JAVA框架-Spring04(事务处理)
在日常开发中,数据访问层(DAO)必然需要进行事务的处理,但是我们会发现,事务处理的代码通常是简单的重复的,编写这样的重复代码会浪费大量的时间,所以我们需要找到一种方案可以将这些重复的代码进行抽取,以便与管理维护和复用,
我们的需求:在一系列数据库操作上的方法上增加额外的事务处理代码,让原来的方法中只关注具体的数据处理,即在原本以及存在的数据库操作方法上添加额外的事务处理逻辑
到这里你应该想到AOP了,没错! 这样的场景下AOP是最好的解决方案;
回顾一下Spring的AOP:在结合目前的需求
-
将目标对象(DAO)放入Spring容器
-
告知Spring你的通知代码是什么(事务处理)
-
告知Spring 哪些方法(DAO的CRUD)要应用那些通知(不同的事务处理代码)
-
从Spring中获取代理对象来完成原本的CRUD,代理对象会自动完成事务处理
Spring事务处理API
Spring作为框架,需要进行详细的设计,全方位的考虑事务处理的各个方面,而不仅是简单的帮你执行commit,rollback;
Spring对事务处理进行了抽象定义,形成了一套具体的API结构,如下:
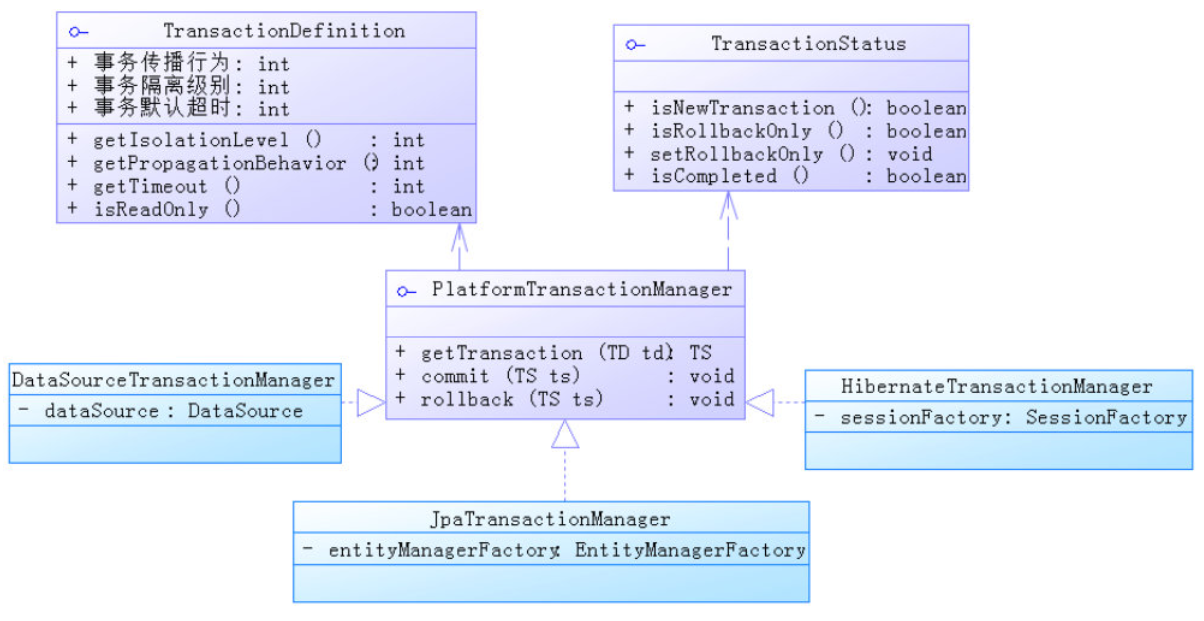
- TransactionDefinition:定义事务的具体属性,如隔离级别,超时设置,传播行为等
- TransactionStatus: 用于获取当前事务的状态信息
- PlatformTransactionMananger: 主要的事务管理接口,提供三个实现类对应不同场景
| 类型 | 场景 |
|---|---|
| DataSourceTransactionManager | 使用Spring JDBC或 iBatis 进行持久化数据时使用 |
| HibernateTransactionManager | 使用Hibernate3.0版本 进行持久化数据时使用 |
| JpaTransactionManager | 使用JPA进行持久化时 使用 |
| JtaTransactionManager | 使用一个JTA实现来管理事务,跨数据源时使用 |
注意其分布在不同的jar包中,使用时根据需要导入对应jar包
事务的传播行为控制
这是一个新概念但是也非常简单,即在一个执行sql的方法中调用了另一个方法时,该如何处理这两个方法之间的事务
Spring定义了7种不同的处理方式:
| 常量名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | 支持当前事务。如果 A 方法已经在事 务中,则 B 事务将直接使用。否则将 创建新事务 |
| PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务。如果 A 方法已经在事 务中,则 B 事务将直接使用。否则将 以非事务状态执行 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 支持当前事务。如果 A 方法没有事 务,则抛出异常 |
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 将创建新的事务,如果 A 方法已经在 事务中,则将 A 事务挂起 |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 不支持当前事务,总是以非事务状态 执行。如果 A 方法已经在事务中,则 将其挂起 |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | 不支持当前事务,如果 A 方法在事务 中,则抛出异常 |
| PROPAGATION.NESTED | 嵌套事务,当外层出现异常则连同内层一起回滚,若外层正常而内部异常,仅回滚内部操作 |
上述涉及的挂起,意思是开启一个独立的事务,已存在的事务暂停执行,等待新事务执行完毕后继续执行,两个事务不会互相影响
Spring整合MyBatis
在开始前我们先完成一个基础的CURD功能,后续开发中Spring + MyBatis项目是很常见的,那要将MyBatis整合到Spring中来,要明确一下两者的关系和定位
- Spring Java开发框架,其本质是一个对象容器,可以帮助我们完成IOC,DI,AOP
- MyBatis是一个持久层框架,用于简化对数据库的操作
将两者整合起来,就是将MyBatis中的对象交给Spring来管理,且将这些对象的依赖也交给Spring来管理;
添加依赖
Spring 3.0 的开发在 MyBatis 3.0 官方发布前就结束了,于是MyBatis社区自己召集开发者完成了这一部分工作,于是有了mybatis-spring项目,后续Spring也就没有必要在开发一个新的模块了,所以该jar是MyBatis提供的
<!-- Spring整合MyBatis依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--JDBC-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.44</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--Spring JDBC-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--事务管理-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--AspectJ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
SM基础使用
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 加载properties system-properties-mode指定是否是否使用系统属性 例如user值为当前系统用户名
该标签只加载一次 若有多个属性文件可以使用逗号隔开-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" system-properties-mode="NEVER"/>
<!-- 数据源 后续可更换为其他更方便的数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${driver}"/>
</bean>
<!-- MyBatis核心对象SqlSessionFactory-->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 扫描Mapper 将代理对象放入Spring -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="dao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
注意:建议在资源文件前添加classpath:可避免在web环境下资源路径发生变化导致的异常
注意:这里扫描Mapper的value指的是Mapper接口l对应的文件夹路径
jdbc.properties:
driver = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url = jdbc:mysql:///SMDB?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
usr = root
password = admin
location = /Users/jeason/.m2/repository/mysql/mysql-connector-java/8.0.17/mysql-connector-java-8.0.17.jar
测试代码
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Test1 {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Test
public void test(){
Student student = studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
编码式事务
编码式事务,即在源代码中加入 事务处理的代码, 即commit,rollback等,这是非常原始的做法仅作为了解
配置文件:
<!-- 在之前的配置中添加内容-->
<!--事务管理器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务定义 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionDefinition">
<!-- 隔离级别 可缺省-->
<property name="isolationLevelName" value="ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ"/>
<!-- 传播行为 可缺省-->
<property name="propagationBehaviorName" value="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/>
</bean>
测试代码
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private DataSourceTransactionManager manager;
@Autowired
private DefaultTransactionDefinition definition;
@Test
public void test(){
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = manager.getTransaction(definition);
try{
Student student = studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
System.out.println(student);
student.setAge(201);
studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(student);
int i = 1/0;
manager.commit(transactionStatus);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
manager.rollback(transaction Status);
}
}java
上述代码仅用于测试事务处理的有效性;
我们已经在Spring中配置了MyBatis,并进行了事务处理,但是没有解决重复代码的问题
事务模板
事务模板原理是将要执行的具体代码交给模板,模板会在执行这写代码的同时处理事务,当这写代码出现异常时则自动回滚事务,以此来简化书写
配置文件:
<!-- 在上述配置基础上删除事务定义 添加模板Bean-->
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<!-- 传播行为隔离级别等参数 可缺省-->
<property name="propagationBehaviorName" value="PROPAGATION_REQUIRED"/>
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
</bean>
测试代码
public class Test2 {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
@Test
public void test(){
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallback() {
public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
Student student = studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
System.out.println(student);
student.setAge(1101);
studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(student);
// int i = 1/0;
return null;
}
});
}
}
可以看到事务模板要求提供一个实现类来提交原始的数据库操作给模板,从而完成事务代码的增强
无论是纯手动管理还是利用模板,依然存在大量与业务无关的重复代码,这也是编码式事务最大的问题;
声明式事务
即不需要在原来的业务逻辑代码中加入任何事务相关的代码,而是通过xml,或者注解的方式,来告诉框架,哪些方法需要添加事务处理代码,让框架来完成在原始业务逻辑前后增加事务处理的代码(通过AOP),这也是AOP使用较多的场景之一;
配置文件:(需要引入aop和tx名称空间)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<import resource="mybatis-beans.xml"/>
<context:component-scan base-package="service"/>
<!-- 添加事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 事务通知-->
<tx:advice id="transactionAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- name指定要应用的方法名称 还有其他事务常用属性如隔离级别传播行为等..-->
<tx:method name="*" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="*update*" read-only="false" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ"/>
<tx:method name="*delete*" read-only="false" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 切点信息-->
<aop:config >
<!-- 根据表达式中的信息可以自动查找到目标对象 从而进行增强 先查找目标再生产代理-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="transactionAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
tx:method属性:
| 属性名 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| name | 匹配的方法名称 |
| isolation | 事务隔离级别 |
| read-only | 是否采用优化的只 读事务 |
| timeout | 超时 |
| rollback-for | 需要回滚的异常类 |
| propagation | 传播行为 |
| no-rollback-for | 不需要回滚的异常类 |
Service:
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
public Student getStudent(int id ){
return studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
public void update(Student student){
studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(student);
int i = 1/0;
}
}
测试代码
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext3.xml")
public class Test3 {
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
@Test
public void test(){
Student student = studentService.getStudent(1);
System.out.println(student);
student.setAge(8818);
studentService.update(student);
}
}
强调:事务增强应该应用到Service层,即业务逻辑层,应为一个业务方法可能涉及多个数据库操作,当某个操作遇到异常时需要将所有操作全部回滚
基于注解的配置
开启注解事务支持:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--为了分离关注点,故将MyBatis相关配置放到其他配置文件了-->
<import resource="mybatis-beans.xml"/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.yh.service"/>
<!-- 添加事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 开启注解事务管理-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
Service中增加方法:
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false)
public void transactionTest(){
Student student = getStudent(1);
student.setAge(1);
update(student);
int i = 1/0;
student.setName("jack");
update(student);
}
//当然注解上的参数都是可选的采用默认值即可
测试代码
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext4.xml")
public class Test4 {
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
@Test
public void test(){
studentService.transactionTest();
}
}
你可能会觉得注解的方式比xml配置简单的多,但是考虑一下,当你的项目特别大,涉及的表很多的时候呢,你可能需要些很多很多的注解,假设后期需要修改某些属性,还得一个个改;
所以大项目建议采用XML,小项目使用注解也ok;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号