第一次个人编程作业
https://github.com/Jimase/Software_Engineering/tree/main/031902515
一、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 72 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 1200 | 1600 |
| Development | 开发 | 700 | 700 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 5 | 55 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 5 | 55 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 5 | 55 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 55 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 120 | 120 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 360 | 720 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 50 | 50 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 50 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 90 | 180 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 30 | 60 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 20 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 10 | 100 |
| · 合计 | 1200 | 1800 |
二、计算模块接口
1.计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
1.命令行参数实现
if __name__ == '__main__':
#print(sys.argv)
#print(len(sys.argv))
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print("参数错误,请以此给出敏感词文件,待检测文件和结果文件")
exit(-1)
args = sys.argv
main(args[1], args[2], args[3])
综合考虑以后决定选择python完成作业,考虑到作业要求,先把命令行实现了。
2.额外库调用
import sys
from pypinyin import pinyin, Style
from hanzi_chaizi.hanzi_chaizi import HanziChaizi
from langconv import Converter
from Pinyin2Hanzi.Pinyin2Hanzi import DefaultHmmParams
from Pinyin2Hanzi.Pinyin2Hanzi import viterbi
- 2021.10.8回来展望,这个地方犯了非常严肃的错误,不应该把别人的组件直接下载到自己的项目中使用,没有充分考虑测试需求,本地能够全测不代表测试组的同学们可以,给测试组的同学们带来了极大的不便和麻烦依然未能解决,如果是在科研项目中代码不可复现,我的做法可能构成学术不端,此处做个纪念,警醒自我。
3.部分核心接口(实现代码略)
view code
#检验是否全是中文字符
def is_all_chinese(strs):
for _char in strs:
if not '\u4e00' <= _char <= '\u9fa5':
return False
return True
def chs_to_cht(sentence): # 传入参数为列表
"""
将简体转换成繁体
:param sentence:
:return:
"""
sentence = ",".join(sentence)
sentence = Converter('zh-hant').convert(sentence)
sentence.encode('utf-8')
return sentence.split(",")
def get_permutation(cstr, pstr, deepth, ans, nowlist):
if deepth == len(cstr):
# print(nowlist)
ans.append(nowlist)
# print("ans: ", ans)
return
for i in range(2):
if i == 0:
# nowlist.append(cstr[deepth])
get_permutation(cstr, pstr, deepth + 1, ans, nowlist + [cstr[deepth]])
# del nowlist[len(nowlist) - 1]
elif i == 1:
# nowlist.append(pstr[deepth])
get_permutation(cstr, pstr, deepth + 1, ans, nowlist + [pstr[deepth]])
# del nowlist[len(nowlist) - 1]
return
def get_bushouword(bushoulist, deepth, ans, noword):
if deepth == len(bushoulist):
ans.append(noword)
return
for bushou in bushoulist[deepth]:
sigleword = ""
for item in bushou:
sigleword += item
get_bushouword(bushoulist, deepth + 1, ans, noword + sigleword)
def get_fantizuhe(array1, array2, deepth, ans, noword):
if deepth == len(array1):
ans.append(noword)
return
for i in range(2):
if i == 0:
get_fantizuhe(array1, array2, deepth + 1, ans, noword + array1[deepth])
elif i == 1:
get_fantizuhe(array1, array2, deepth + 1, ans, noword + array2[deepth])
def get_fpyzu(array1, array2, deepth, ans, noword):
if deepth == len(array1):
ans.append(noword)
return
for i in range(2):
if i == 0:
get_fpyzu(array1, array2, deepth + 1, ans, noword + array1[deepth])
elif i == 1:
get_fpyzu(array1, array2, deepth + 1, ans, noword + array2[deepth])
def get_xieyinzuhe(array, deepth, ans, noword):
if deepth == len(array):
ans.append(noword)
return
for i in range(len(array[deepth])):
get_xieyinzuhe(array, deepth + 1, ans, noword + array[deepth][i])
4.DFA算法部分
view code
# DFA算法
class DFAFilter(object):
# 构造函数的参数为关键词文件路径
def __init__(self, senstive_path, result_path):
# 关键词字典
self.keyword_chains = {}
# 限定读
self.delimit = '\x00'
self.parse(senstive_path)
self.result_path = result_path
self.total = 0
self.rp = open(self.result_path, "w")
# 向关键词字典中插入关键字
def add(self, keyword, rawkeyword):
# 关键词英文变为小写
chars = keyword.lower()
if not chars: return
level = self.keyword_chains
# 遍历关键字的每个字
for i in range(len(chars)):
# 如果这个字已经存在字符链的key中就进入其子字典
if chars[i] in level:
level = level[chars[i]]
else:
if not isinstance(level, dict):
break
for j in range(i, len(chars)):
level[chars[j]] = {}
last_level, last_char = level, chars[j]
level = level[chars[j]]
last_level[last_char] = {self.delimit: rawkeyword}
break
# 构建关键词字典
def parse(self, path):
with open(path, encoding='utf-8') as f:
for keyword in f.readlines():
ckeyword = keyword.strip()
if is_all_chinese(ckeyword):
# 构建拼音敏感字
x = pinyin(ckeyword, style=Style.NORMAL)
pkeyword = [item[0] for item in x]
ans = []
get_permutation(ckeyword, pkeyword, 0, ans, [])
for ansitem in ans:
tkeyword = ""
for item in ansitem:
tkeyword += item
self.add(tkeyword, ckeyword)
# 得到首字母类型的拼音
py = pinyin(ckeyword, style=Style.FIRST_LETTER)
fpy = ""
for item in py:
fpy += item[0]
fpzu = []
get_fpyzu(ckeyword, fpy, 0, fpzu, "")
for item in fpzu:
# print(item)
self.add(item, ckeyword)
# 构建谐音敏感字
# 首先得到文字的拼音
py = pinyin(ckeyword, style=Style.NORMAL)
hmmparams = DefaultHmmParams()
xieyin = []
for item in py:
result = viterbi(hmm_params=hmmparams, observations=(item))
xieyin.append([item2.path[0] for item2 in result])
xieyinzuhe = []
get_xieyinzuhe(xieyin, 0, xieyinzuhe, "")
for item in xieyinzuhe:
print(item)
self.add(item, ckeyword)
# 构建部首敏感字
hc = HanziChaizi()
bushou = []
for item in ckeyword:
ans = hc.query(item)
bushou.append(ans)
ans = []
get_bushouword(bushou, 0, ans, "")
for bushouword in ans:
self.add(bushouword, ckeyword)
# 构建繁体字字典
fanti = chs_to_cht(ckeyword)
fjti = []
get_fantizuhe(fanti, ckeyword, 0, fjti, "")
for item in fjti:
self.add(item, ckeyword)
else:
self.add(ckeyword, ckeyword)
print(self.keyword_chains)
# 根据关键字字典过滤出输入字符串message中的敏感词
def filter(self, message, linenumber):
rawmessage = message
message = message.lower()
start = 0
while start < len(message):
level = self.keyword_chains
# 当字符不在关键字字典时
if message[start] not in level:
start += 1
continue
if is_all_chinese(message[start]): mode = "c"
else: mode = "e"
step_ins = 0
sensitive_word = ""
left, right = start, 0
ok = False
for char in message[start:]:
if char.isdigit():
step_ins += 1
continue
if char not in level and mode == "c" and char.encode("utf-8").isalpha():
step_ins += 1
continue
# 特殊字符判断,当一个字符既不是中文又不是英文和数字时被认定为为特殊字符
if not is_all_chinese(char) and not char.encode("utf-8").isalpha()\
and not char.isdigit():
step_ins += 1
continue
# 新字在敏感词字典链表中
if char in level:
# sensitive_word += char
step_ins += 1
# 特定字符不在当前字的value值里,嵌套遍历下一个
if self.delimit not in level[char]:
level = level[char]
else:
start += step_ins - 1
right = start
ok = True
sensitive_word = level[char][self.delimit]
break
# 新字不在敏感词字典链表中
else: break
if ok:
anstr = "Line{}: <{}> {}\n".format(linenumber, sensitive_word, rawmessage[left: right + 1])
print(anstr, end="")
self.rp.write(anstr)
self.total += 1
start += 1
def __del__(self):
self.rp.write(str(self.total))
self.rp.close()
2.计算模块接口部分的性能改进
1.模块改进与时间消耗主要如下:
- 单一库改为字典树实现(120min)
- 暴力对比改为略优化的DFA
- 性能分析图
- 能力有限,查阅了相关的资料,主流的方法只有2.5种:
- DFA:即Deterministic Finite Automaton,也就是确定有穷自动机。核心是建立了以敏感词为基础的许多敏感词树。考虑文本复杂性,最终采取了此法,将检索难度转移到了字典树的建立
- DFA:算法直观上怎么做?
- 当我们开始考虑状态的离开转换时,将其设置为“已标记的”。DFA的开始状态是firstpos(root),root代表抽象语法树的根结点,DFA的终结状态是那些包含了#所在位置的状态。下面我们给出构造算法的伪代码描述
- AC自动机:字典树的基础上:变形KMP算法+失配指针
- 自然语言处理:盲猜出题人的课题是这个,这也是比较合理的方法
3.计算模块部分单元测试展示
1、白盒测试
- 由于测试组未明确指示后台15个测试点类型:分类如下,为避免屏蔽,用化名为例
- 纯粹敏感词类型:line 250:<你好> 你好 (√)
- 纯粹拼音类型:line 250:<你好> nihao(√)
- 谐音类型:line 250:<你好> 泥豪(√)
- 繁体类型:line 111:<苏> 蘇(√)
- 插入英文字符类型:line 250:<你好> 你abc好(√)
- 插入无效字符:line 250:<你好> 你@@@###好(√)
- 以及嵌套类型:"你abc_++++好"、"ni好"、"N好"、"你_郝"
view code
class functionTest(unittest.TestCase):
def test_seperate(self): #左右结构拆分
word="你好"
org="亻尔女字"
self.text()
def test_pinyin(self): #拼音大小写、拼音首字母
word="你好"
org=["nihao"、"Nhao]
self.text()
def test_insert(self): #插入字母或特殊字符
word="你好"
org="你ABC好"
self.text()
def test_homophones(self): #插入字母或特殊字符
word="你好"
org="你!@#¥%……*())————好"
self.test()
def test_english(self): #大小写转换以及插入特殊字符
word="hello"
org="Hel8!lo13"
self.test(text,"Hel8!lo")
2、 样例测试(给予的样例涵盖了所有潜在敏感词):
- ans.txt文档共计504行(测试组一共给了三个版本,明确指出其中仍有问题,但为了考验大家手动数据处理能力,后续不以更新)我们假设ans.txt一共504行
- sensitive_dec0版本 399行
- sensitive_dec2版本 470行 欠妥输出
- sensitive_dec3版本 475行 仍未能达到ans要求。当然,我也不知道ans.txt长啥样,只知道约有500行
- sensitive_dec4.7版本(2021.9.14),使用cProfile做基本测试,结果有点诡异:
1、为啥有516行结果呢?标准答案ans.txt才504啊
2、为啥只需要1.462秒呢?(不应该这么快的,非自谦,是真的不应该)
3、为啥有437103个函数被调用呢,我哪写了这么多啊?
- 解答上述问题:
1、我的未必对,但明显测试组的给的ans.txt有问题,所谓白盒测试盲盒测试(确信)
2、不知道,见鬼了吧。
3、cprofile按时间排序看下调用前几的函数吧,里面大部分是库的初始化函数。当然还有很大一部分是我自己的检测部分。只展示时间排序靠前的(为了测试额外加了三个,所以是519)
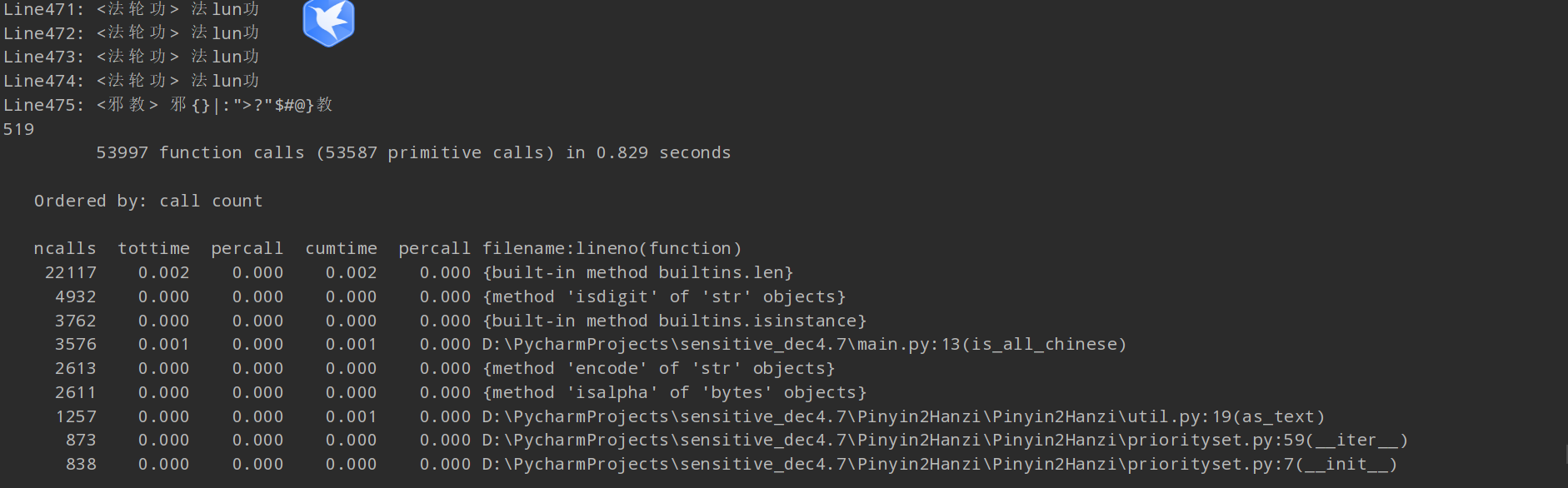
程序中消耗最大的函数(耗时与空间内存)无疑是DFA实现部分:
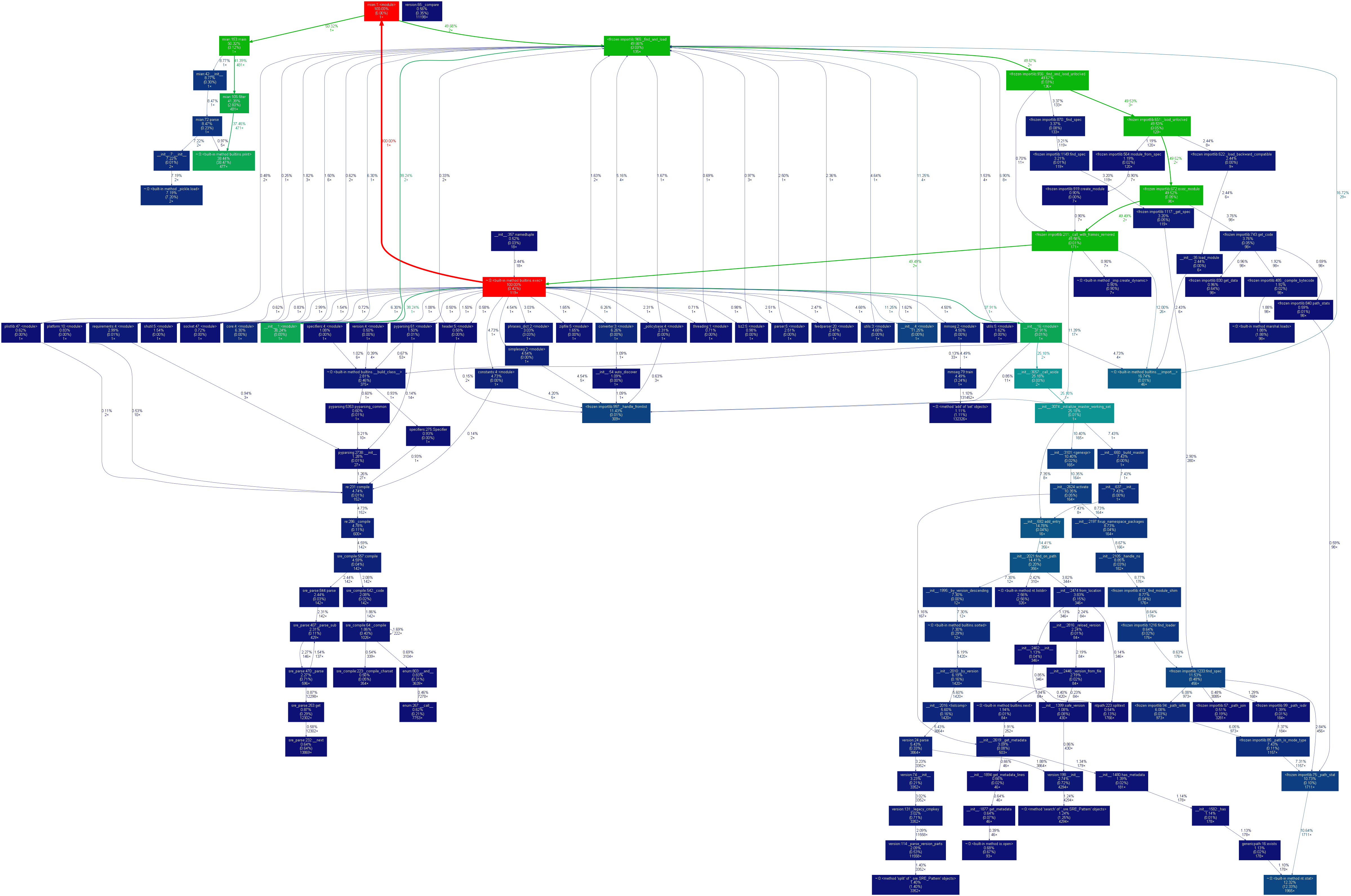
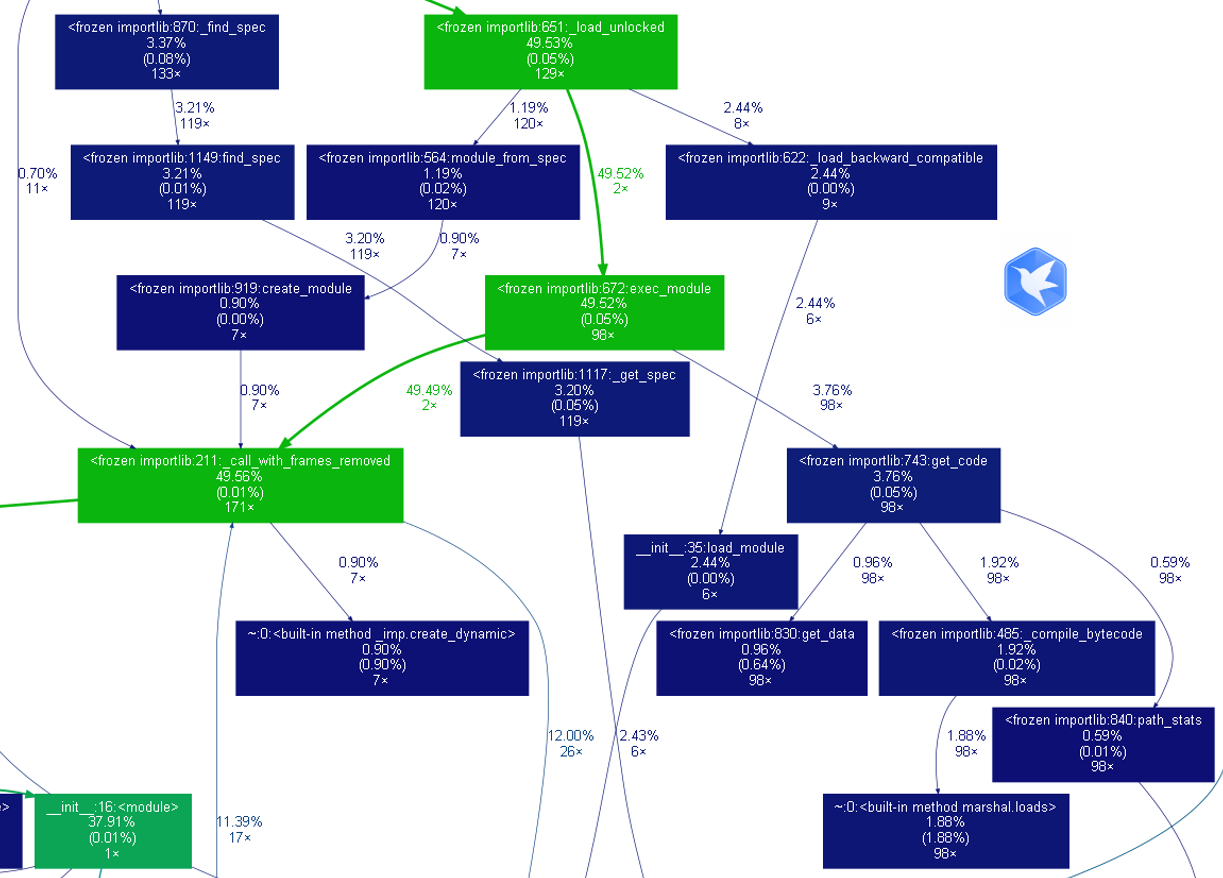
- 在拼音和部首的初始化上面废了很多时间,而且在我的能力范围内无能为力。。。。
- 最后一天改完 累死了。sensitive_dec7.0 516应该没错了。
4.计算模块部分异常处理说明
1.命令行异常处理:
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
print("参数错误,请以此给出敏感词文件,待检测文件和结果文件")
exit(-1)
args = sys.argv
main(args[1], args[2], args[3])
2.字典序更新过程之中,额外字典问考虑输出形式要求
# 根据关键字字典过滤出输入字符串message中的敏感词
def filter(self, message, linenumber):
rawmessage = message
message = message.lower()
start = 0
while start < len(message):
level = self.keyword_chains
# 当字符不在关键字字典时
if message[start] not in level:
start += 1
continue
if is_all_chinese(message[start]): mode = "c"
else: mode = "e"
step_ins = 0
sensitive_word = ""
left, right = start, 0
ok = False
for char in message[start:]:
if char.isdigit():
step_ins += 1
continue
if char not in level and mode == "c" and char.encode("utf-8").isalpha():
step_ins += 1
continue
# 特殊字符判断,当一个字符既不是中文又不是英文和数字时被认定为为特殊字符
if not is_all_chinese(char) and not char.encode("utf-8").isalpha()\
and not char.isdigit():
step_ins += 1
continue
# 新字在敏感词字典链表中
if char in level:
# sensitive_word += char
step_ins += 1
# 特定字符不在当前字的value值里,嵌套遍历下一个
if self.delimit not in level[char]:
level = level[char]
else:
start += step_ins - 1
right = start
ok = True
sensitive_word = level[char][self.delimit]
break
# 新字不在敏感词字典链表中
else: break
if ok:
anstr = "Line{}: <{}> {}\n".format(linenumber, sensitive_word, rawmessage[left: right + 1])
print(anstr, end="")
self.rp.write(anstr)
self.total += 1
start += 1
- 部分字典树展示
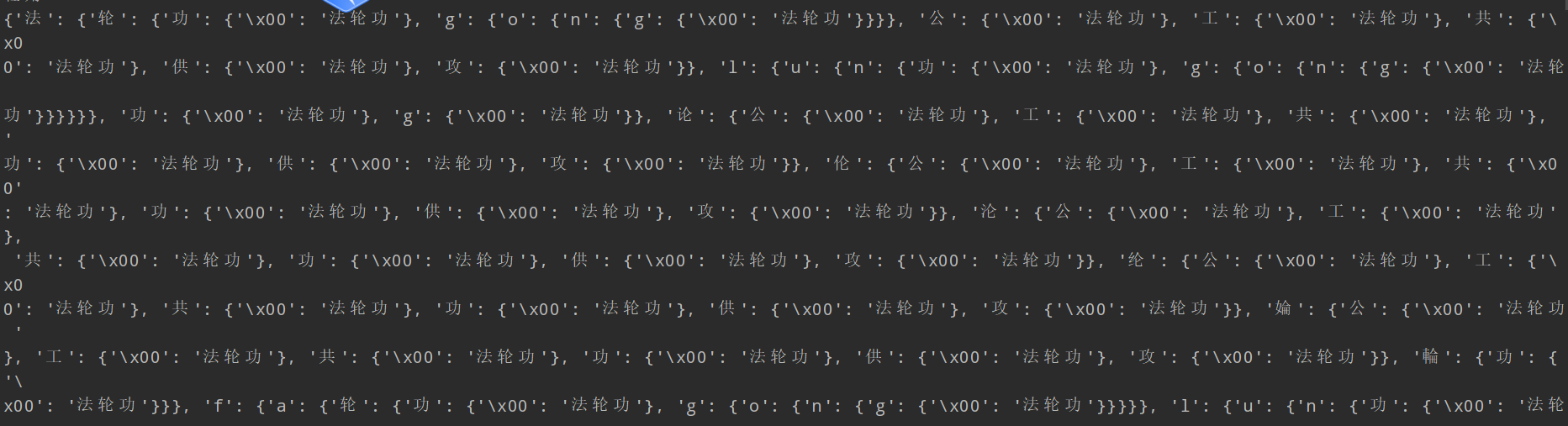
三、心得
1.一些小记录:
- 删掉输入文本的无关字符包括标点、空格、各种奇怪字符
- 把输入文本转化为拼音?用AC自动机的算法?(暂时不完成部首的解决问题)
- 部首和拼音都有现成的库,不过处理方式不同。
- 核心的难点在于复现,这一点真的很难!!!考虑到时间要求,必须动态处理
- DFA?
- 更新words.txt和ans.txt给我的体验极差,改来改去还不是一回事,为啥一开始不能弄好。
2.心得总结(平复一下怨气写了下)
- 突击学了python,总不能C++写吧!,没有很系统化,但能看出来,python在很多方面确实比C++方便得多。
- git指令学了好久,才传到GitHub上。
- cprofile生成性能图还要用可视化工具,弄了好久。应该多做好区块化,要做单元测试应该从一开始就设计好。
- 算法真的太难理解,费了好大的功夫,平常应该多花些时间在有意义的学习中,目前主流的人工智能机器学习研究生项目,对算法要求很高。
- 我心里只有感恩。