Week 7 - 714. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Transaction Fee & 718. Maximum Length of Repeated Subarray
714. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock with Transaction Fee - Medium
Your are given an array of integers prices, for which the i-th element is the price of a given stock on day i; and a non-negative integer fee representing a transaction fee.
You may complete as many transactions as you like, but you need to pay the transaction fee for each transaction. You may not buy more than 1 share of a stock at a time (ie. you must sell the stock share before you buy again.)
Return the maximum profit you can make.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [1, 3, 2, 8, 4, 9], fee = 2
Output: 8
Explanation: The maximum profit can be achieved by:
Buying at prices[0] = 1
Selling at prices[3] = 8
Buying at prices[4] = 4
Selling at prices[5] = 9
The total profit is ((8 - 1) - 2) + ((9 - 4) - 2) = 8.
Note:
-
0 < prices.length <= 50000. -
0 < prices[i] < 50000. -
0 <= fee < 50000.
My Solution:
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices, int fee) {
int p1 = 0, p2 = INT32_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.size(); i++) {
int temp = p1;
p1 = max(p1, p2 + prices[i]);
p2 = max(p2, temp - prices[i] - fee);
}
return p1;
}
int max(int i, int j) {
if (i >= j) return i; else return j;
}
};
这道题主要的思想是动态规划,难点在于如何想到用两个状态来进行迭代。用一次循环扫整个价格数组,用p1记录无库存状态下的利润,p2记录有库存状态下的利润,当买入时更新p2,卖出时更新p1。
718. Maximum Length of Repeated Subarray - Medium
Given two integer arrays A and B, return the maximum length of an subarray that appears in both arrays.
Example 1:
Input:
A: [1,2,3,2,1]
B: [3,2,1,4,7]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The repeated subarray with maximum length is [3, 2, 1].
Note:
- 1 <= len(A), len(B) <= 1000
- 0 <= A[i], B[i] < 100
my solution:
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int findLength(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) {
vector<int> D(B.size()+1, 0);
vector<vector<int>> C(A.size() + 1, D);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < B.size(); j++) {
if (A[i] == B[j]) {
C[i + 1][j + 1] = C[i][j] + 1;
}
if (C[i + 1][j + 1] > res) res = C[i + 1][j + 1];
}
}
return res;
}
};
考虑这样一个表格:
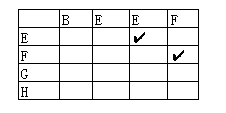
如果两个字符串中有一个子串相同,那么在这个表格中,这个子串就会以斜线的方式显示。利用这个性质对子串的长度计数,就可以得到这道题的动态规划解。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号