LeetCode:二叉树(三)
本组囊括二叉树中由前中后序中某两序来重新构造树的题目,难度均为中等。三题采取统一模板。
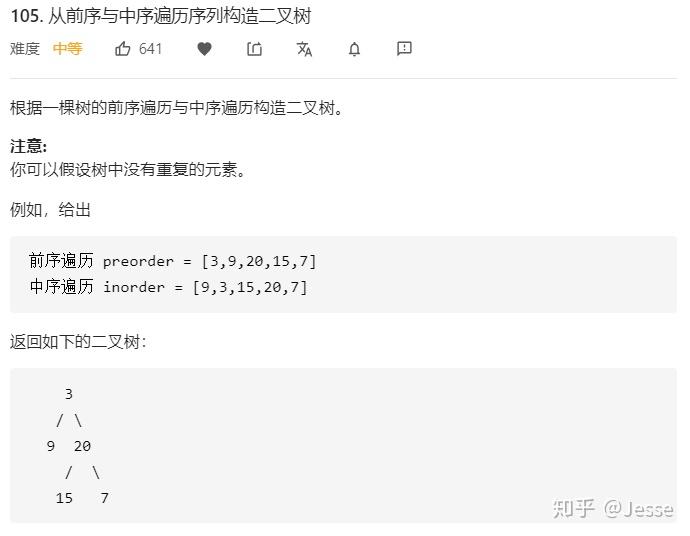
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
题目描述:中等
解法一:递归
递归的dfs想法很直接,就是通过相对位置来递归地构造左右子树。
dfs函数的参数分别当前树在给定的原树中前序和后序中的边界。
具体请参照代码注释:
1 class Solution: 2 def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode: 3 # 解法一:递归,递归地构造左子树右子树 4 def buildMyTree(preorder_left, preorder_right, inorder_left, inorder_right): 5 if preorder_left > preorder_right: # 必要的结束条件 6 return None 7 preorder_root = preorder_left # 定位根在前序中的位置,即为0 8 inorder_root = dic[preorder[preorder_root]] # 借助hashmap定位根在中序的位置 9 root = TreeNode(preorder[preorder_root]) # 先建以根节点展开的树 10 size_left_subtree = inorder_root - inorder_left # 计算左子树节点的数目:中序中根位置-中序左边界 11 # 开始递归地构造左子树,并与根节点相连 12 root.left = buildMyTree(preorder_left + 1, preorder_left + size_left_subtree, inorder_left, inorder_root - 1) # 左子树的四个边界,分别到原树的前序和中序中找位置,较好理解 13 # 开始递归地构造右子树,并与根节点相连 14 root.right = buildMyTree(preorder_left + size_left_subtree + 1, preorder_right, inorder_root + 1, inorder_right) # 右子树的四个边界 15 return root # 返回整棵树 16 17 n = len(preorder) # 一棵树的前序和中序长度是相同的,左右边界分别为0和n-1 18 dic = {element : i for i, element in enumerate(inorder)} # 构造哈希映射, 键为中序的值,值为中序的位置 19 return buildMyTree(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1) 20 # 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是树中的节点个数。 21 # 空间复杂度:O(n),除去返回的答案需要的 O(n) 空间之外,我们还需要使用 O(n) 的空间存储哈希映射,以及 O(h)(其中 h 是树的高度)的空间表示递归时栈空间。这里 h<n,所以总空间复杂度为 O(n)。
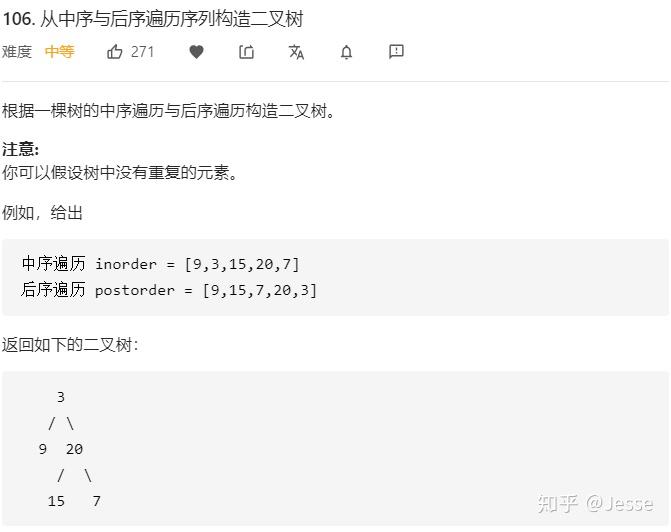
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
题目描述:中等
解法一:递归
简单地来说,这道题和上一题思路基本相同,边界的具体值稍微变一下就行。
具体请参照代码注释:
1 class Solution: 2 def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode: 3 # 解法一,递归,同上一题 4 # 具体看注释 5 def buildMyTree(inorder_left: int,inorder_right: int, postorder_left: int, postorder_right: int): 6 if inorder_left > inorder_right or postorder_left > postorder_right: 7 return None 8 postorder_root = postorder_right # 找到根在后序中的位置,即在右边界 9 inorder_root = dic[postorder[postorder_root]] # 找到根在中序的位置 10 root = TreeNode(postorder[postorder_root]) # 先建树 11 size_left_subtree = inorder_root - inorder_left # 计算左子树的节点数 12 root.left = buildMyTree(inorder_left, inorder_root - 1, postorder_left, postorder_left + size_left_subtree - 1) # 递归构建左子树 13 root.right = buildMyTree(inorder_root + 1, inorder_right, postorder_left + size_left_subtree, postorder_right - 1) # 递归构建右子树 14 return root 15 16 n = len(inorder) 17 dic = {element : i for i, element in enumerate(inorder)} # 构建哈希映射,中序的 18 return buildMyTree(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1) 19 # 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是树中的节点个数。 20 # 空间复杂度:O(n),除去返回的答案需要的 O(n) 空间之外,我们还需要使用 O(n) 的空间存储哈希映射,以及 O(h)(其中 h 是树的高度)的空间表示递归时栈空间。这里 h<n,所以总空间复杂度为 O(n)。
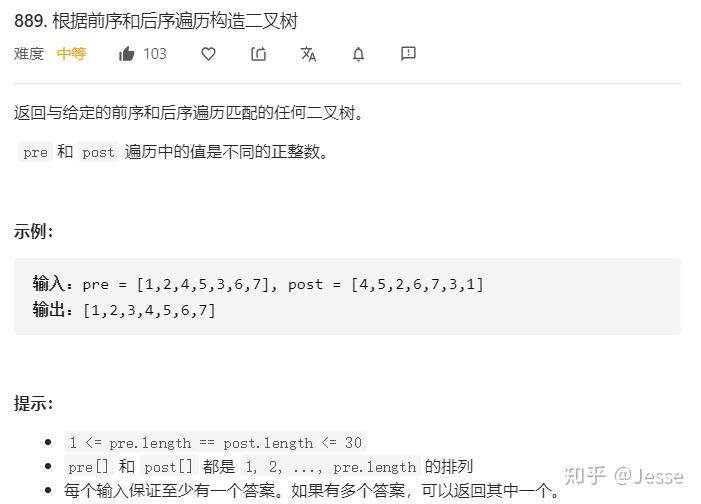
889. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal
题目描述:中等
解法一:递归
基本也同上两道题,但这道题稍微麻烦些:重点是要找出左子树结束的位置;
前序中第二个位置的节点,即是左子树的根节点,通过这个根节点找到后序中这个节点的位置,这个即是后序中左子树的结束位置。
具体请参照代码注释:
1 class Solution: 2 def constructFromPrePost(self, pre: List[int], post: List[int]) -> TreeNode: 3 # 解法一: 递归 4 # 前序中第二个位置的节点,即是左子树的根节点,通过这个根节点找到后序中这个节点的位置,这个即是后序中左子树的结束位置。 5 def buildMyTree(pre_left, pre_right, post_left, post_right): 6 if pre_left > pre_right or post_left > post_right: 7 return None 8 pre_root = pre_left # 确定根在前序的位置 9 root = TreeNode(pre[pre_root]) # 建树 10 if pre_left == pre_right: # 记住这一行,不然数组会越界 11 return root 12 index = dic[pre[pre_left + 1]] # 左子树在后序的结束位置 13 # 通过这个index可以计算出左子树的节点数目 14 siz_left_subtree = index - post_left 15 # 开始递归构建左右子树 16 root.left = buildMyTree(pre_left + 1, pre_left + 1 + siz_left_subtree, post_left, index) 17 root.right = buildMyTree(pre_left + 1 + siz_left_subtree + 1, pre_right, index + 1, post_right - 1) # 边界一定要准确 18 return root 19 20 n = len(post) 21 dic = {element : i for i, element in enumerate(post)} # 后序的哈希映射 22 return buildMyTree(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1) 23 # 时间复杂度:O(N),N是树的节点数 24 # 空间复杂度:O(N),N用来存储返回的结果,N用来构造hashmap,h为递归栈的高度。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号