python 读取坐标数据画出最大面积的轮廓
项目要求,现需要一个能根据Excel的坐标数据,在图像上进行描点连线,并且连线的方式是以所有的点进行最大轮廓连线。现在实现了要求,但是由于代码写得太乱,我只是简单的说一下实现算法就好了,代码也会贴出来,时间过于久,我也有些地方忘记了,但是整体算法还是记得的~
下面开始简单的说一下:
首先,所有点的坐标数据就像下图所示:
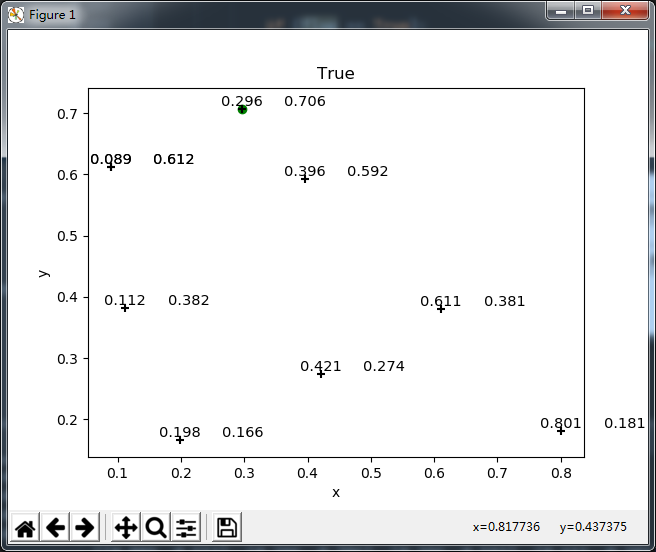
问题:如何将所有的点以最大的轮廓连线呢??
思路:应该是数学问题,如何将坐标列表重新排序成以最大轮廓的坐标列表,因为matplotlib库可以根据一个列表里面的坐标数据直接生成连线。
我的排序算法是:
1.首先,将所有坐标进行排序,可以以x排序,然后找到最左边的坐标点和最右边的坐标;
2.以最左边和最右边的坐标进行求解方程,两点确定一条直线,就是求该直线的方程;
3.将剩余的所有坐标x代入步骤2的方程组,求出解和坐标y进行比较,将线下方的点和上方的点坐标分别求出来,然后存入一个列表备份;
4.将下方坐标的列表进行排序,由小到大,然后存入一个最终列表中,最终列表第一个肯定是最左边的点,然后就是下方的点;
5.将下方坐标的列表进行排序,由大到小,然后继续分别存入最终列表,最后在最终列表中在加上最左边的坐标点,使连线闭合;
6.然后用matplotlib里面的pyplot函数,将最终列表连线即可。
上面的算法我写在了一个函数里面,这是非常不对的,但是如今还是不想将其整理出来,哈哈,思维不乱就行~~

1 try: 2 # 先提取成一个个位置坐标 3 coordinate = [] 4 for i in range(len(x)): 5 coordinate.append([x[i], y[i]]) 6 7 # print(coordinate) 8 9 # 这是基准列表,x最小最大,y最小最大 10 sort_list = [] 11 # 剩下的坐标数据 12 ret_list = [] 13 # 下方的点数据 14 under_list = [] 15 # 总的排序结果 16 final_list = [] 17 # 临时列表 18 temp = [] 19 20 # 下方的点 21 down_dot = [] 22 # 上方的点 23 up_dot = [] 24 25 y_max_and_y_min = [] 26 27 # 进行x排序 28 sort_x(coordinate) 29 30 # 排序完成肯定是第一个最小,最后一个最大,将这两个数据添加到确定的基准列表里面 31 sort_list.append(coordinate[0]) 32 sort_list.append(coordinate[len(coordinate) - 1]) 33 34 # 这下面进行以y大小进行排序,,重新存储在一个新列表里面 35 sort_y(coordinate) 36 y_max_and_y_min.append(coordinate[0]) 37 y_max_and_y_min.append(coordinate[len(coordinate) - 1]) 38 39 # 这句代码实现的功能是和基准列表进行比对,求除了基准列表剩下的所有坐标数据 40 ret_list = [item for item in coordinate if item not in sort_list] + [item for item in sort_list if 41 item not in coordinate] 42 43 print("确定的坐标:" + str(sort_list)) 44 45 print("剩余的坐标: " + str(ret_list)) 46 47 # 最左坐标 48 left_x = sort_list[0][0] 49 left_y = sort_list[0][1] 50 51 # 最右坐标 52 right_x = sort_list[1][0] 53 right_y = sort_list[1][1] 54 55 # 最下坐标 56 down_x = y_max_and_y_min[0][0] 57 down_y = y_max_and_y_min[0][1] 58 59 # 最上坐标 60 up_x = y_max_and_y_min[1][0] 61 up_y = y_max_and_y_min[1][1] 62 63 # 实现两点之间的公式 64 # y = k*x + b 65 66 # 总判断公式,,蛮重要 67 k = (right_y - left_y) / (right_x - left_x) 68 b = left_y - k * left_x 69 70 print("y=" + str(k) + "x" + '+' + str(b)) 71 72 # 开始进行比对,判断剩余列表里面的每一个点,如果在直线下方,就加入下方列表里面 73 for i in range(len(ret_list)): 74 # print(ret_list[i]) 75 if (under(k, b, ret_list[i])): 76 under_list.append(ret_list[i]) 77 78 print("下面列表的数据", under_list) 79 80 # 对下方列表再以x为基准进行排序 81 under_list = sort_x(under_list) 82 83 # 排序完成直接都添加到确定的列表里面,先添加一个最左的坐标,在循环结束之后再添加最右的数据 84 final_list.append(sort_list[0]) 85 86 for t in under_list: 87 final_list.append(t) 88 # 边添加还边让数据从剩余列表里面去掉 89 ret_list.remove(t) 90 91 final_list.append(sort_list[1]) 92 93 ################################################################################ 94 # 到此,,下方的排序已经结束 95 print(final_list) 96 num_under = len(final_list) 97 98 print(ret_list) 99 100 # 剩下的列表进行冒泡排序,还是由小到大,但是最后翻转一下列表就可以 101 ret_list = sort_x(ret_list) 102 ret_list = (list(reversed(ret_list))) 103 104 print(ret_list) 105 106 for t in ret_list: 107 """将剩下的坐标添加到处理后的列表里面""" 108 final_list.append(t) 109 110 # 这个是再补一个坐标,使曲线闭合 111 final_list.append(sort_list[0]) 112 113 print(ret_list) 114 print("最终列表-----------", final_list) 115 116 # 分离后的x,y坐标数据 117 final_x = [] 118 final_y = [] 119 120 for i in range(len(final_list)): 121 """将坐标数据从新分离成两个列表""" 122 final_x.append(final_list[i][0]) 123 final_y.append(final_list[i][1]) 124 125 # print(final_x) 126 # print(final_y) 127 128 # 在这需要将列表翻装一下,调试好久才发现 129 final_list = list(reversed(final_list)) 130 131 # 将图像显示出来 132 # showResult(final_x, final_y,'title', 'x', 'y')
连线起来的最终效果图:

项目要求2: 判断一个点是否在所围的轮廓内。
实现方法:
1.首先判断是否在x坐标是否在最左,最右之间,y坐标是否在最上,最下坐标之间,如果不在,直接判定不在;
2.判断是否为原来数据的点,如果是直接判定在轮廓内;
3.然后将需要判断的坐标代入最左最右组成的方程上,判断该坐标是该直线的上方还是下方。
4.若在下方,判断在下方的坐标点哪两个坐标之间,根据左右两个坐标点进行直线方程的求解,然后将需判断坐标的x代入,求解是否大于y坐标,如果大于就判定是在轮廓里面;
5.若在上方,判定条件改成小于才在轮廓里面;
代码如下:

# 下面进行判断一个点是否在圈内 # x_judge = 0.396 # y_judge = 0.592 x_get = self.input_x.text() y_get = self.input_y.text() if (len(x_get)==0): QMessageBox.critical(self, 'reslult', '请输入x,y') x_judge = final_x[0] y_judge = final_y[0] judge = [float(x_judge), float(y_judge)] self.input_x.setText(str(x_judge)) self.input_y.setText(str(y_judge)) else: x_judge = float(x_get) y_judge = float(y_get) judge = [float(x_judge), float(y_judge)] if judge == sort_list[0] or judge == sort_list[1] or judge == y_max_and_y_min[0] or judge == \ y_max_and_y_min[1]: """先判断是否是基准点""" print("在--相等") flag=True QMessageBox.critical(self,'reslult' , 'in') elif is_midle(judge[0], left_x, right_x) and is_midle(judge[1], down_y, up_y): """先判断是否在大圈之内""" # 先判断是在上方的点还是上方的点,如果在下方用下方的公式,否则,相反 if not under(k, b, judge): print("在下方") for i in range(len(down_dot) - 1): if is_midle(judge[0], down_dot[i][0], down_dot[i + 1][0]): # print(down_dot[i][0],down_dot[i+1][0]) print(down_dot[i], down_dot[i + 1]) k_test, b_test = generate_equation(down_dot[i], down_dot[i + 1]) print(k_test, b_test) if not (under(k_test, b_test, judge)): print("不在") flag = False QMessageBox.critical(self,'reslult' , 'not in') break else: print("在") flag = True QMessageBox.critical(self, 'reslult' ,'in') break else: pass elif not up_under(k, b, judge): print("在上方") for i in range(len(up_dot) - 1): if is_midle(judge[0], up_dot[i + 1][0], up_dot[i][0]): print(up_dot[i], up_dot[i + 1]) k_test, b_test = generate_equation(up_dot[i], up_dot[i + 1]) print(k_test, b_test) if (up_under(k_test, b_test, judge)): print("在") flag = True QMessageBox.critical(self, 'reslult' ,'in') break else: print("不在") flag=False QMessageBox.critical(self,'reslult' , 'not in') break else: pass else: print("不在") flag = False QMessageBox.critical(self,'reslult' ,'not in') if (flag == True): plt.scatter(x_judge, y_judge, color='green', marker='o') elif (flag == False): plt.scatter(x_judge,y_judge,color='red',marker='o') plt.plot(final_x, final_y, color='black', linewidth=2.0) plt.scatter(final_x, final_y, color='black', marker='+') plt.title(str(flag)) plt.xlabel('x') plt.ylabel('y') for x1, y1 in zip(final_x, final_y): plt.text(x1,y1, str(x1), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5) for x2, y2 in zip(final_x, final_y): plt.text(x2+0.1,y2, str(y2), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=10.5) plt.show()
至此,项目的要求算为完成,然后组成了GUI界面,所用的库是PYQT5。其实这个库真的挺好用的。
说下打包成exe 的时候遇到的问题,最新版的matplotlib库用pyinstaller根据打包不成功,如果按照网上的说法一个个依赖去寻找,太过于麻烦,
我查了半天资料,发现有个大佬说旧版的matplotlib可以,我连忙卸载新版的,下载旧版的,打包,,成功。就很完美~~~
至此,项目结束。
完成代码我放在了我的网盘上,有点点乱~下面是网盘链接:
https://wws.lanzous.com/i7xTKiz7o7g



