[已满分]CMU数据库(15-445)实验1-BufferPoolManager
0. 关于环境搭建请看#
https://www.cnblogs.com/JayL-zxl/p/14307260.html
好了时隔超久我来填坑了,这次重构代码和修复之前博客中的一些错误。主要是为了复习数据库嘿嘿,防止误导大家和我自己复习的时候出现问题。
1. Task1 LRU REPLACEMENT POLICY#
0. 任务描述#
这个任务要求我们实现在课堂上所描述的LRU算法最近最少使用算法。
你需要实现下面这些函数。请确保他们都是线程安全的。
Victim(T*): Remove the object that was accessed the least recently compared to all the elements being tracked by theReplacer, store its contents in the output parameter and returnTrue. If theReplaceris empty returnFalse.Pin(T): This method should be called after a page is pinned to a frame in theBufferPoolManager. It should remove the frame containing the pinned page from theLRUReplacer.Unpin(T): This method should be called when thepin_countof a page becomes 0. This method should add the frame containing the unpinned page to theLRUReplacer.Size(): This method returns the number of frames that are currently in theLRUReplacer.
关于Lock和Lathes的区别请看下文。
1. 实现#
其实这个任务还是蛮简单的。你只需要清楚什么是最近最少使用算法即可。
LRU 算法的设计原则是:如果一个数据在最近一段时间没有被访问到,那么在将来它被访问的可能性也很小。也就是说,当限定的空间已存满数据时,应当把最久没有被访问到的数据淘汰。
这个题我熟啊。leetcode上有原题。而且要求在o(1)的时间复杂度实现这一任务。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache/
为了实现在O(1)时间内进行查找。因此我们可以用一个hash表。而且我们要记录一个时间戳来完成记录最近最少使用的块是谁。这里我们可以用list来实现。
如果我们访问了链表中的一个元素。就把这个元素放在链表头部。这样放在链表尾部的元素一定就是最近最少使用的元素。
为了让插入和删除均为O(1)我们可以用链表来实现。
这里对于pin和unpin操作实际上对于了task2。我们为什么需要pin。书上给了我们答案。下面我们也进行了分析
1.1 数据结构设计#
std::mutex latch; // thread safety
int capacity; // max number of pages LRUReplacer can handle
std::list<frame_id_t> lru_list;
std::unordered_map<frame_id_t, std::list<frame_id_t>::iterator> lruMap;
这里我们用了链表 + hash表。主要是为了删除和插入均为0(1)的时间复杂度。引入hash表就是可以根据frame_id快速找到其在list中对应的位置。否则的话你需要遍历链表这就不是o(1)了
1.2 Victim 函数实现#
注意这里必须要加锁,以防止并发错误。
- 如果没有可以牺牲的页直接返回false
- 如果有的话选择在链表尾部的页。remove它即可。这里的删除涉及链表和hash表两个数据结构的删除
bool LRUReplacer::Victim(frame_id_t *frame_id) {
// 选择一个牺牲frame
latch.lock();
if (lruMap.empty()) {
latch.unlock();
return false;
}
// 选择列表尾部 也就是最少使用的frame
frame_id_t lru_frame = lru_list.back();
lruMap.erase(lru_frame);
// 列表删除
lru_list.pop_back();
*frame_id = lru_frame;
latch.unlock();
return true;
}
1.3 pin 函数实现#
注意这里必须要加锁,以防止并发错误。
- pin函数表示这个frame被某个进程引用了
- 被引用的frame不能成为LRU算法的牺牲目标,所以这里把它从我们的数据结构中删除
void LRUReplacer::Pin(frame_id_t frame_id) {
// 被引用的frame 不能出现在lru list中
latch.lock();
if (lruMap.count(frame_id) != 0) {
lru_list.erase(lruMap[frame_id]);
lruMap.erase(frame_id);
}
latch.unlock();
}
1.4 unpin 函数实现#
注意这里必须要加锁,以防止并发错误。
- 先看一下这个页是否在可替换链表中
- 如果它不存在的话。则需要看一下当前链表是否还有空闲位置。如果有的话则直接加入
- 如果没有则需要移除链表尾部的节点知道有空余位置
void LRUReplacer::Unpin(frame_id_t frame_id) {
// 加入lru list中
latch.lock();
if (lruMap.count(frame_id) != 0) {
latch.unlock();
return;
}
// if list size >= capacity
// while {delete front}
while (Size() >= capacity) {
frame_id_t need_del = lru_list.front();
lru_list.pop_front();
lruMap.erase(need_del);
}
// insert
lru_list.push_front(frame_id);
lruMap[frame_id] = lru_list.begin();
latch.unlock();
}
2. 测试#
执行下面的语句即可
cd build
make lru_replacer_test
./test/lru_replacer_test
Task2 BUFFER POOL MANAGER#
0. 任务描述#
接下来,您需要在系统中实现缓冲池管理器(BufferPoolManager)。BufferPoolManager负责从DiskManager获取数据库页面并将它们存储在内存中。BufferPoolManage还可以在有要求它这样做时,或者当它需要驱逐一个页以便为新页腾出空间时,将脏页写入磁盘。为了确保您的实现能够正确地与系统的其余部分一起工作,我们将为您提供一些已经填写好的功能。您也不需要实现实际读写数据到磁盘的代码(在我们的实现中称为DiskManager)。我们将为您提供这一功能。
系统中的所有内存页面均由Page对象表示。 BufferPoolManager不需要了解这些页面的内容。 但是,作为系统开发人员,重要的是要了解Page对象只是缓冲池中用于存储内存的容器,因此并不特定于唯一页面。 也就是说,每个Page对象都包含一块内存,DiskManager会将其用作复制从磁盘读取的物理页面内容的位置。 BufferPoolManager将在将其来回移动到磁盘时重用相同的Page对象来存储数据。 这意味着在系统的整个生命周期中,相同的Page对象可能包含不同的物理页面。Page对象的标识符(page_id)跟踪其包含的物理页面。 如果Page对象不包含物理页面,则必须将其page_id设置为INVALID_PAGE_ID。
每个Page对象还维护一个计数器,以显示“固定”该页面的线程数。BufferPoolManager不允许释放固定的页面。每个Page对象还跟踪它的脏标记。您的工作是判断页面在解绑定之前是否已经被修改(修改则把脏标记置为1)。BufferPoolManager必须将脏页的内容写回磁盘,然后才能重用该对象。
BufferPoolManager实现将使用在此分配的前面步骤中创建的LRUReplacer类。它将使用LRUReplacer来跟踪何时访问页对象,以便在必须释放一个帧以为从磁盘复制新的物理页腾出空间时,它可以决定取消哪个页对象
你需要实现在(src/buffer/buffer_pool_manager.cpp):的以下函数
FetchPageImpl(page_id)NewPageImpl(page_id)UnpinPageImpl(page_id, is_dirty)FlushPageImpl(page_id)DeletePageImpl(page_id)FlushAllPagesImpl()
1. 分析#
1.1 为什么需要pin#
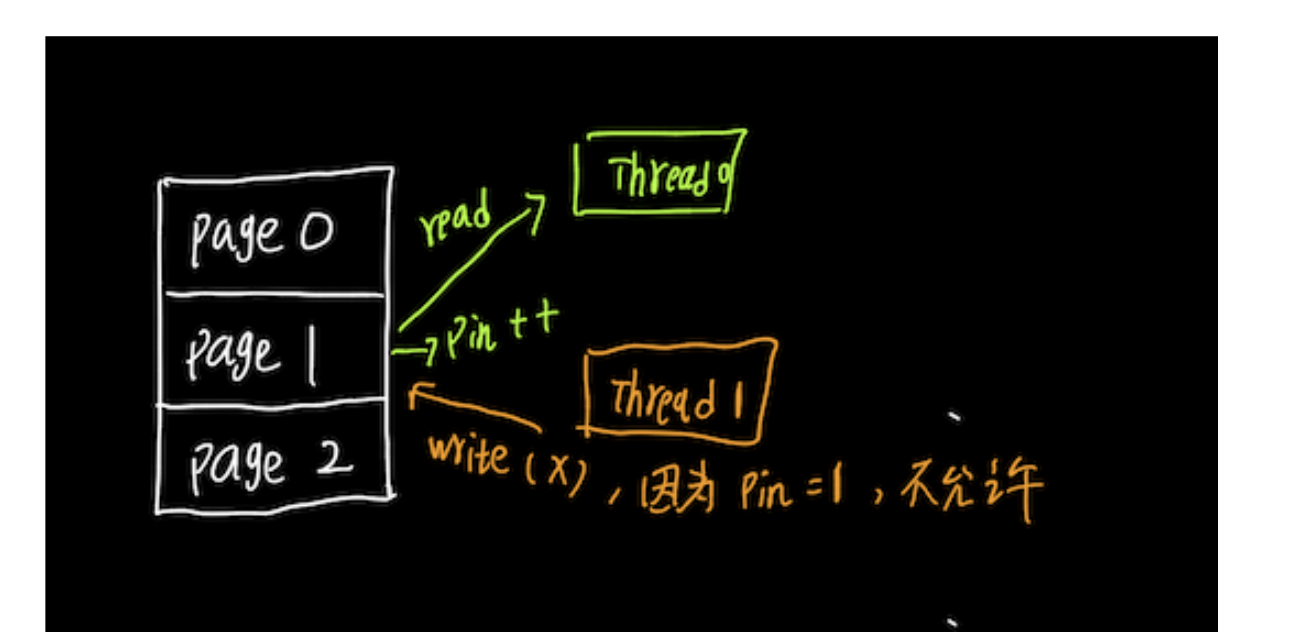
其实大抵可以如下图。
考虑这样一种情况。一个块被放入缓冲区,进程从缓冲区内存中读取块的内容。但是,当这个块被读取的时候,如果一个并发进程将这个块驱逐出来,并用一个不同的块替换它,读取旧块内容的进程(reader)将看到不正确的数据;如果块被驱逐时正在写入它,那么写入者最终会破坏替换块的内容。
因此,在进程从缓冲区块读取数据之前,确保该块不会被逐出是很重要的。为此,进程在块上执行一个pin操作;缓冲区管理器从不清除固定的块(pin值不为0的块)。当进程完成读取数据时,它应该执行一个unpin操作,允许在需要时将块取出。
因此我们需要一个pin_couter来记录pin的数量。其实也就是引用计数的思想。
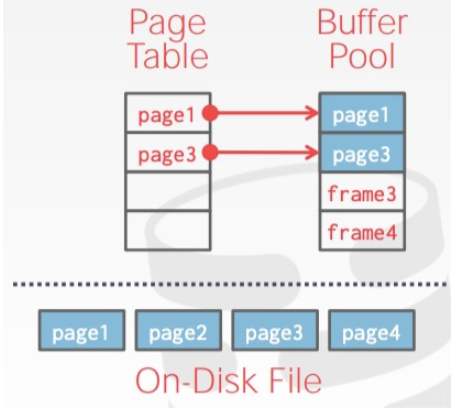
1.2 如何管理页和访问页#
一句话基地址+偏移量
page(基地值)+frame_id(偏移量) 实际上就是数组寻址
同时 DBMS 会维护一个 page table,负责记录每个 page 在内存中的位置,以及是否被写过(Dirty Flag),是否被引用或引用计数(Pin/Reference Counter)等元信息,如下图所示:
这里用了hash表来实现page_table来映射page_id和frame_id
2. 实现#
2.1 find_replace()函数#
- 如果空闲链表非空,则不需要进行替换算法。直接返回一个空闲frame就okay啦。这个情况是buffer pool未满
- 如果空闲链表为空,则表示当前buffer pool已经满了,这个时候必须要执行LRU算法
寻找替换frame过程
- 调用前面实现的
Victim函数获取牺牲帧的frame id - 在
pages_中找到对应的牺牲页,如果该页dirty则需要写回磁盘,并且reset pin count - 然后在page_table中删除对应映射关系 [page_id --> frame_id]
一定要注意2和3的顺序不能颠倒、不然没有办法找到对应的牺牲页
bool BufferPoolManager::find_replace(frame_id_t *frame_id) {
// if free_list not empty then we don't need replace page
// return directly
if (!free_list_.empty()) {
*frame_id = free_list_.front();
free_list_.pop_front();
return true;
}
// else we need to find a replace page
if (replacer_->Victim(frame_id)) {
// Remove entry from page_table
int replace_frame_id = -1;
for (const auto &p : page_table_) {
page_id_t pid = p.first;
frame_id_t fid = p.second;
if (fid == *frame_id) {
replace_frame_id = pid;
break;
}
}
if (replace_frame_id != -1) {
Page *replace_page = &pages_[*frame_id];
// If dirty, flush to disk
if (replace_page->is_dirty_) {
char *data = pages_[page_table_[replace_page->page_id_]].data_;
disk_manager_->WritePage(replace_page->page_id_, data);
replace_page->pin_count_ = 0; // Reset pin_count
}
page_table_.erase(replace_page->page_id_);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
2.2 FetchPageImpl 实现#
Page *BufferPoolManager::FetchPageImpl(page_id_t page_id)
这个函数就是我们要拿到一个page。这个函数可以分为三种情况分析
- 如果该页在缓冲池中直接访问并且记得把它的
pin_count++,然后把调用Pin函数通知replacer - 否则调用
find_replace函数,无论缓冲池是否有空闲,都可以获得可用的frame_id - 当然如果替换页为空,择要
- 然后建立新的
page_table映射关系
latch_.lock();
std::unordered_map<page_id_t, frame_id_t>::iterator it = page_table_.find(page_id);
// 1.1 P exists
if (it != page_table_.end()) {
frame_id_t frame_id = it->second;
Page *page = &pages_[frame_id];
//
page->pin_count_++; // pin the page
replacer_->Pin(frame_id); // notify replacer
latch_.unlock();
return page;
}
// 1.2 P not exist
frame_id_t replace_fid;
if (!find_replace(&replace_fid)) {
latch_.unlock();
return nullptr;
}
Page *replacePage = &pages_[replace_fid];
// 2. write it back to the disk
if (replacePage->IsDirty()) {
disk_manager_->WritePage(replacePage->page_id_, replacePage->data_);
}
// 3
page_table_.erase(replacePage->page_id_);
// create new map
// page_id <----> replaceFrameID;
page_table_[page_id] = replace_fid;
// 4. update replacePage info
Page *newPage = replacePage;
disk_manager_->ReadPage(page_id, newPage->data_);
newPage->page_id_ = page_id;
newPage->pin_count_++;
newPage->is_dirty_ = false;
replacer_->Pin(replace_fid);
latch_.unlock();
return newPage;
2.3 UnpinPageImpl 实现#
bool BufferPoolManager::UnpinPageImpl(page_id_t page_id, bool is_dirty)
函数定义如上。
这个函数就是如果我们这个进程已经完成了对这个页的操作。我们需要unpin操作
-
如果这个页的
pin_couter>0我们直接-- -
如果这个页的
pin _couter==0我们需要给它加到Lru_replacer中。因为没有人引用它。所以它可以成为被替换的候选人
bool BufferPoolManager::UnpinPageImpl(page_id_t page_id, bool is_dirty) {
latch_.lock();
// 1. 如果page_table中就没有
auto iter = page_table_.find(page_id);
if (iter == page_table_.end()) {
latch_.unlock();
return false;
}
// 2. 找到要被unpin的page
frame_id_t unpinned_Fid = iter->second;
Page *unpinned_page = &pages_[unpinned_Fid];
if (is_dirty) {
unpinned_page->is_dirty_ = true;
}
// if page的pin_count == 0 则直接return
if (unpinned_page->pin_count_ == 0) {
latch_.unlock();
return false;
}
unpinned_page->pin_count_--;
if (unpinned_page->GetPinCount() == 0) {
replacer_->Unpin(unpinned_Fid);
}
latch_.unlock();
return true;
}
2.4 FlushPageImpl 实现#
bool BufferPoolManager::FlushPageImpl(page_id_t page_id)
这个函数是要把一个page写入磁盘。
- 首先找到这一个页在缓冲池之中的位置
- 写入磁盘
// Make sure you call DiskManager::WritePage!
auto iter = page_table_.find(page_id);
if (iter == page_table_.end() || page_id == INVALID_PAGE_ID) {
latch_.unlock();
return false;
}
frame_id_t flush_fid = iter->second;
disk_manager_->WritePage(page_id, pages_[flush_fid].data_);
return false;
2.5 NewPageImpl 实现#
Page *BufferPoolManager::NewPageImpl(page_id_t *page_id)
分配一个新的page。
- 利用
find_replace函数在我们的缓冲池找到合适的地方建立page_id --> frame_id的映射 - 更新 新页的元数据
这里注意新创建的页要写回磁盘
Page *BufferPoolManager::NewPageImpl(page_id_t *page_id) {
latch_.lock();
// 0.
page_id_t new_page_id = disk_manager_->AllocatePage();
// 1.
bool is_all = true;
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(pool_size_); i++) {
if (pages_[i].pin_count_ == 0) {
is_all = false;
break;
}
}
if (is_all) {
latch_.unlock();
return nullptr;
}
// 2.
frame_id_t victim_fid;
if (!find_replace(&victim_fid)) {
latch_.unlock();
return nullptr;
}
// 3.
Page *victim_page = &pages_[victim_fid];
victim_page->page_id_ = new_page_id;
victim_page->pin_count_++;
replacer_->Pin(victim_fid);
page_table_[new_page_id] = victim_fid;
victim_page->is_dirty_ = false;
*page_id = new_page_id;
// [attention]
// if this not write to disk directly
// maybe meet below case:
// 1. NewPage
// 2. unpin(false)
// 3. 由于其他页的操作导致该页被从buffer_pool中移除
// 4. 这个时候在FetchPage, 就拿不到这个page了。
// 所以这里先把它写回磁盘
disk_manager_->WritePage(victim_page->GetPageId(), victim_page->GetData());
latch_.unlock();
return victim_page;
}
2.6 DeletePageImpl 实现#
bool BufferPoolManager::DeletePageImpl(page_id_t page_id)
这里是要我们把缓冲池中的page移出
- 如果这个page根本就不在缓冲池则直接返回
- 如果这个page 的引用计数大于0(pin_counter>0)表示我们不能返回
- 如果这个page被修改过则要写回磁盘
- 否则正常移除就好了。(在hash表中erase)
bool BufferPoolManager::DeletePageImpl(page_id_t page_id) {
// 0. Make sure you call DiskManager::DeallocatePage!
// 1. Search the page table for the requested page (P).
// 1. If P does not exist, return true.
// 2. If P exists, but has a non-zero pin-count, return false. Someone is using the page.
// 3. Otherwise, P can be deleted. Remove P from the page table, reset its metadata and return it to the free list.
latch_.lock();
// 1.
if (page_table_.find(page_id) == page_table_.end()) {
latch_.unlock();
return true;
}
// 2.
frame_id_t frame_id = page_table_[page_id];
Page *page = &pages_[frame_id];
if (page->pin_count_ > 0) {
latch_.unlock();
return false;
}
if (page->is_dirty_) {
FlushPageImpl(page_id);
}
// delete in disk in here
disk_manager_->DeallocatePage(page_id);
page_table_.erase(page_id);
// reset metadata
page->is_dirty_ = false;
page->pin_count_ = 0;
page->page_id_ = INVALID_PAGE_ID;
// return it to the free list
free_list_.push_back(frame_id);
latch_.unlock();
return true;
}
3. 源码解析#
3.1 ResetMemory()#
这个非常简单就是一个简单的内存分配。给我们的frame分配内存区域
3.2 ReadPage#
void DiskManager::ReadPage(page_id_t page_id, char *page_data)
void DiskManager::ReadPage(page_id_t page_id, char *page_data) {
int offset = page_id * PAGE_SIZE; //PAGE_SIZE=4kb 先计算偏移。判断是否越界(因为文件大小有限制)
// check if read beyond file length
if (offset > GetFileSize(file_name_)) {
LOG_DEBUG("I/O error reading past end of file");
// std::cerr << "I/O error while reading" << std::endl;
} else {
// set read cursor to offset
db_io_.seekp(offset); //把读写位置移动到偏移位置处
db_io_.read(page_data, PAGE_SIZE); //把数据读到page_data中
if (db_io_.bad()) {
LOG_DEBUG("I/O error while reading");
return;
}
// if file ends before reading PAGE_SIZE
int read_count = db_io_.gcount();
if (read_count < PAGE_SIZE) {
LOG_DEBUG("Read less than a page");
db_io_.clear();
// std::cerr << "Read less than a page" << std::endl;
memset(page_data + read_count, 0, PAGE_SIZE - read_count); //如果读取的数据小于4kb剩下的补0
}
}
}
3.3 WritePage#
void DiskManager::WritePage(page_id_t page_id, const char *page_data) {
size_t offset = static_cast<size_t>(page_id) * PAGE_SIZE; //先计算偏移
// set write cursor to offset
num_writes_ += 1; //记录写的次数
db_io_.seekp(offset);
db_io_.write(page_data, PAGE_SIZE); //向offset处写data
// check for I/O error
if (db_io_.bad()) {
LOG_DEBUG("I/O error while writing");
return;
}
// needs to flush to keep disk file in sync
db_io_.flush(); //刷新缓冲区
}
3.4 DiskManager 构造函数
就是获取文件指针
DiskManager::DiskManager(const std::string &db_file)
: file_name_(db_file), next_page_id_(0), num_flushes_(0), num_writes_(0), flush_log_(false), flush_log_f_(nullptr) {
std::string::size_type n = file_name_.rfind('.');
if (n == std::string::npos) {
LOG_DEBUG("wrong file format");
return;
}
log_name_ = file_name_.substr(0, n) + ".log";
log_io_.open(log_name_, std::ios::binary | std::ios::in | std::ios::app | std::ios::out);
// directory or file does not exist
if (!log_io_.is_open()) {
log_io_.clear();
// create a new file
log_io_.open(log_name_, std::ios::binary | std::ios::trunc | std::ios::app | std::ios::out);
log_io_.close();
// reopen with original mode
log_io_.open(log_name_, std::ios::binary | std::ios::in | std::ios::app | std::ios::out);
if (!log_io_.is_open()) {
throw Exception("can't open dblog file");
}
}
db_io_.open(db_file, std::ios::binary | std::ios::in | std::ios::out); //获取文件指针。并且打开输入输出流
// directory or file does not exist
if (!db_io_.is_open()) {
db_io_.clear();
// create a new file
db_io_.open(db_file, std::ios::binary | std::ios::trunc | std::ios::out);
db_io_.close();
// reopen with original mode
db_io_.open(db_file, std::ios::binary | std::ios::in | std::ios::out);
if (!db_io_.is_open()) {
throw Exception("can't open db file");
}
}
buffer_used = nullptr;
}
4. 测试#
4.1 本地测试#
cd build
make buffer_pool_manager_test
./test/buffer_pool_manager_test
4.2 cmu官网测试#
后面发现原来不是cmu自己的学生也可以用它们的软件进行测试。修改了好久同时得到了大佬的帮助。才成功实现满分#
cmu的测试网站如下 https://www.gradescope.com/courses/195440
如何使用测试网站的教程在 课程的FAQ 的最下面





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!