Spring深入浅出(二)IOC的单例 ,继承,依赖,JDBC,工厂模式以及自动装载
IOC的单例模式--Bean
Spring中的bean是根据scope来决定的。
scope有4种类型:
1.singleton:单例模型,表示通过Spring容器获取的该对象是唯一的。常用并且默认。
2.prototype:多例模型,表示通过Spring容器获取的对象都是不同的(类似于Java基础中new出来的对象地址是唯一的)。
3.reqeust:请求,表示在一次http请求内有效。
4.session:会话,表示在一个用户会话内有效。
1.创建一个对象
public class User { private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
2.在spring的l配置文件中将User的实例化。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="User1"></property> </bean> </beans>
3.测试类中通过Spring容器获取两个User实例化对象,并且通过==方法判断是否为同一个对象。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User u1 = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user"); User u2 = (User) applicationContext.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u1 == u2); } }
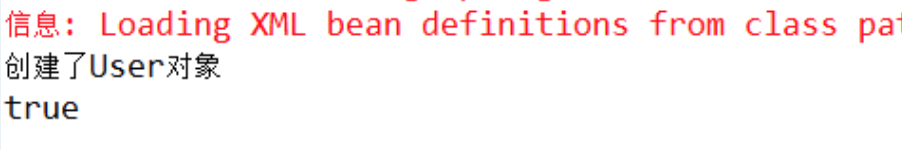
总结:看到结果打印true,表示user1和user2是同一个对象,所以scope默认值为singleton(单例模式),也就是用spring创建的对象是单例的。
改成多例模式的代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User" scope="prototype"> <property name="id" value="2"></property> <property name="name" value="User2"></property> </bean> </beans>
Spring的继承
Spring的继承,与Java的继承不一样,子bean和父bean的方法一样,子bean可以继承父bean中的属性。
如果子bean继承父bean,同时子bean给属性赋值,那么会覆盖掉父bean的值。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三1"></property> </bean> <bean id="user2" class="com.test.entity.User" parent="user"> <!-- 覆盖掉user的name属性值 --> <property name="name" value="张三2"></property> </bean>
</beans>
Spring的依赖
与继承类似,依赖也是bean和bean之间的一种关联方式,配置依赖关系后,被依赖的bean一定先创建,再创建依赖的bean。
使用的关键字是depends-on="被依赖的bean的id"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- user依赖于car --> <bean id="user" class="com.test.entity.User" depends-on="car"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> </bean> <bean id="car" class="com.test.entity.Car"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="brand" value="宝马"></property> </bean> </beans>
上述代码执行顺序是:car-->user。先创建car,再创建user
Spring读取外部资源。
在开发中,类似于数据库等文件的配置会保存在一个properties文件中,便于维护,因此使用Spring需要来读取数据源对象。
1.先创建一个peoperties文件在路径下,具体位置根据项目需求来放置。
##key==value的形式
driverName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shop user = root pwd = root
2.spring的配置文件中配置数据源,这里用到的是C3P0数据源。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 导入外部的资源文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder> <!-- 创建数据源 ,通过${}读取资源文件中的数据,${}中填写key,name中的值根据连接池的不同名字可能不同,尽量反编译代码去找一下对应的属性名--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="user" value="${user}"></property> <property name="password" value="${pwd}"></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${driverName}"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${url}"></property> </bean> </beans>
3.测试
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); DataSource ds = (DataSource) applicationContext.getBean("dataSource"); Connection conn = null; try { conn = ds.getConnection(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(conn); } }
IOC通过工厂方法创建对象
Spring中的IOC是典型的工厂模式,那么如何使用工厂模式来创建bean?
IOC通过工厂模式创建bean有两种方式:
1.静态工厂方法
2.实例工厂方法
静态工厂实例化
1.先创建一个实体类
2.创建静态工厂类,静态工厂方法。
3.编写Spring的配置文件
4.编写测试类
1 //步骤1:创建一个实体类 2 public class Car { 3 private int num; 4 private String brand; 5 public int getNum() { 6 return num; 7 } 8 public void setNum(int num) { 9 this.num = num; 10 } 11 public String getBrand() { 12 return brand; 13 } 14 public void setBrand(String brand) { 15 this.brand = brand; 16 } 17 public Car(int num, String brand) { 18 super(); 19 this.num = num; 20 this.brand = brand; 21 } 22 public Car() { 23 super(); 24 } 25 @Override 26 public String toString() { 27 return "Car [num=" + num + ", brand=" + brand + "]"; 28 } 29 }
//步骤2:创建一个静态类 public class StaticCarFactory { private static Map<Integer,Car> cars; //静态代码块 static{ cars = new HashMap<Integer,Car>(); cars.put(1, new Car(1,"奥迪")); cars.put(2, new Car(2,"宝马")); } //静态方法 public static Car getCar(int num){ return cars.get(id); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置静态工厂创建car对象 --> <!-- factory-method:指向静态方法 getCar() --> <bean id="car1" class="com.test.entity.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar"> <!-- value为要生成的哪个对象的key --> <constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
//步骤4:测试类 public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Car car = (Car) applicationContext.getBean("car1"); System.out.println(car); } }
![]()
实例工厂方法
1.创建实例工厂类,工厂方法 。
2.spring的配置文件中配置bean。
3.在测试类中直接获取car2对象。
//步骤1:创建实例工厂类 public class InstanceCarFactory { private Map<Integer,Car> cars; public InstanceCarFactory() { cars = new HashMap<Integer,Car>(); cars.put(1, new Car(1,"奥迪")); cars.put(2, new Car(2,"宝马")); } public Car getCar(int num){ return cars.get(num); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 配置实例工厂对象 --> <bean id="carFactory" class="com.test.entity.InstanceCarFactory"></bean> <!-- 通过实例工厂对象创建car对象 factory-bean:放置实例化的工厂对象bean的id,然后再设置factory-method:调用方法 --> <bean id="car2" factory-bean="carFactory" factory-method="getCar"> <constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
测试类与静态工程的方式一样,并且结果也是生成key为1的car对象。
总结
两种方式的区别:
(1)使用静态工厂方法的方式创建car对象,不需要实例化工厂对象,因为静态工厂的静态方法,不需要创建对象即可调用。所以spring的配置文件只需要配置一个Car的bean,而不需要配置工厂bean。
(2)使用实例工厂方法创建car对象,必须先实例化工厂对象,因为调用的是非静态方法,必须通过对象调用,不能直接通过类来调用,所以spring的配置文件中需要先配置工厂bean,再配置Car bean。
IOC的自动装载
Spring框架提供了一种更加简便的方式:自动装载,不需要手动配置property,IOC容器会根据bean的配置自动选择bean完成依赖注入(DI)。
自动装载有两种方式:
byName:通过属性名自动装载。
byType:通过属性对应的数据类型自动装载。
//先创建一个实体类,并且生成setter/getter方法和toString方法 public class Person { private int id; private String name; private Car car; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 创建person对象时,没有在property中配置car属性 所以IOC容器会自动进行装载 autowire="byName"表示通过匹配属性名的方式去装载对应的bean Person实体类中有car属性,所以就将的bean注入到person中。 --> <bean id="p1" class="com.test.entity.Person" autowire="byName"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="ZhangSan"></property> </bean> <bean id="car1" class="com.test.entity.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar"> <constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- byType即通过属性的数据类型来配置。 关键字:autowire="byType" --> <bean id="p2" class="com.test.entity.Person" autowire="byType"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> </bean> <bean id="car2" class="com.test.entity.StaticCarFactory" factory-method="getCar"> <constructor-arg value="1"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
注意:
(1)使用了byType进行自动装载,如果spring的配置文件中配置了两个Car的bean,但是IOC容器不知道应该将哪一个bean装载到person对象中,因此可能会报错。所以在使用byType进行自动装载时,spring的配置文件中只能配置一个Car的bean才能使用byType。
(2)通过property标签手动进行属性的注入优先级更高,若自动注入和手动配置两种方式同时存在,则以property的配置为主。
所以在日常的代码编写过程中,尽量避免的使用byType去自动装配。


