JAVA框架-Mybatis上(配置和基础使用)
什么是Mybatis?
MyBatis是java平台下一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Ordinary Java Object,简单普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
其前身为apache的ibatis后来迁移到Gihub并更名为MyBatis
特点
1.轻量级自身不依赖其他任何JAR,但需要提供JDBC实现
2.灵活,更加适用于需求变化频繁的互联网应用
3.学习成本低,相比ORM框架而言,掌握MyBatis的使用是很轻松的
在项目中的位置

可以看出MyBatis处在DAO(数据访问对象)的位置,回顾一下DAO的工作职责:
-
连接数据库
-
接收输入数据
-
拼接并执行SQL
-
解析并返回结果
其实Mybatis就是一个数据库的框架
特色功能
MyBatis在解决上述问题的同时提供了更多实用的功能
- 动态SQL,即在SQL语句中可以包含逻辑处理(判断,循环等....)
- 高级映射,支持一对一,一对多映射
- 动态代理Mapper,使得可以用面向对象的方式来完成数据库操作
- 逆向工程,根据表结构自动生成,POJO,Mapper映射和Mapper接口,包含简单的CRUD
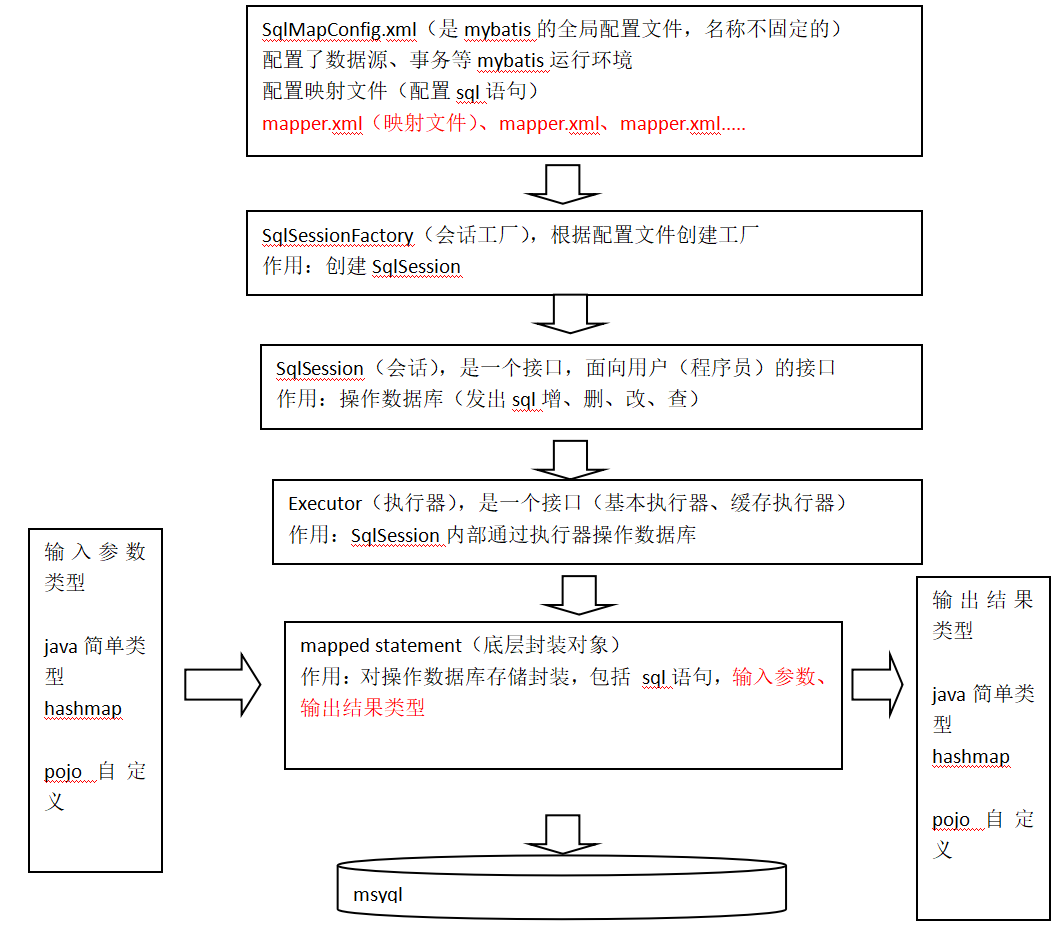
Mybatis环境搭建
官方文档:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/getting-started.html
这里我们直接创建Maven项目,然后把Mybatis当做依赖添加过来,在porm.xml文件中添加如下依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
然后顺手配置一下log4j.properties
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
# Console output... 设置输出格式
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
然后我们还需要配置mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<!-- 可配置多个环境 并指定默认使用的环境-->
<environment id="development">
<!-- 指定事务管理器-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 指定数据源 就是数据来自哪里 这里默认使用MyBatis自带的连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<!-- 表示本机 localhost &就是& xml中&需要转译-->
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatisDB?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=utf8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="3692512"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 指定要加载的映射文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/ProductsMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
到了这一步,要注意,其实我们的sql语句都是写在mapper文件夹下的ProductsMapper.xml中,这样我们就避免了数据库语言的硬编码,目前为止所有的配置文件对应的目录应该如下:

Mybatis的基本CRUD
首先为了演示方便,先建立一个数据库
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `mybatisDB` CHARACTER SET utf8;
USE `mybatisDB`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `products`;
CREATE TABLE `products` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`price` DOUBLE DEFAULT NULL,
`date` DATE DEFAULT NULL,
`cid` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`pid`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC;
INSERT INTO `products` VALUES (1,'东北大米',40,NULL,'s002'),(2,'新疆大枣',38,NULL,'s002'),(3,'新疆切糕',68,NULL,'s001'),(4,'十三香',10,NULL,'s002'),(5,'老干爹',20,NULL,'s002'),(6,'泰
国咖喱2',50.5,'2020-01-02','s001'),(7,'泰国咖喱2',50.5,'2020-01-02','s001');
普通查询和模糊查询
刚才说了,我们的查询语言应该都是写在mapper文件夹下ProductsMapper.xml的,现在我们先写一个简单的查询
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace 用于多个Mapper出现相同的sql时区分不同包-->
<mapper namespace="Bean.ProductMapper">
<!--查询语句
id用于表示这条sql
parameterType 表示 sql语句接受一个整数参数
resultType表示 将结果映射到Products对象中
#{} 表示一个站位符等同于 ?
如果在字符串中 要把#换成$
若输入参数是基础数据类型则可以随意写
若输入是一个POJO则写属性名称-->
<select id="selectProductById" parameterType="int" resultType="Bean.Product">
select * from products where id = #{id}
</select>
<!--多个参数查询-->
<select id="selectProductByIdAndPrice" parameterType="map" resultType="Bean.Product">
select *from products where id = #{id} and cid = #{cid}
</select>
<!--模糊查询-->
<select id="selectProductLikeName" parameterType="string" resultType="Bean.Product">
select * from products where name like "%${name}%"
</select>
</mapper>
然后我们进行测试
public class MyTest {
private SqlSessionFactory factory;
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
//获取的工厂构造器
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//加载配置文件
InputStream stream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
//获得会话工厂
factory = builder.build(stream);
}
@Test
public void selectTest() throws IOException {
//获得会话
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//执行sql
Product product = sqlSession.selectOne("selectProductById", 2);
System.out.println(product);
}
@Test
public void selectTest2() throws IOException {
//获得会话
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("id",4);
map.put("cid","s002");
//执行sql
Product product = sqlSession.selectOne("selectProductByIdAndPrice", map);
System.out.println(product);
}
@Test
public void selectTest3() throws IOException {
//获得会话
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//执行sql
List<Product> products = sqlSession.selectList("selectProductLikeName", "新疆");
System.out.println(products);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
插入数据
在mapper文件夹下ProductsMapper.xml添加:
<!-- insert没有返回值-->
<insert id="insertProduct" parameterType="Bean.Product">
insert into products values(null,#{name},#{price},#{pdate},#{cid})
</insert>
测试代码
@Test
public void insertTest() {
//设置自动提交为true 默认为false
SqlSession session = factory.openSession(true);
//实例化一个商品
Product p = new Product();
p.setName("虎邦辣酱");
p.setPrice(5.5f);
p.setPdata(new Date());
p.setCid("s001");
session.insert("insertProduct",p);
//session.commit();//手动commit
session.close();
}
这里注意,mybatis是默认开启事务回滚的,所以我们要么在创建session的时候,设置属性factory.openSession(true);,要么需要手动设置回滚确认session.commit();
获取当前插入数据的ID
很多情况下需要获取刚刚添加的记录的id用来做表关联,要获得id有两种方式
-
对于支持自增的数据库MySQL,我们只需要指定这两个属性即可:
keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true",第一个就是要告诉mybatis谁是主键,MyBatis会把id存储到传入对象的pid属性中<insert id="insertProduct" parameterType="Bean.Product" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true"> insert into products values(null,#{pname},#{price},#{pdate},#{cid}) </insert>
随后我们在java中插入数据后,只需要访问Bean的pid属性就好了
@Test
public void insertTest() {
//设置自动提交为true 默认为false
SqlSession session = factory.openSession(true);
//实例化一个商品
Product p = new Product();
p.setName("虎邦辣酱");
p.setPrice(5.5f);
p.setPdata(new Date());
p.setCid("s001");
session.insert("insertProduct",p);
//session.commit();//手动commit
session.close();
System.out.println("输入数据的行数:"+p.getPid());
}
-
不支持自增的数据库
<!--插入数据 --> <insert id="insertProduct" parameterType="Bean.Product" > insert into products values(null,#{name},#{price},#{date},#{cid}) <!--指定如何获取id 并放入对象某个属性中 --> <selectKey resultType="int" keyProperty="pid" order="AFTER" > select last_insert_id(); </selectKey> </insert>注意:select last_insert_id();是mysql的函数,oracle没有,那就需要将其替换为oracle中生产id的函数,selectKey的原理是执行这个sql函数,然后将结果放入对象的属性中,order指定id放入对象属性是在执行sql前或者后。关于before和after的选择,要根据id的来源是自增的还是自己编写语句获取的.
更新数据
<!--更新数据 -->
<update id="updateProduct" parameterType="Bean.Product">
update products set
name = #{name},
price = #{price},
date = #{date},
cid = #{cid}
where id = #{id}
</update>
@Test
public void updateTest() {
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//先获取一条记录
Products p = session.selectOne("selectProductBtId", 1);
//更新属性
p.setPrice(99.99f);
//执行更新
int count = session.update("updateProduct", p);
System.out.println("update count :"+count);
//提交事务
session.commit();
session.close();
}
删除数据
<!--通过id删除 -->
<delete id="deleteProductById" parameterType="int">
delete from products where
id = #{id}
</delete>
@Test
public void deleteTest() {
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
int count = session.delete("deleteProductById", 2);
System.out.println("delete count :"+count);
session.commit();
session.close();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号