15. 3Sum[M]三数之和
题目
Given an array nums of n integers, are three elements a, b, c in nums such that a+b+c=0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
Note:
The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example:
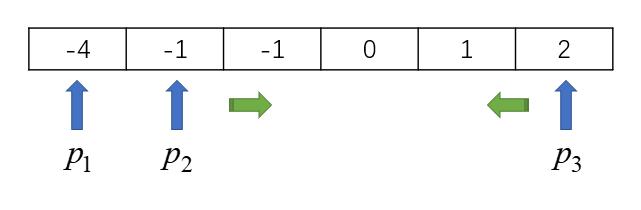
> Given array nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
A solution set is:
[[-1, 0, 1],[-1, -1, 2]]
思路
双指针法变种——三指针法(这里的指针指的是数组下标)
- 要保证三个数a+b+c=0;
- 至少要保证有一个数是0或者负数,
- 但是由于数组是乱序排列的,很难直接判断是否有0或负数,于是想到将数组排序
- 将等式改写为b+c = -a,如何找到
- 首先保证a是非正数(0或负数)
- 如何找到b和c使之与-a相等?
- 定义中间指针p2、尾指针p3,移动的方向为往中间移动
- 不能有重复结果
- 在最外层循环时,跳过已经判断过的数字
- p2、p3往中间移动时,跳过重复元素
于是
Step1:将数组排序
Step2:以第一个数p1作为最外层循环,其中如果第一个数如果为正,说明和不可能为0
Step3:定义中间指针p2,尾指针p3,
- 如果num[p2] + num[p3] > -nums[p1],则说明和太小了,应该往数值大的方向的移动,p2++
- 如果num[p2] + num[p3] < -nums[p1],则说明和太大了,应该往数值小的方向的移动,p3--
- 如果num[p2] + num[p3] = -nums[p1],将结果保存,同时将p2、p3往中间移动,为了保证结果的唯一性,需要跳过重复元素
Tips
列表方法(python)
方法是作用于Python中特定类型对象的函数。列表类型拥有9个只作用于列表的方法,分为两类
- 改变列表的方法
- 不改变列表的方法
以列表aList = [ 2, 1, 3, 'a', 4 ]为例(假设每个方法下的例子都是独立的,不会互相影响):
1. 不修改列表的方法
index(x)返回列表中与x值相等的第一个元素的索引。如果在列表中没有找到这样的元素,Python将报错。
aList.index(3) #输出2
count(x)返回列表中x出现的次数。如果列表中不包含x,返回0。
aList.count(1) #输出1
2. 修改列表的方法
append(x)在列表的末尾添加元素。列表长度增加1,如果append的参数时列表,则该列表(包括方括号)将作为单个元素加入列表中。
aList.append(5) #输出是[2, 1, 3, 'a', 4, 5]
aList.append([5, 6, 7]) #输出是[2, 1, 3, 'a', 4, [5, 6, 7] ]
pop()删除列表末尾的元素,并返回此元素。列表变短,少了一个元素。如果指定索引值,则array.pop(index)将删除该索引位置的元素并返回该项。
aList.pop() #输出4
extend(A)需要一个集合作为参数。将该集合中的每个元素添加到列表的末尾,从而扩展列表。
anotherList=[5, 6]
aList.extend(anotherList) #输出是[2, 1, 3, 'a', 4, 5, 6]
insert(index, x)在指定位置插入元素。第一个参数是元素插入前的索引。如果x是一个列表,则该列表(包括方括号)将作为单个元素加入列表中。
aList.insert(2, 'b') #输出是[2, 1, 'b', 3, 'a', 4]
remove(x)删除列表中第一个值为x的元素。如果没有该元素,将出错。
aList.remove(2) #输出是[1, 3, 'a', 4]
sort()将列表中的元素进行排序。与sorted函数比较,sorted返回排好序的列表,但是不改变原列表。如果要对列表的列表进行排序,则只考虑每个列表的首元素。
aList.sort() #输出是[1, 2, 3, 4, 'a']
reverse()将列表中的元素反向排列。
aList.reverse() #输出是['a', 4, 3, 2, 1]
C++
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int> > resVec;
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end()); //将nums从小到大排序
for(int p1=0;p1<nums.size();p1++){
if(nums[p1] >0) //如果第一个数为正数,说明肯定不存在三个数
return resVec;
if(p1>0 && nums[p1] == nums[p1-1]) //由于结果需要唯一性,故去除nums中的重复元素
continue;
int p2 = p1+1;//中间指针
int p3 = nums.size()-1;//尾指针
while(p2<p3){
int a = nums[p1];//非正
int b = nums[p2];
int c = nums[p3];
if(b+c== -a){
vector<int> tempVec(3);
tempVec[0] = a;
tempVec[1] = b;
tempVec[2] = c;
resVec.push_back(tempVec);
while (p2 < p3 && nums[p2] == nums[p2 + 1]) //去除重复元素
p2++;
while (p2 < p3 && nums[p3 - 1] == nums[p3]) //去除重复元素
p3--;
p2++;
p3--;
}
else if(b+c < -a){ //如果b+c之和小于-a,说明和太小了,应该往数值大的方向的移动
p2++;
}
else{ //反之,如果b+c之和大于-a,说明和太大了,应该往数值小的方向的移动
p3--;
}
}
}
return resVec;
}
Python
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
result = [ ]
for p1 in range(len(nums)):
if nums[p1] > 0:
return result
if p1 > 0 and nums[p1] == nums[p1-1]:
continue
p2 = p1 + 1
p3 = len(nums) - 1
while p2 < p3:
a = nums[p1]
b = nums[p2]
c = nums[p3]
if(b + c == -a):
result.append([a, b, c])
while p2 < p3 and nums[p2] == nums[p2+1]:
p2 += 1
while p2 < p3 and nums[p3-1] == nums[p3]:
p3 -= 1
p2 += 1
p3 -= 1
elif(b + c < -a):
p2 += 1
else:
p3 -= 1
return result
参考
[1] Python入门经典



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号