227:Puzzle
A children’s puzzle that was popular 30 years ago consisted of a 5×5 frame which contained 24 smallsquares of equal size. A unique letter of the alphabet was printed on each small square. Since therewere only 24 squares within the frame, the frame also contained an empty position which was the samesize as a small square. A square could be moved into that empty position if it were immediately to theright, to the left, above, or below the empty position. The object of the puzzle was to slide squaresinto the empty position so that the frame displayed the letters in alphabetical order.
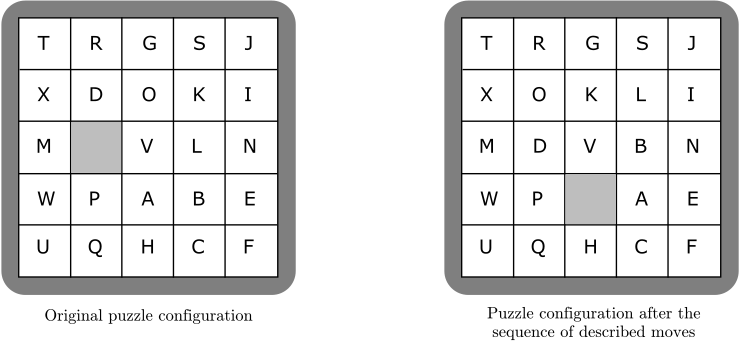
The illustration below represents a puzzle in its original configuration and in its configuration afterthe following sequence of 6 moves:
1) The square above the empty position moves.
2) The square to the right of the empty position moves.
3) The square to the right of the empty position moves.
4) The square below the empty position moves.
5) The square below the empty position moves.
6) The square to the left of the empty position moves.
Write a program to display resulting frames given their initial configurations and sequences of moves.
Input
Input for your program consists of several puzzles. Each is described by its initial configuration andthe sequence of moves on the puzzle. The first 5 lines of each puzzle description are the startingconfiguration. Subsequent lines give the sequence of moves.
The first line of the frame display corresponds to the top line of squares in the puzzle. The otherlines follow in order. The empty position in a frame is indicated by a blank. Each display line containsexactly 5 characters, beginning with the character on the leftmost square (or a blank if the leftmostsquare is actually the empty frame position). The display lines will correspond to a legitimate puzzle.
The sequence of moves is represented by a sequence of As, Bs, Rs, and Ls to denote which squaremoves into the empty position. A denotes that the square above the empty position moves; B denotesthat the square below the empty position moves; L denotes that the square to the left of the emptyposition moves; R denotes that the square to the right of the empty position moves. It is possible thatthere is an illegal move, even when it is represented by one of the 4 move characters. If an illegal moveoccurs, the puzzle is considered to have no final configuration. This sequence of moves may be spreadover several lines, but it always ends in the digit 0. The end of data is denoted by the character Z.
Output
Output for each puzzle begins with an appropriately labeled number (Puzzle #1, Puzzle #2, etc.). Ifthe puzzle has no final configuration, then a message to that effect should follow. Otherwise that finalconfiguration should be displayed.
Format each line for a final configuration so that there is a single blank character between twoadjacent letters. Treat the empty square the same as a letter. For example, if the blank is an interiorposition, then it will appear as a sequence of 3 blanks — one to separate it from the square to the left,one for the empty position itself, and one to separate it from the square to the right.
Separate output from different puzzle records by one blank line.Note: The first record of the sample input corresponds to the puzzle illustrated above.
Sample Input
TRGSJ
XDOKI
M VLN
WPABE
UQHCF
ARRBBL0
ABCDE
FGHIJ
KLMNO
PQRS
TUVWX
AAA
LLLL0
ABCDE
FGHIJ
KLMNO
PQRS
TUVWX
AAAAABBRRRLL0
Z
Sample Output
Puzzle #1:
T R G S J
X O K L I
M D V B N
W P A E
U Q H C F
Puzzle #2:
A B C D
F G H I E
K L M N J
P Q R S O
T U V W X
Puzzle #3:
This puzzle has no final configuration.
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 85;
char table[5][5];
char s[maxn];
int x,y;
map<char, pair<int,int> > orders;
bool move(char order){
int tx = x + orders[order].first;
int ty = y + orders[order].second;
if(0 <= tx && tx < 5 && 0 <= ty && ty < 5){
table[x][y] = table[tx][ty];
table[tx][ty] = ' ';
x = tx,y = ty;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int i,j,cnt = 0;
orders['A'] = make_pair(-1,0);
orders['B'] = make_pair(1,0);
orders['L'] = make_pair(0,-1);
orders['R'] = make_pair(0,1);
while(gets(table[0])){
if(table[0][0] == 'Z') break;
for(i = 1;i < 5;i++){
gets(table[i]);
}
x = y = -1;
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++){
for(j = 0;j < 5;j++){
if(table[i][j] == ' '){
x = i,y = j;
break;
}
}
if(x >= 0) break;
}
//读取orders
while(s[strlen(s) - 1] != '0') scanf("%s",s + strlen(s));
for(i = 0;s[i] != '0';i++){
if(!move(s[i])) break;
}
printf("Puzzle #%d\n",++cnt);
if(s[i] == '0'){
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++){
for(j = 0;j < 4;j++){
printf("%c ",table[i][j]);
}
printf("%c\n",table[i][4]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
else printf("%s\n","This puzzle has no final configuration.");
memset(table,'\0',sizeof(table));
memset(s,'\0',sizeof(s));
//的确要gets两次才可以。。暂时不知道为什么
gets(table[0]);
}
return 0;
}参考了这位博主 依次读取单个字符的方式,修改之后的代码如下:
#include<map>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 85;
char table[5][5];
char s[maxn];
int x,y;
map<char, pair<int,int> > orders;
bool move(char order){
//if(orders.count(order) == 0) return false;
int tx = x + orders[order].first;
int ty = y + orders[order].second;
if(0 <= tx && tx < 5 && 0 <= ty && ty < 5){
table[x][y] = table[tx][ty];
table[tx][ty] = ' ';
x = tx,y = ty;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int i,j,cnt = 0;
char c;
orders['A'] = make_pair(-1,0);
orders['B'] = make_pair(1,0);
orders['L'] = make_pair(0,-1);
orders['R'] = make_pair(0,1);
while((c = getchar()) != 'Z'){
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++){
for(j = 0;j < 5;j++){
table[i][j] = c;
if(c == ' ' || c == '\n'){
x = i,y = j;
table[i][j] = ' ';
}
c = getchar();
if(j == 5-1 && c == '\n') c = getchar();
}
}
//这句不能少
s[0] = c;
//读取orders,如果下一行还有的话,就从这次读取之前的最后一位字符之后开始读入,我觉得还是比较巧妙的哈哈哈
while(s[strlen(s) - 1] != '0') scanf("%s",s + strlen(s));
for(i = 0;s[i] != '0';i++){
if(!move(s[i])) break;
}
if(++cnt > 1) putchar('\n');
printf("Puzzle #%d:\n",cnt);
if(s[i] == '0'){
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++){
for(j = 0;j < 4;j++){
printf("%c ",table[i][j]);
}
printf("%c\n",table[i][4]);
}
}
else printf("%s\n","This puzzle has no final configuration.");
memset(table,'\0',sizeof(table));
memset(s,'\0',sizeof(s));
c = getchar();
}
return 0;
}可是运行时间为10ms ,远低于别人的0ms,考虑是用了map的原因,直接用数组替代即可,运行时间为0ms,另外修改了读取table 的代码,事实证明那位博主的代码中的那部分我不知道为啥的代码的确是没用的,代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 85;
const int ox[4] = {-1,1,0,0};
const int oy[4] = {0,0,-1,1};
int x,y;
int p[26];
char s[maxn];
char table[5][5];
bool move(char order){
int tx = x + ox[p[order - 'A']];
int ty = y + oy[p[order - 'A']];
if(0 <= tx && tx < 5 && 0 <= ty && ty < 5){
table[x][y] = table[tx][ty];
table[tx][ty] = ' ';
x = tx,y = ty;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int i,j,cnt = 0;
char c;
char tmp[] = {'A','B','L','R'};
for(i = 0;i < 4;i++) p[tmp[i] - 'A'] = i;
while((c = getchar()) != 'Z'){
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++){
for(j = 0;j < 5;j++){
table[i][j] = c;
if(c == ' ') x = i,y = j;
c = getchar();
if(c == '\n') c = getchar();
}
}
//这句不能少
s[0] = c;
//读取orders,如果下一行还有的话,就从这次读取之前的最后一位字符之后开始读入,还是比较巧妙的哈哈哈
while(s[strlen(s) - 1] != '0') scanf("%s",s + strlen(s));
for(i = 0;s[i] != '0';i++){
if(!move(s[i])) break;
}
if(++cnt > 1) putchar('\n');
printf("Puzzle #%d:\n",cnt);
if(s[i] == '0'){
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++){
for(j = 0;j < 4;j++){
printf("%c ",table[i][j]);
}
printf("%c\n",table[i][4]);
}
}
else printf("%s\n","This puzzle has no final configuration.");
memset(table,'\0',sizeof(table));
memset(s,'\0',sizeof(s));
c = getchar();
}
return 0;
}