实验一
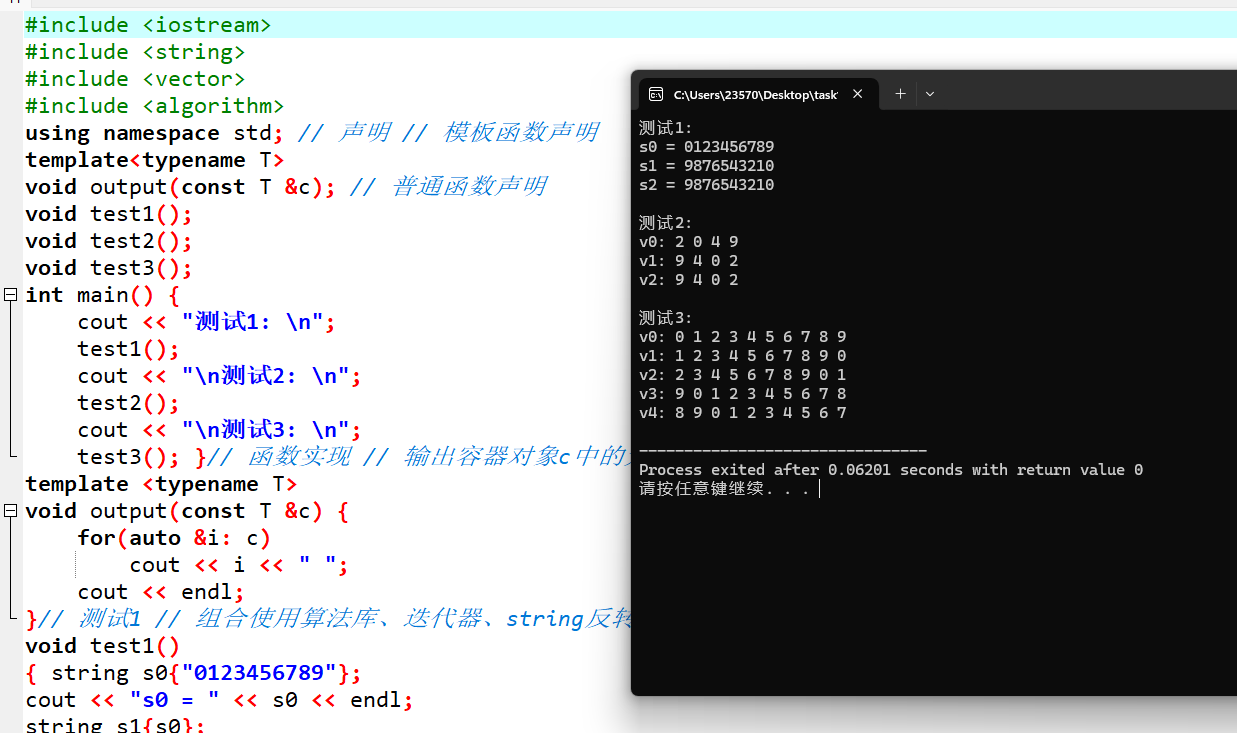
任务1
#include #include #include #include using namespace std; // 声明 // 模板函数声明 template void output(const T &c); // 普通函数声明 void test1(); void test2(); void test3(); int main() { cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); cout << "\n测试3: \n"; test3(); }// 函数实现 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 template void output(const T &c) { for(auto &i: c) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; }// 测试1 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、string反转字符串 void test1() { string s0{"0123456789"}; cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl; string s1{s0}; reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); // 反转指定迭代器区间的元素 cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; string s2{ s0 }; reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin()); // 将指定迭代区间的元素拷贝 到指定迭代器开始的目标区间,并且在复制过程中反转次序 cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; }// 测试2 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector反转动态数组对象vector内数据 void test2() { vector v0{2, 0, 4, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector v1{v0}; reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector v2{v0}; reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); }// 测试3 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector实现元素旋转移位 void test3() { vector v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector v1{v0}; rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end()); cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector v2{v0}; rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end()); cout << "v2: "; output(v2); vector v3{v0}; rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end() - 1, v3.end()); cout << "v3: "; output(v3); vector v4{ v0 }; rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end() - 2, v4.end()); cout << "v4: "; output(v4); }
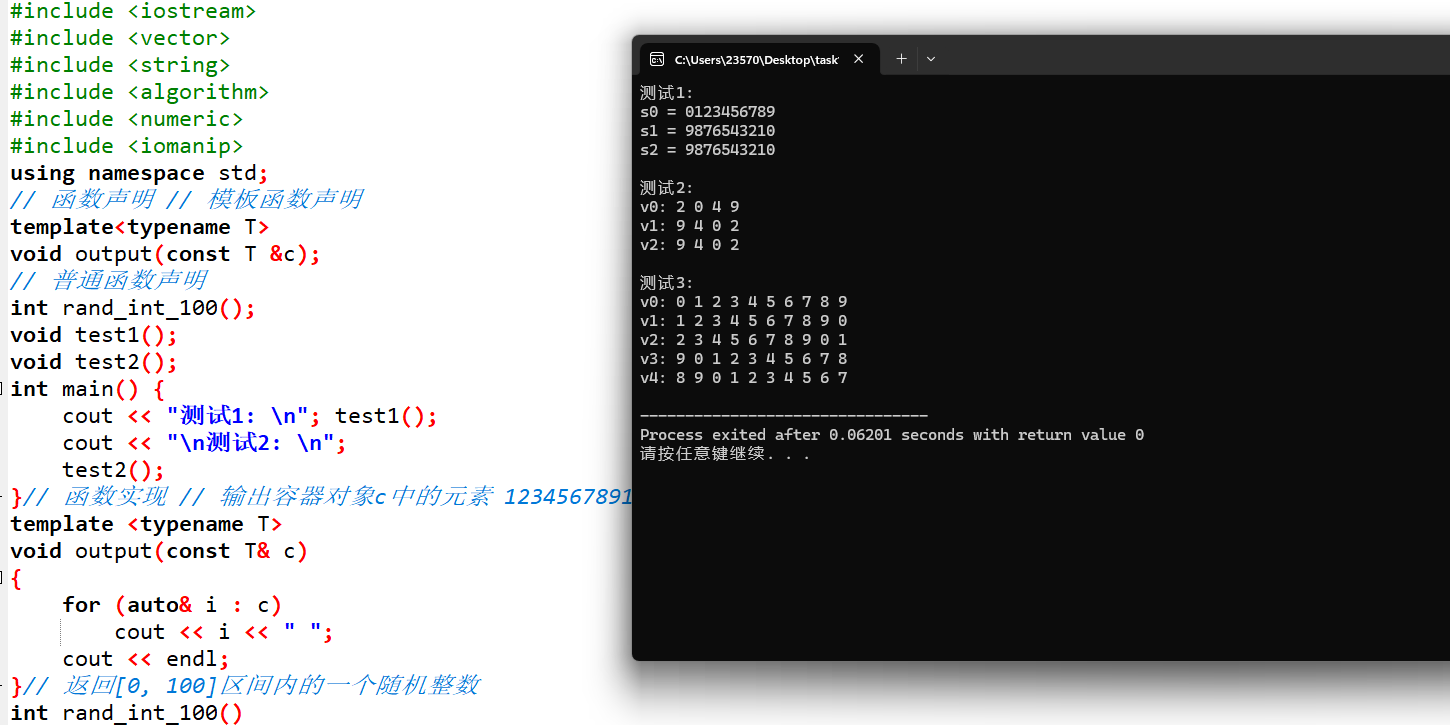
任务2
#include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std; // 函数声明 // 模板函数声明 template void output(const T &c); // 普通函数声明 int rand_int_100(); void test1(); void test2(); int main() { cout << "测试1: \n"; test1(); cout << "\n测试2: \n"; test2(); }// 函数实现 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829 template void output(const T& c) { for (auto& i : c) cout << i << " "; cout << endl; }// 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数 int rand_int_100() { return rand() % 101; }// 测试1 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、排序 void test1() { vector v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); // 产生[0, 100]之间的随机整数 赋值给指定迭代器区间[v0.begin(), v0.end())内的每个数据项 cout << "v0: "; output(v0); vector v1{v0}; sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())内数据 项进行升序排序 cout << "v1: "; output(v1); vector v2{v0}; sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1)内数据项进行升序排序 cout << "v2: "; output(v2); }// 测试2 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值 void test2() { vector v0(10); generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); cout << "v0: "; output(v0); auto iter1 = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *iter1 << endl; auto iter2 = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最大值: " << *iter2 << endl; auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0)/v0.size(); cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; cout << endl; vector v1{ v0 }; cout << "v0: "; output(v0); sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); double avg2 = accumulate(v1.begin() + 1, v1.end() - 1, 0) / (v1.size() - 2); cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; }
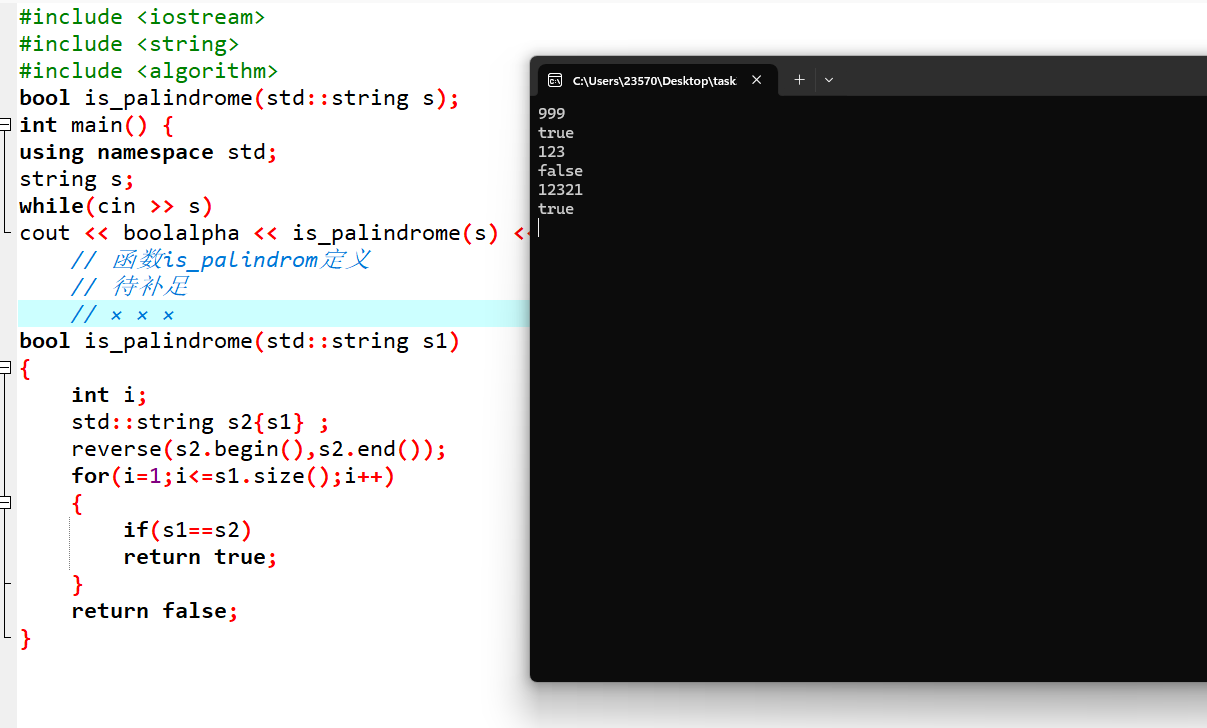
任务3
#include #include #include bool is_palindrome(std::string s); int main() { using namespace std; string s; while(cin >> s) cout << boolalpha << is_palindrome(s) << endl; }// 函数is_palindrom定义 // 待补足 // ××× 123456789101112 // 函数is_palindrom定义 // 待补足 // ××× bool is_palindrome(std::string s1) { int i; std::string s2{s1} ; reverse(s2.begin(),s2.end()); for(i=1;i<=s1.size();i++) { if(s1==s2) return true; } return false; }
实验4
#include #include #include std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2); int main() { using namespace std; int x; while(cin >> x) { cout << "十进制: " << x << endl; cout << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << endl; cout << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << endl; cout << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << endl << endl; } } // 函数dec2n定义 // 待补足 // ××× std::string dec2n(int x,int n){ if(x==0) return "0"; char element[16]={'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','A','B','C','D','E','F'}; std::string ans; int m; while(x>0){ m=x%n; x/=n; ans.push_back(element[m]); } reverse(ans.begin(),ans.end()); return ans; }
实验5
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ vector member; char ch; cout<<" "; for(int i=0;i<26;i++){ ch='a'+i; cout<<ch<<' '; member.push_back(ch-32); } cout<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=26;i++){ cout<<i<<' '; for(int j=i;j<26;j++) cout<<member[j]<<' '; for(int k=0;k<i;k++) cout<<member[k]<<' '; cout<<endl; } }

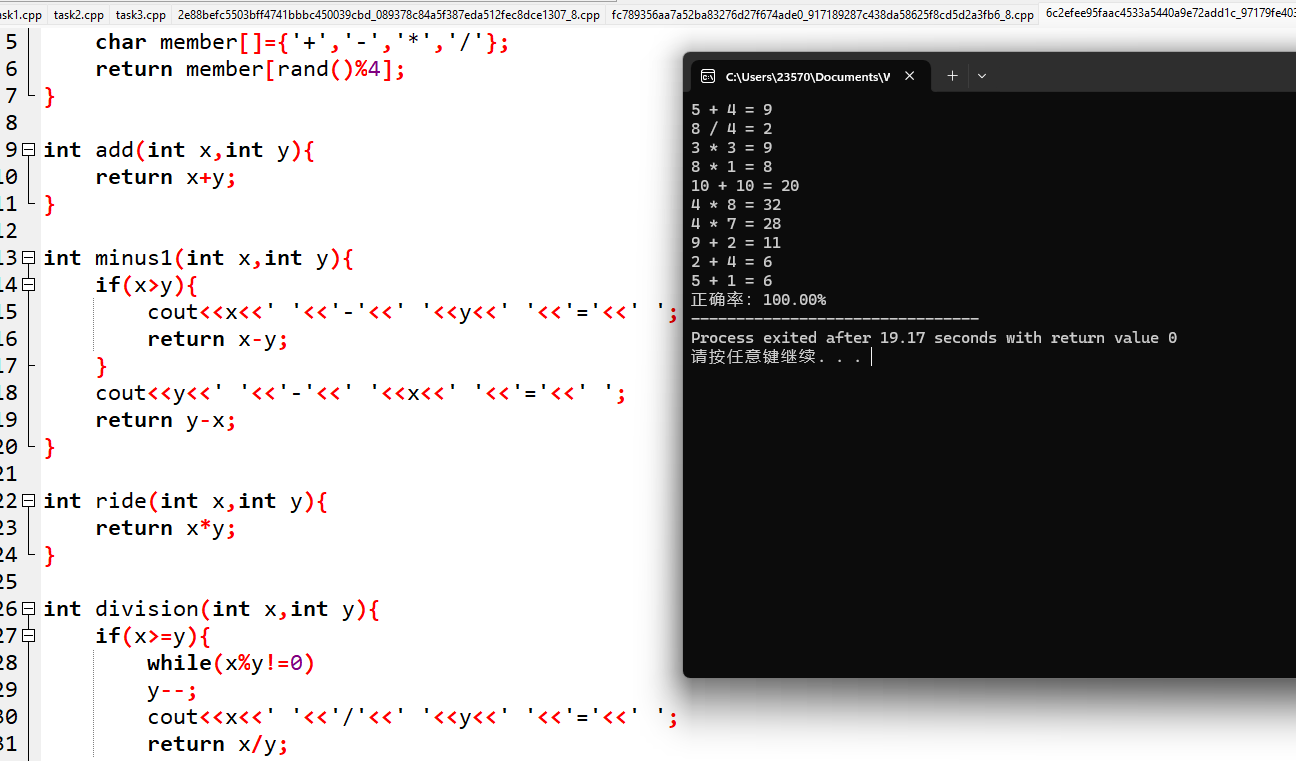
实验6
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; char solution(){ char member[]={'+','-','*','/'}; return member[rand()%4]; } int add(int x,int y){ return x+y; } int minus1(int x,int y){ if(x>y){ cout<<x<<' '<<'-'<<' '<<y<<' '<<'='<<' '; return x-y; } cout<<y<<' '<<'-'<<' '<<x<<' '<<'='<<' '; return y-x; } int ride(int x,int y){ return x*y; } int division(int x,int y){ if(x>=y){ while(x%y!=0) y--; cout<<x<<' '<<'/'<<' '<<y<<' '<<'='<<' '; return x/y; } while(y%x!=0) x--; cout<<y<<' '<<'/'<<' '<<x<<' '<<'='<<' '; return y/x; } int judge(int x,int y){ if(x==y)return 1; return 0; } int main(){ srand(time(0)); char ch; int ans,userans,num1,num2,sum=0; double right; for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ ch=solution(); num1=rand()%10+1; num2=rand()%10+1; if(ch=='+'){ ans=add(num1,num2); cout<<num1<<' '<<'+'<<' '<<num2<<' '<<'='<<' '; cin>>userans; sum+=judge(ans,userans); } else if(ch=='-'){ ans=minus1(num1,num2); cin>>userans; sum+=judge(ans,userans); } else if(ch=='*'){ ans=ride(num1,num2); cout<<num1<<' '<<'*'<<' '<<num2<<' '<<'='<<' '; cin>>userans; sum+=judge(ans,userans); } else{ ans=division(num1,num2); cin>>userans; sum+=judge(ans,userans); } } right=sum*10.0; cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2); cout<<"正确率:"<<right<<'%'; }