在Visual Studio 2010[VC++]中使用ffmpeg类库
1,准备工作
很多播放器都使用了ffmpeg这个类库来编解码,使用没有关系,但总是有些人不守规则。在耻辱榜上我看到了腾讯(QQPlayer),还有另一家深圳的公司。
我对GPL协议也不太了解,issue tracker中显示QQPlayer需要提供完整项目代码。我的疑问是:
如果是QQPlayer。其中集成了QQ的一些登陆模块,但这些代码不方便公开。但Player相关的代码已经公开。这样违反GPL吗?
NOTE:下文中DLL或LIB(大写指文件即avcodec.dll,avcodec.lib.etc.),dll或lib(小写,指目录)。
继上篇在MinGW中编译ffmpeg之后,我们便可以得到一些LIB和DLL,我们可以使用这些LIB和DLL来使用ffmpeg的相关功能函数。
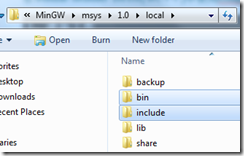
其中头文件在include目录下,LIB及DLL在bin目录下。其实这些LIB并不是传统的静态库文件(真正的静态库文件是在lib目录下的*.a文件),他们是dll的导出文件。
另外,C99中添加了几个新的头文件,VC++中没有,所以需要你自己下载。并放至相应目录。对于VS2010来说通常是:C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\VC\include。
2,示例代码
网上的ffmpeg的示例代码大多过时了,在2009年初img_convert这个函数被sws_scale取代了,所以可能你从网上找到的示例代码并不可以运行(但代码运作原理还是一样的)。
我这里贴出一份当前可以运行的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 | // ffmpeg-example.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.//#include "stdafx.h"#define inline _inline#ifndef INT64_C#define INT64_C(c) (c ## LL)#define UINT64_C(c) (c ## ULL)#endif#ifdef __cplusplusextern "C" {#endif /*Include ffmpeg header file*/#include <libavformat/avformat.h>#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>#include <libswscale/swscale.h>#ifdef __cplusplus}#endif#include <stdio.h>static void SaveFrame(AVFrame *pFrame, int width, int height, int iFrame);int main (int argc, const char * argv[]){ AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx; int i, videoStream; AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx; AVCodec *pCodec; AVFrame *pFrame; AVFrame *pFrameRGB; AVPacket packet; int frameFinished; int numBytes; uint8_t *buffer; // Register all formats and codecs av_register_all(); // Open video file if(av_open_input_file(&pFormatCtx, argv[1], NULL, 0, NULL)!=0) return -1; // Couldn't open file // Retrieve stream information if(av_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx)<0) return -1; // Couldn't find stream information // Dump information about file onto standard error dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, argv[1], false); // Find the first video stream videoStream=-1; for(i=0; i<pFormatCtx->nb_streams; i++) if(pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type==CODEC_TYPE_VIDEO) { videoStream=i; break; } if(videoStream==-1) return -1; // Didn't find a video stream // Get a pointer to the codec context for the video stream pCodecCtx=pFormatCtx->streams[videoStream]->codec; // Find the decoder for the video stream pCodec=avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id); if(pCodec==NULL) return -1; // Codec not found // Open codec if(avcodec_open(pCodecCtx, pCodec)<0) return -1; // Could not open codec // Hack to correct wrong frame rates that seem to be generated by some codecs if(pCodecCtx->time_base.num>1000 && pCodecCtx->time_base.den==1) pCodecCtx->time_base.den=1000; // Allocate video frame pFrame=avcodec_alloc_frame(); // Allocate an AVFrame structure pFrameRGB=avcodec_alloc_frame(); if(pFrameRGB==NULL) return -1; // Determine required buffer size and allocate buffer numBytes=avpicture_get_size(PIX_FMT_RGB24, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); //buffer=malloc(numBytes); buffer=(uint8_t *)av_malloc(numBytes*sizeof(uint8_t)); // Assign appropriate parts of buffer to image planes in pFrameRGB avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)pFrameRGB, buffer, PIX_FMT_RGB24, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); // Read frames and save first five frames to disk i=0; while(av_read_frame(pFormatCtx, &packet)>=0) { // Is this a packet from the video stream? if(packet.stream_index==videoStream) { // Decode video frame avcodec_decode_video(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &frameFinished, packet.data, packet.size); // Did we get a video frame? if(frameFinished) { static struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx;#if 0 // Older removed code // Convert the image from its native format to RGB swscale img_convert((AVPicture *)pFrameRGB, PIX_FMT_RGB24, (AVPicture*)pFrame, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); // function template, for reference int sws_scale(struct SwsContext *context, uint8_t* src[], int srcStride[], int srcSliceY, int srcSliceH, uint8_t* dst[], int dstStride[]);#endif // Convert the image into YUV format that SDL uses if(img_convert_ctx == NULL) { int w = pCodecCtx->width; int h = pCodecCtx->height; img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(w, h, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, w, h, PIX_FMT_RGB24, SWS_BICUBIC, NULL, NULL, NULL); if(img_convert_ctx == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Cannot initialize the conversion context!\n"); exit(1); } } int ret = sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height, pFrameRGB->data, pFrameRGB->linesize);#if 0 // this use to be true, as of 1/2009, but apparently it is no longer true in 3/2009 if(ret) { fprintf(stderr, "SWS_Scale failed [%d]!\n", ret); exit(-1); }#endif // Save the frame to disk if(i++<=5) SaveFrame(pFrameRGB, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, i); } } // Free the packet that was allocated by av_read_frame av_free_packet(&packet); } // Free the RGB image //free(buffer); av_free(buffer); av_free(pFrameRGB); // Free the YUV frame av_free(pFrame); // Close the codec avcodec_close(pCodecCtx); // Close the video file av_close_input_file(pFormatCtx); return 0;}static void SaveFrame(AVFrame *pFrame, int width, int height, int iFrame){ FILE *pFile; char szFilename[32]; int y; // Open file sprintf(szFilename, "frame%d.ppm", iFrame); pFile=fopen(szFilename, "wb"); if(pFile==NULL) return; // Write header fprintf(pFile, "P6\n%d %d\n255\n", width, height); // Write pixel data for(y=0; y<height; y++) fwrite(pFrame->data[0]+y*pFrame->linesize[0], 1, width*3, pFile); // Close file fclose(pFile);} |
显示代码中有几个地方需要注意一下。就是开头的宏定义部分。第一个是C99中添加了inline关键字,第二个是对ffmpeg头文件中INT64_C的模拟(可能也是为了解决与C99的兼容问题)。第三个是使用extern C在C++代码中使用C的头文件。
3,设置Visual Studio
在你编译,调用上面的代码之前你还要在Visual Stuido中做相应的设置,才可以正确引用ffmpeg的库。
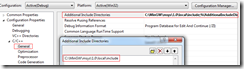
3.1 设置ffmpeg头文件位置
右击项目->属性,添加Include文件目录位置:
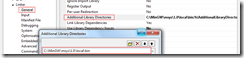
3.2 设置LIB文件位置
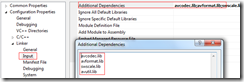
3.3 设置所引用的LIB文件
如果一切正常,这时你便可以编译成功。
4,可能出现的问题
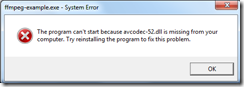
4.1 运行时出错
虽然你可以成功编译,但你F5,调试时会出现以下错误。
原因是,你虽然引用了LIB文件,但这并不是真正的静态库文件,而是对DLL的引用,所以当你调用ffmpeg库函数时,需要DLL文件在场。你可以用dumpbin(VS自带工具)来查看你生成的exe中引用了哪些DLL文件。你在命令行输入:
>dumpbin ffmpeg-example.exe /imports
你可以从输出中看出你实际引用以下几个的DLL文件。
avcodec-52.dll
avformat-52.dll
swscale-0.dll
avutil-50.dll
还有些朋友可能想将ffmpeg库进行静态引用,这样就不需要这些DLL文件了。这样做是可行的,但是不推荐的。
4.2 av_open_input_file失败
在VS的Command Argumetns中使用全路径。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库