POJ 3723 - Conscription ( 最大权森林 / 最小生成树 )
题意
挑选N个女兵,M个男兵,雇佣每个人都需要支付10000元的费用,如果男a和女b存在亲密度d,只要他们其中有一个已经被选中,那么在选另一个人需要的费用为100000-d,给定R个关系,输出一个最低费用,每个关系只能使用一次。
思路
最大权森林转换为负权最小生成树( MST )
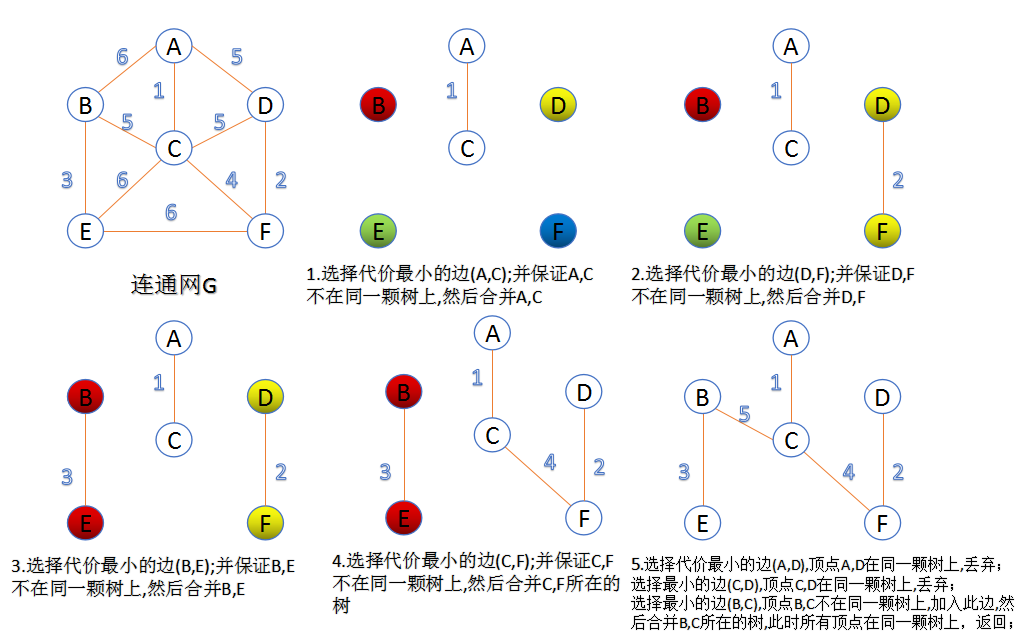
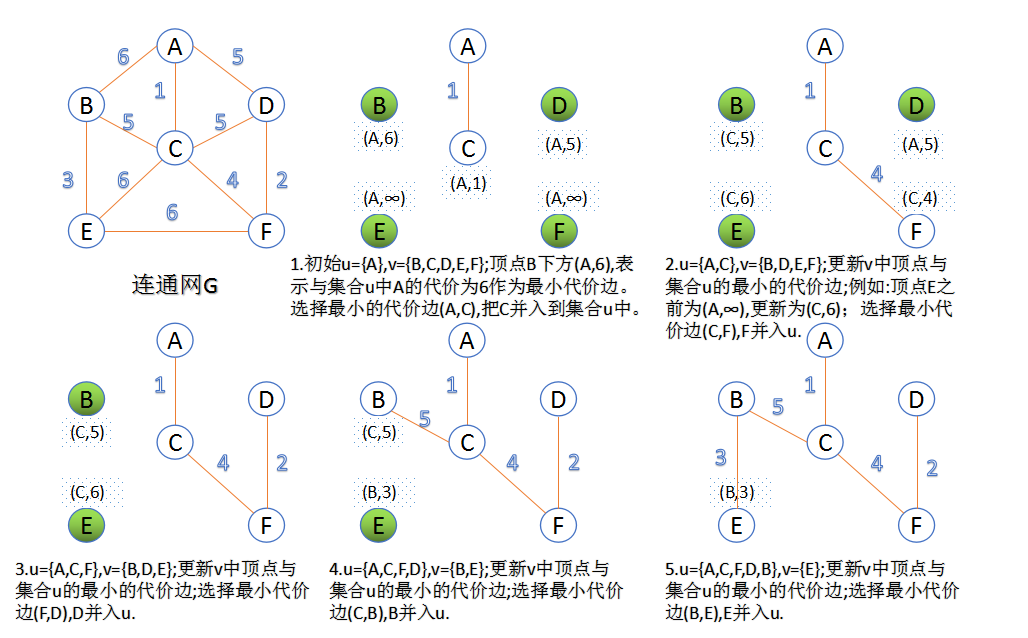
当时学最小生成树就这个博客上的图感觉非常好理解:
算法导论–最小生成树(Kruskal和Prim算法)
Kruskal
Prim
这个题用Prim居然MLE了….
用并查集维护Kruskal可以过
数据范围1 ≤ N, M ≤ 10000 , 0 ≤ R ≤ 50,000
如果用Prim应该是 20000*20000的邻接表, 用Kruskal则是50000条边, 显然用Kruskal更优~
最小生成树Prim与Kruskal算法的比较
AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#define mst(a) memset(a, 0, sizeof a)
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 50000+5;
int f[20000+5];
struct edge{
int f, t, cost;
}cst[maxn];
bool cmp(const edge& a, const edge& b){
return a.cost < b.cost;
}
int all, n, m, r;
void bcj_init(){
for( int i = 0; i < all; i++ )
f[i] = i;
}
int _find(int a){
if( a != f[a] ) f[a] = _find(f[a]);
return f[a];
}
void unite(int a, int b){
int aa = _find(a);
int bb = _find(b);
if( aa != bb ){
f[bb] = aa;
}
}
int kruskal(){
int res = 0;
bcj_init();
sort(cst, cst+r, cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < r; i++){
edge e = cst[i];
if( _find(e.f) != _find(e.t) ){
unite(e.f, e.t);
res += e.cost;
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int T, a, b, c;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &r);
all = n+m;
for(int i = 0; i < r; i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&a, &b, &c);
cst[i] = (edge){a, b+n, -c};
}
int res = kruskal();
printf("%d\n",all*10000+res);
}
return 0;
}