六、 面向对象基础
java面向对象
面向对象思想:
1.设计类,并设计类的成员(成员变量&成员方法);
2.通过类,来创建类的对象(也称作类的实例化);
3.通过“对象.属性” 或“对象.方法”来调用,完成相应的功能;
如何定义一个人的类,对其进行属性方法的操作。
package day006; /* * 1.面向对象的编程关注于类的设计 * 2.设计类实际上就是设计类的成员 * 3.基本的类的成员:属性(成员变量或Field) & 方法(Method) */ public class personClass { public static void main(String[] args) { // 实例化一个人 person man = new person(); man.name = "jeff"; man.age = 111; man.sex = true; man.info(); man.setName("frank"); man.info(); } } //设计一个人的类 class person{ //1.属性 String name; int age; boolean sex; //2.方法 public void eat(){ System.out.println("eat some food"); } public void sleep(){ System.out.println("sleep"); } public void setName(String n){ name = n; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void info(){ System.out.println(name+"\tis\t"+age+"\tand\t"+sex); } }
创建的多个对象,彼此各自拥有一套类的属性。当对其中一个对象的属性进行修改时,* 不会影响到其他对象的属性值。
对象在内存空间的存储:
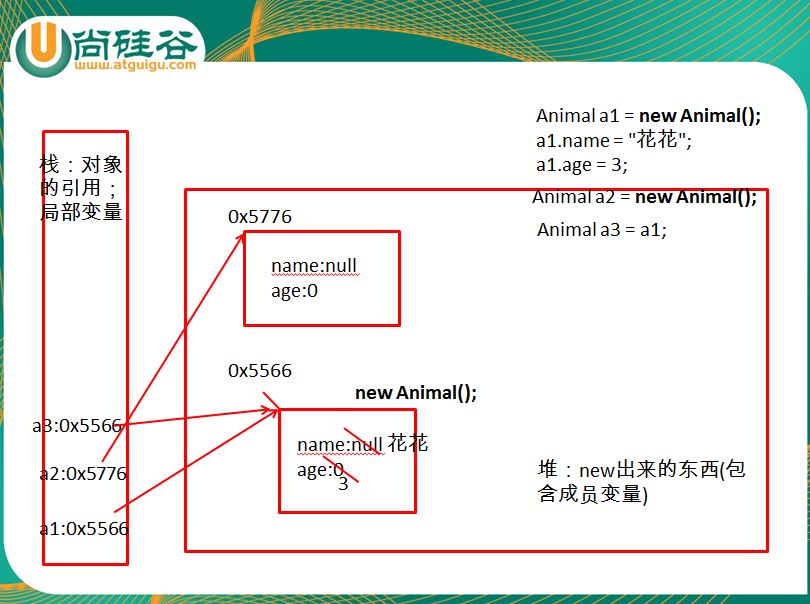
所以不同的对象的属性值并不是同一个,a1和a2只是修改相同属性互不影响,但是a3与a1实际上指向同一个堆中的内存,也就是指向了相同的属性,所以改变相同属性会导致互相影响。
下面的例子可以证明出结果:
package day006; public class zoo { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //基本数据类型的声明:数据类型 变量名 = 初始化值 int i = 10; //类的实例化:如下的a1就是一个实实在在的对象 animal a1 = new animal(); //int[] arr = new int[10]; System.out.println("name:" + a1.name + " age:" + a1.age); //通过对象调用属性 a1.name = "花花"; a1.age = 3; System.out.println("name:" + a1.name + " age:" + a1.age); //通过对象调用方法 a1.eat(); a1.sleep(); //再创建一个类的对象 animal a2 = new animal(); System.out.println("name:" + a2.name + " age:" + a2.age);//null 0 a2.name = "小花"; System.out.println("name:" + a1.name + " age:" + a1.age); System.out.println("name:" + a2.name + " age:" + a2.age); //a3不意味着相较于a1重新创建的一个对象,而是a1与a3共用一个对象实体 animal a3 = a1; System.out.println("name:" + a3.name + " age:" + a3.age);//与a1一样 a3.name = "维尼熊"; System.out.println("a1:name:" + a1.name + " age:" + a1.age); System.out.println(a2.getName());//a2.name; System.out.println(a2.desc()); } } class animal{ //1.属性 String name; int age; //2.方法 public void eat(){ System.out.println("动物进食"); } public void sleep(){ System.out.println("动物休眠"); //return; } public String getName(){ return name; } public int getAge(){ System.out.println("hello"); return age; //其后不可以声明语句 //System.out.println("hello"); } //当通过对象调用此方法时,会将方法的方法的返回值提供给方法的调用者,也就是当前的对象。 public String desc(){ if(age > 2){ return "恰同学少年"; }else{ return "还是看动画片的年龄"; } } public void setName(String n){//n:局部变量 name = n; } public void addAge(){ int i = 0;//局部变量 age += i; } public void info(){ // 可以在方法内调用本类的其他方法,但是不可以在方法内定义新的方法 eat(); sleep(); // public void breath(){ // System.out.println("呼吸"); // } } }
定义在方法里面的叫做局部变量。
成员变量与局部变量的对比
相同点:1.遵循变量声明的格式: 数据类型 变量名 = 初始化值;
2.都有作用域
不同点:1.声明的位置的不同 :成员变量:声明在类里,方法外,局部变量:声明在方法内,方法的形参部分,代码块内。
2.成员变量的修饰符有四个:public private protected 缺省;局部变量没有修饰符,与所在的方法修饰符相同。
3.初始化值:一定会有初始化值。
成员变量:如果在声明的时候,不显式的赋值,那么不同数据类型会有不同的默认初始化值。
byte short int long ==>0
float double ==>0.0
char ==>空格
boolean ==>false
引用类型变量==>null
局部变量:一定要显式的赋值。(局部变量没有默认初始化值)
4.二者在内存中存放的位置不同:成员变量存在于堆空间中;局部变量:栈空间中
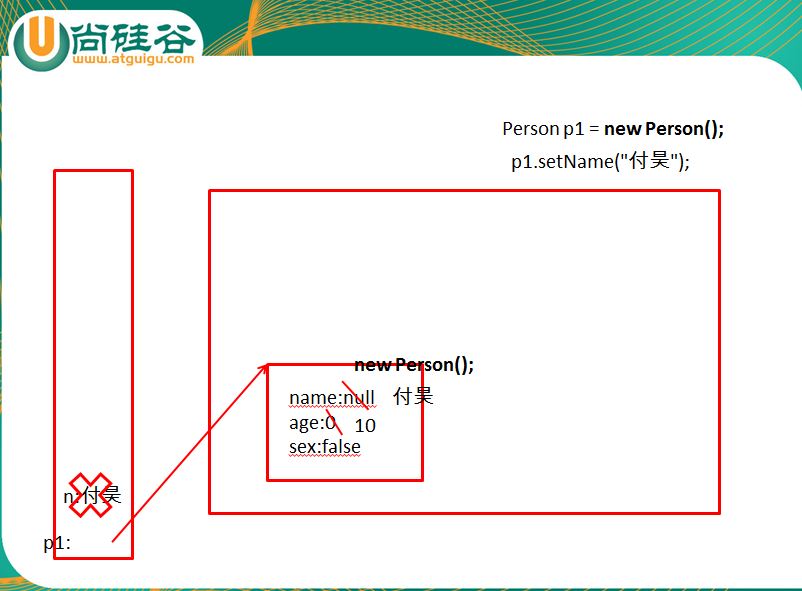
局部变量n赋给成员变量name后就结束了。
类的方法:
实例方式:
实例:public void eat(){//方法体}
public String getName(){}
public void setName(String n){}
关于返回值类型:void:表明此方法不需要返回值
有返回值的方法:在方法的最后一定有return + 返回值类型对应的变量
方法内可以调用本类的其他方法或属性,但是不能在方法内再定义方法!
练习写一个求圆面积的类

//利用面向对象的编程方法,设计类Circle计算圆的面积。 public class TestCircle { public static void main(String[] args) { Circle c1 = new Circle(); c1.radius = 2.3; //c1.findArea(); double area = c1.findArea(); System.out.println(area); c1.setRadius(4.5);//c1.radius = 4.5; System.out.println(c1.findArea()); } } class Circle{ double radius = 1.0;//半径 //提供方法,用于获取圆的面积 // public void findArea(){ // //此处的radius为调用findArea()方法的对象的属性radius // System.out.println(3.14 * radius * radius); // } public double findArea(){ return 3.14 * radius * radius; } //返回圆的半径 public double getRadius(){ return radius; } //设置圆的半径 public void setRadius(double r){ radius = r; } }

package day006; public class array_util { public int getMax(int[] arr){ int max = arr[0]; for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(max < arr[i]){ max = arr[i]; } } return max; } public int getMin(int[] arr){ int min = arr[0]; for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(min > arr[i]){ min = arr[i]; } } return min; } public int getSum(int[] arr){ int sum = 0; for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){ sum +=arr[i]; } return sum; } public int getAvg(int[] arr){ int sum = getSum(arr); return sum/arr.length; } public int[] getReverse(int[] arr){//返回的类型也要是数组 for(int i=0,j=arr.length-1;i<j;i++,j--){ int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } return arr; } // 实现数组的复制 public int[] copy(int[] arr) { // int[] arr1 = arr; // return arr1; int[] arr1 = new int[arr.length]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr1[i] = arr[i]; } return arr1; } // 对数组进行排序 public void sort(int[] arr, String desc) { if (desc == "asc") {// ascend:从小到大 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { swap(arr,j,j+1); //swap(arr[j],arr[j + 1]); } } } } else if (desc == "desc") {// 从大到小 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[j + 1]) { swap(arr,j,j+1); //swap(arr[j],arr[j + 1]); } } } } else { System.out.println("您输入的排序方式有误!"); } } //交换数组中指定位置的元素:交换arr数组中索引为i和j的两个元素 public void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){ int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } }

package day006; public class array_method { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] arr = new int[]{2, -2, 78, -18, 23, 3,10,-2}; array_util au = new array_util(); int max = au.getMax(arr); System.out.println("最大值为:" + max); int min = au.getMin(arr); int sum = au.getSum(arr); System.out.println("和为:" + sum); int[] reverse = au.getReverse(arr); System.out.println("倒序为:" ); for(int i=0;i<reverse.length;i++){ System.out.print(arr[i]+"\t"); } } }
对于我们刚才使用的类,只有当输入的数组为int类型的时候才可以正常使用,所以要适用于各种类型,那么要使用到方法的重载。
重载要求:1.同一个类中 2.方法名必须相同 3.方法的参数列表不同(参数的个数不同,参数类型不同,参数顺序不同)4.与是否有返回值或返回值类型无关。

package day006; public class reload_method { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 4; int j = 8; int k = 6; overload ol = new overload(); int sum = ol.getsum(i, j);//12 System.out.println(sum); int sum1 = ol.getsum(i, j, k); System.out.println(sum1);//18 } } class overload{ public int getsum(int a, int b){ return a+b; } public int getsum(int a, int b, int c){ return a+b+c; } public double getsum(double d1,double d2){ return d1 + d2; } //以下的两个方法构成重载。 public void method1(int i,String str){ } public void method1(String str1,int j){ } }

package day006; public class car_factory { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub factory f= new factory(); car newCar = f.producerCar(); newCar.info(); car newCar1 = f.producerCar("卡车",8); newCar1.info(); } } //先定义一个车子类 class car{ String name; int wheel; public void info(){ System.out.println("name:" + name + " wheel:" + wheel); } } //定义一个工厂类 class factory{ public car producerCar(){ return new car(); } //重载一个生产汽车方法 public car producerCar(String n,int w){ car c = new car(); c.name=n; c.wheel = w; return c; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号