Python数据结构之字节,字节数组
1、bytes、bytearray
---Python3 引入的!
bytes:不可变字节序列,bytearray:字节属组,可变
都是连续的空间。
2、字符串与bytes
字符串是字符组成的有序的序列,字符可以使用编码来理解
bytes 是戒子组成的有序的不可变序列
bytearray 是戒子组成的有序的可变序列
3、编码、解码
字符串按照不同的字符集编码encode返回字节序列bytes
encode(encoding = ‘utf-8', errors = 'strict') ---> bytes
1 1 In [139]: 'abd'.encode() # 默认是utf-8 2 2 Out[139]: b'abd' # 应该是数字,但是为了让人看,所以显示成这样,所以前面有一个b
字节序列按照不同的字符集解码decode返回字符串、
bytes.decode(encoding='utf-8' , errors= 'strict' ) ---> str
bytearray.decode(encoding= 'utf-8',errors = 'strict') ---> str
1 In [140]: print(b'abd') 2 b'abd' 3 4 In [141]: _.decode() # _ 表示上次的结果 5 Out[141]: 'abd'
ASCII:American Standard Code for Information
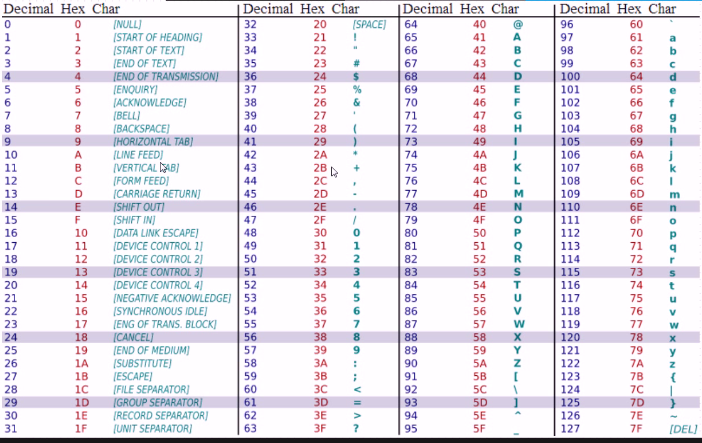
3、bytes定义:
定义:
bytes()空bytes
bytes(int)指定字节的bytes,被0 填充(0是ASCII 0)
In [142]: bytes(5) Out[142]: b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
bytes(iterable_of_ints) --> bytes [0-255]的int组成的可迭代对象
bytes(string, encoding[, errors]) ---> bytes等价于string,encode()
bytes(bytes_or_buffer) ---> immutable copy of bytes_or_buffer 从一个字节序列或buffer中复制一个新的不可变的bytes对象。
使用b 前缀定义:
只允许基本的ASCII使用字符形式b'abc9'
使用16进制表示b"\x41\x61" 字符串就用 \x41 数字 0x61

1 In [158]: a = bytes(7) # 定义一个字节长度,用ASCII的十六进制的0填充 2 3 In [160]: a 4 Out[160]: b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00' 5 6 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 7 8 In [161]: c = bytes(range(10)) # 创建一个字节类型,从0-9 9 10 In [162]: c 11 Out[162]: b'\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06\x07\x08\t'# python为了让人看懂,所以显示如上所示,如:x09 对ASCII中的 \t, 而其他的对应的字符无法表示,所以以源字节码显示。 12 13 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 14 15 In [163]: d = bytes('efg',encoding='utf-8') #这样用很少,一般都是string.encoding()---默认是utf-8编码 16 17 In [164]: d 18 Out[164]: b'efg' 19 20 In [165]: e = bytes(d) 相当于copy了一份 21 22 In [166]: e 23 Out[166]: b'efg'
bytes操作:
和 str 类型类似,都是不可变,所以方法很多都一样,只不过bytes方法,输入是bytes,输出是bytes
b'abcdef'.replace(b'f', b'k')
b'abc'.find(b'b')
类方法 bytes,formhex(string)
string 必须是2个字符的16进制的形式,'1662 6a 6b' ,空格将被忽略!
1 In [172]: bytes.fromhex('616263 09 6a 6b00') 2 Out[172]: b'abc\tjk\x00' # 忽略空格,00没法显示,所以用\x00表示
索引:b'abcde'[2] 返回该字节对应的数,int类型
1 In [173]: b'abcde'[2] 2 Out[173]: 99 3 4 In [174]: 'abc'.encode() 5 Out[174]: b'abc' 6 7 In [175]: 'abc'.encode()[1] 8 Out[175]: 98
4、bytearray定义
定义:
bytearray() 空bytearray
bytearray(int) 指定字节的bytearray ,被0 填充
bytearray(iterable_of_ints) --> bytearray [0,255] de int 组成的可迭代对象
bytearray(string, encoding[, errors]) ---> bytearray 近似string.encode(),(但是这个是返回的字节类型),返回可变对象
bytearray( bytes_or_buffer) 从一个字节序列或buffer复制出一个新的可变的bytearray对象
注: b前缀定义的类型是bytes类型
操作:
和bytes类型的方法相同:
bytearray(b'abcd').replace(b'f',b'k')
bytearrya(b'abc').find(b'b')
类方法bytearray.fromhex(string)
sting 必须是2个字符的16进制的形式,'6162 6a6vb' ,空格将被忽略!
In [176]: bytearray.fromhex('6261 6a') Out[176]: bytearray(b'baj')
hex():返回16进制表示的字符串
1 In [177]: bytearray('abc'.encode()).hex() 2 Out[177]: '616263'
索引:bytearray(b'abcdeff')[2] 返回该字节对应的数,int类型
其他操作:

1 In [205]: a 2 Out[205]: bytearray(b'asdfa') 3 4 In [206]: a.append(0x61) 5 6 In [207]: a.append(91) 7 8 In [208]: a 9 Out[208]: bytearray(b'asdfaa[') 10 11 In [209]: a.insert(0,91) 12 13 In [210]: a 14 Out[210]: bytearray(b'[asdfaa[') 15 16 In [211]: a.extend(range(2)) 17 18 In [212]: a 19 Out[212]: bytearray(b'[asdfaa[\x00\x01') 20 21 In [213]: a.pop() 22 Out[213]: 1 23 24 In [214]: a 25 Out[214]: bytearray(b'[asdfaa[\x00') 26 27 In [217]: a.remove(97) 28 29 In [218]: a 30 Out[218]: bytearray(b'[sdfaa[\x00') 31 32 In [220]: a.reverse() 33 34 In [221]: a 35 Out[221]: bytearray(b'\x00[aafds[') 36 37 In [222]: a.clear 38 Out[222]: <function bytearray.clear()> 39 40 In [223]: a.clear() 41 42 In [224]: a 43 Out[224]: bytearray(b'')
注:上述方法使用int,且在【0-255】 之间
5、int 和 bytes
int,from_bytes( bytes,byteordes)
将一个字节数组表示成整数
int.to_bytes(length, byteorder)
byteorder 字节序
将一个整数表示成一个指定长度的字节数组
str-----> bytes ---> int:
1 In [227]: i = int.from_bytes(b'abc','big') 2 3 In [228]: i 4 Out[228]: 6382179 5 6 In [229]: hex(i) 7 Out[229]: '0x616263' 8 9 10 In [231]: i.to_bytes(3,'big') # 数字只能大于等于长度,否则报错 11 Out[231]: b'abc' 12 13 In [232]: i.to_bytes(5,'big') # 大于就补0 14 Out[232]: b'\x00\x00abc'
大端模式,小端模式:
mac:大端模式
network:大端模式
Windows:小端模式
字节序:b'\x61\x62' 61应该放在高地址,还是低地址,如果低字节放在高地址,就是大端模式,即 big




