管道通信
有名管道(命名管道)
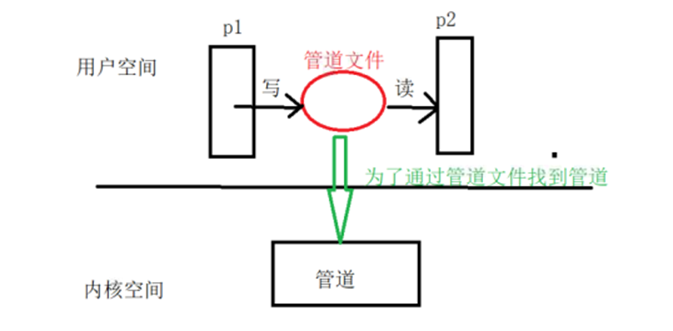
注意:管道文件存在的意义:为了让任意的进程之间完成通信(非血缘关系)管道文件存储在磁盘上,但是大小永远为0意味着数据不会被存储在管道文件中,而是每一次的读写都是往内核中的管道进行读写。
有名管道特点:
1、 有名管道可以适用于任意两个进程之间的通信
2、 有名管道可以实现双工通信
3、 存储在内核中,但在文件系统中可以见到一个文件类型为p的管道文件,但这个管道文件不储存信息,大小为0;
主要函数
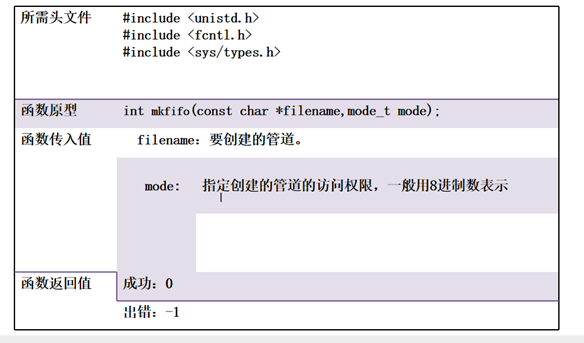
1、mkfifo(文件名,文件权限):创建管道文件。
案例:(双工通信)
qy.c:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <errno.h> void *fun_1(void *arg)//线程1 { int ret = mkfifo("Myfifo_Q_W",0666); //EEXIST解释 //如果因为文件存在而报错的话就表示正常 //说明另一边已经创建好了 if(ret < 0 && EEXIST != errno) { perror("mkfifo error"); exit(-1); } printf("mkfifo success!\n"); int fw = open("Myfifo_Q_W",O_RDWR); if(fw < 0) { perror("open error"); exit(-1); } printf("open Myfifo_Q_W success!\n"); char buf[100] = {'\0'}; while(1) { printf("\nQY:"); gets(buf); int count = write(fw,buf,strlen(buf)); if(count < 0) { perror("write error"); exit(-1); } memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf)); } close(fw); exit(0); } void *fun_2(void *arg)//线程2 { int ret = mkfifo("Myfifo_W_Q",0666); //EEXIST解释 //如果因为文件存在而报错的话就表示正常 //说明另一边已经创建好了 if(ret < 0 && EEXIST != errno) { perror("mkfifo error"); exit(-1); } printf("mkfifo success!\n"); int fr = open("Myfifo_W_Q",O_RDWR); if(fr < 0) { perror("open error"); exit(-1); } printf("open Myfifo_W_Q success!\n"); char buf[100] = {'\0'}; while(1) { printf("\nWF:"); int count = read(fr,buf,sizeof(buf)); if(count == 0) { printf("对方未发消息!\n"); exit(-1); } printf("%s",buf); memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf)); } close(fr); exit(0); } int main()//main函数内为主线程,主线程在运行子线程才能正常运行。 { pthread_t tid_1; pthread_t tid_2; if(0 != pthread_create(&tid_1, NULL, fun_1, NULL)) { perror("pthread_create1"); return -1; } if(0 != pthread_create(&tid_2, NULL, fun_2, NULL)) { perror("pthread_create2"); return -1; } pthread_join(tid_1,NULL); pthread_join(tid_2,NULL); return 0; }
wf.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <errno.h> void *fun_1(void *arg)//线程1 { int ret = mkfifo("Myfifo_W_Q",0666); //EEXIST解释 //如果因为文件存在而报错的话就表示正常 //说明另一边已经创建好了 if(ret < 0 && EEXIST != errno) { perror("mkfifo error"); exit(-1); } printf("mkfifo success!\n"); int fw = open("Myfifo_W_Q",O_RDWR); if(fw < 0) { perror("open error"); exit(-1); } printf("open Myfifo_W_Q success!\n"); char buf[100] = {'\0'}; while(1) { printf("\nWF:"); gets(buf); int count = write(fw,buf,strlen(buf)); if(count < 0) { perror("write error"); exit(-1); } memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf)); } close(fw); exit(0); } void *fun_2(void *arg)//线程2 { int ret = mkfifo("Myfifo_Q_W",0666); //EEXIST解释 //如果因为文件存在而报错的话就表示正常 //说明另一边已经创建好了 if(ret < 0 && EEXIST != errno) { perror("mkfifo error"); exit(-1); } printf("mkfifo success!\n"); int fr = open("Myfifo_Q_W",O_RDWR); if(fr < 0) { perror("open error"); exit(-1); } printf("open Myfifo_Q_W success!\n"); char buf[100] = {'\0'}; while(1) { printf("\nQY:"); int count = read(fr,buf,sizeof(buf)); if(count == 0) { printf("对方未发消息!\n"); exit(-1); } printf("%s",buf); memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf)); } close(fr); exit(0); } int main()//main函数内为主线程,主线程在运行子线程才能正常运行。 { pthread_t tid_1; pthread_t tid_2; if(0 != pthread_create(&tid_1, NULL, fun_1, NULL)) { perror("pthread_create1"); return -1; } if(0 != pthread_create(&tid_2, NULL, fun_2, NULL)) { perror("pthread_create2"); return -1; } pthread_join(tid_1,NULL); pthread_join(tid_2,NULL); return 0; }
makefile:
APP: gcc qy.c -o qy -lpthread gcc wf.c -o wf -lpthread


