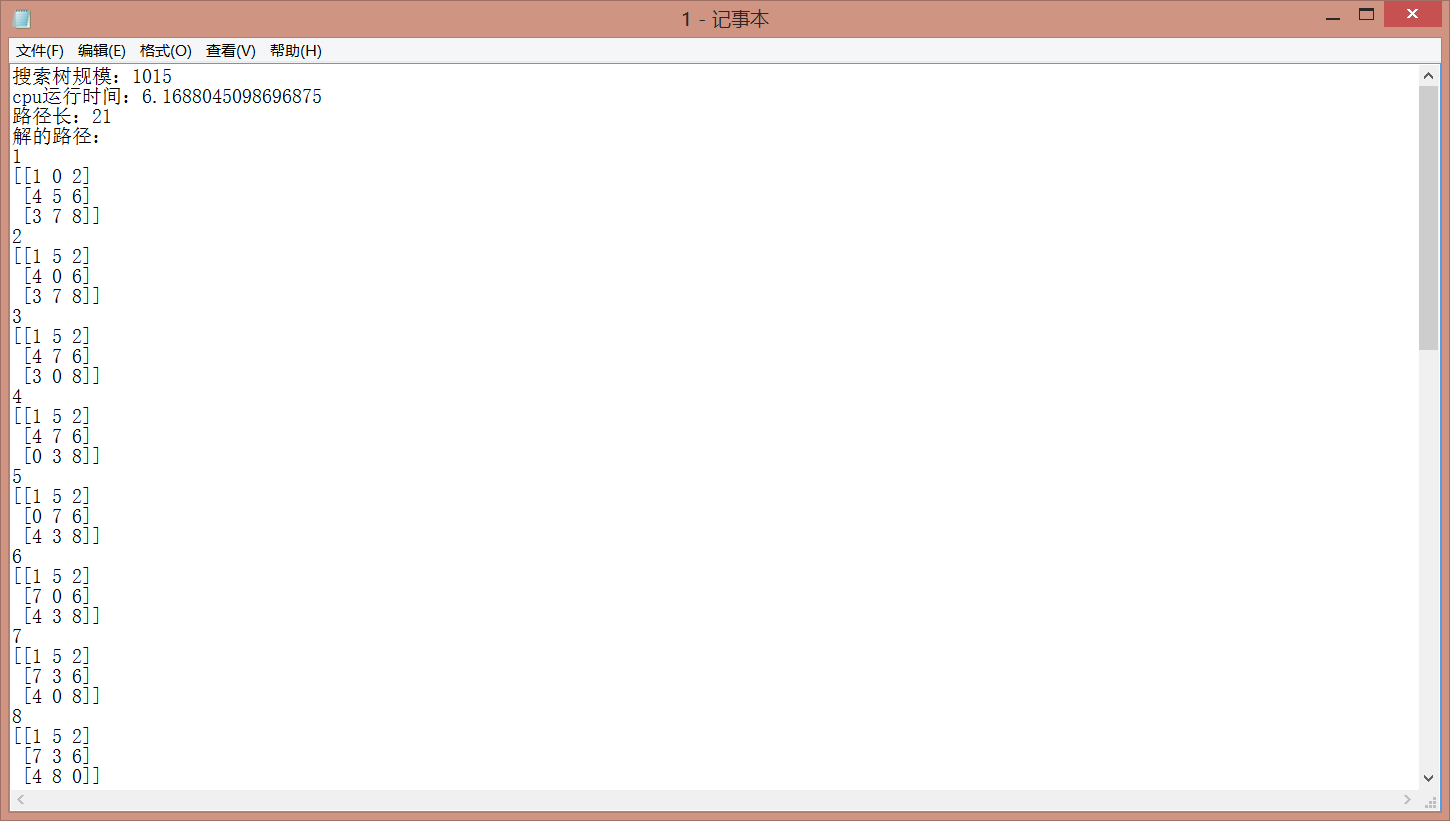
图 3
- 五、总结
通过这次编程了解到了搜索具有探索性,要提高搜索效率(尽快地找到目标节点),或要找最佳路径(最佳解)就必须注意搜索策略。对于状态图搜索,已经提出了许多策略,它们大体可分为盲目搜索(bland search)和启发式搜索(heuristic search)两大类。其中盲目搜索是无向导搜索。启发式搜索是有向导搜索,即利用启发信息(函数)引导去寻找问题解。通过A*算法解决N数码问题实验过程中也遇到很多问题,比如节点扩展的方向问题等,通过这次实验不仅锻炼了自己python编程能力,也让自己对N数码求解最优路径问题有了更清晰的认识,希望自己能在老师和同学的帮助下,能不断进步,当然最重要的是自己得付出,只会幻想而不行动的人,永远也体会不到收获果实时的喜悦。加油!!




