mysql中游标的使用案例详解(学习笔记)
1.游标是啥玩意?
简单的说:游标(cursor)就是游动的标识,啥意思呢,通俗的这么说,一条sql取出对应n条结果资源的接口/句柄,就是游标,沿着游标可以一次取出一行。我给大家准备一张图:
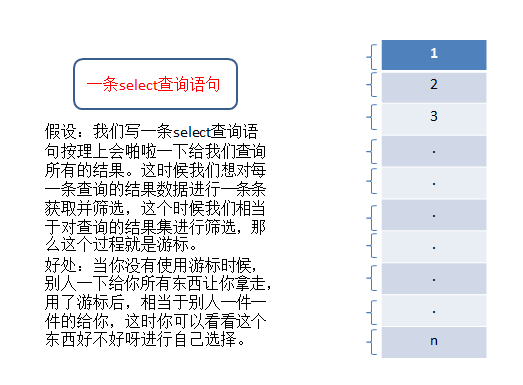
2.怎么使用游标?
//1.声明/定义一个游标
declare 声明;declare 游标名 cursor for select_statement;
//2.打开一个游标
open 打开;open 游标名
//3.取值
fetch 取值;fetch 游标名 into var1,var2[,...]
//4.关闭一个游标
close 关闭;close 游标名;
3.游标实战
未使用游标:
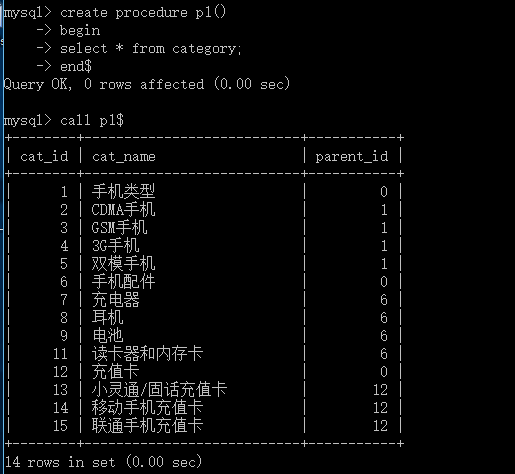
create procedure p1()
begin
select * from category;
end$
call p1$
执行结果:
使用游标:
/**
注释
*/
create procedure p2()
begin
//一下定义的三个变量用于将fetch取值出来的值放到对应的变量中
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name int;
declare row_parent_id int;
//定义游标
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
//打开游标
open getcategory;
//取值
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
//关闭游标
close getcategory;
end$
/**
未注释
*/
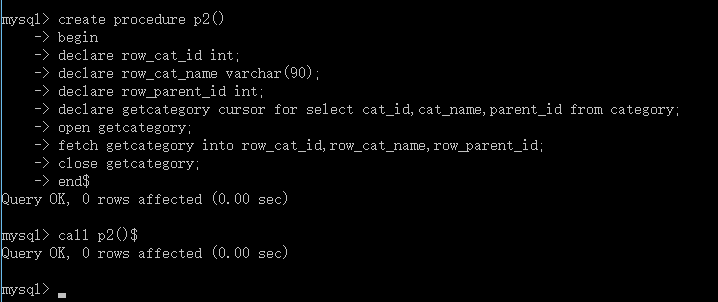
create procedure p2()
begin
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name varchar(90);
declare row_parent_id int;
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
open getcategory;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
close getcategory;
end$
//执行的时候你会发现是0行,这时因为我们将查询出的结果赋给了变量,我们有没有对赋值后的变量进行查询显示。所以是0行。因此,我们要重新改进。
call p2()$
执行结果为:
//改进
//删除游标重新执行
drop procedure p2$
create procedure p2()
begin
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name varchar(90);
declare row_parent_id int;
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
open getcategory;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
close getcategory;
end$
call p2()$
执行结果如下:
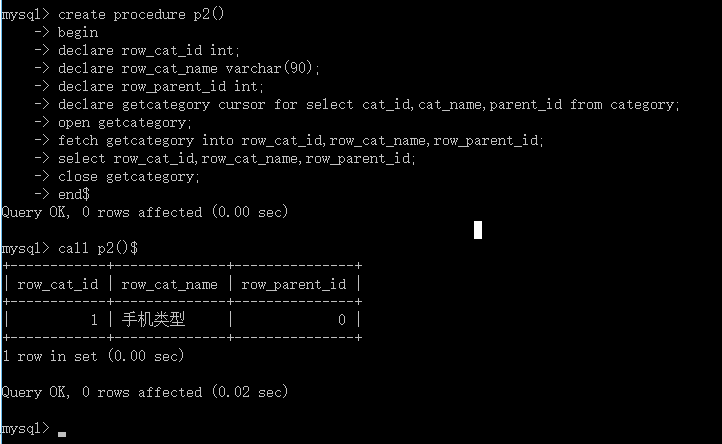
这时候你会发现我们只得到了一个查询结果,这时为什么呢?这时因为控制权在我们这里,我愿意取一行就一行,愿意取两行就两行。因此,我在把刚才的动作变一下。
create procedure p3()
begin
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name varchar(90);
declare row_parent_id int;
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
open getcategory;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
close getcategory;
end$
我fetch六次,查询五次,这时候我们会得到什么呢?试一下嘛!
call p4()$
执行结果如下:
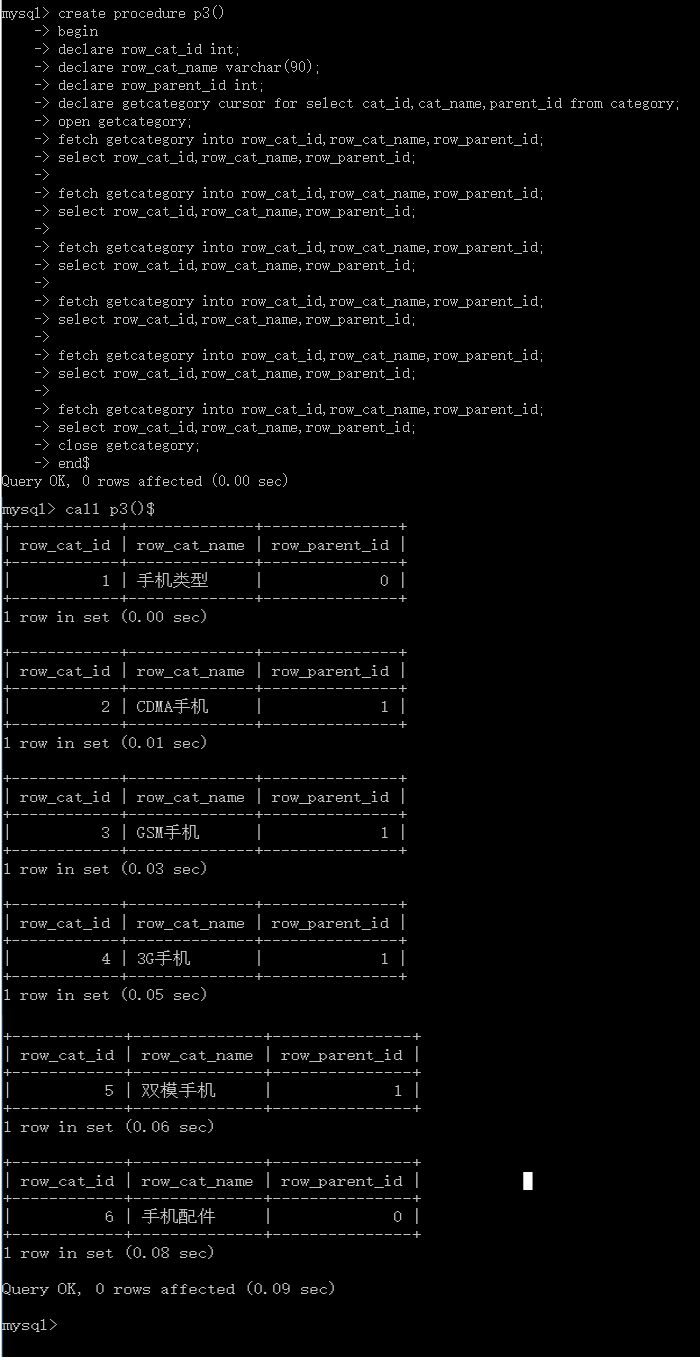
提示:发现什么了吗?相同的语句,我们每取一次就往后游一次,有几次就游几次,直到你把游完所有标识,这时候系统就会报【02000】这个错误,告诉我们游标已经走完了。我们这里游了六次,因此会打印前六条记录。
所以啊,我们如何循环游标来取出所有行?
思路:
1.计算所有行select count(*)
create procedure p4()
begin
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name varchar(90);
declare row_parent_id int;
declare cnt int default 0;//定义总行数
declare i int default 0;
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
select count(*) into cnt from category;//计算得出的总行数查询后赋给cnt变量
open getcategory;
repeat
set i:=i+1;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
until i>=cnt end repeat;
close getcategory;
end$
call p4()$
执行结果为:
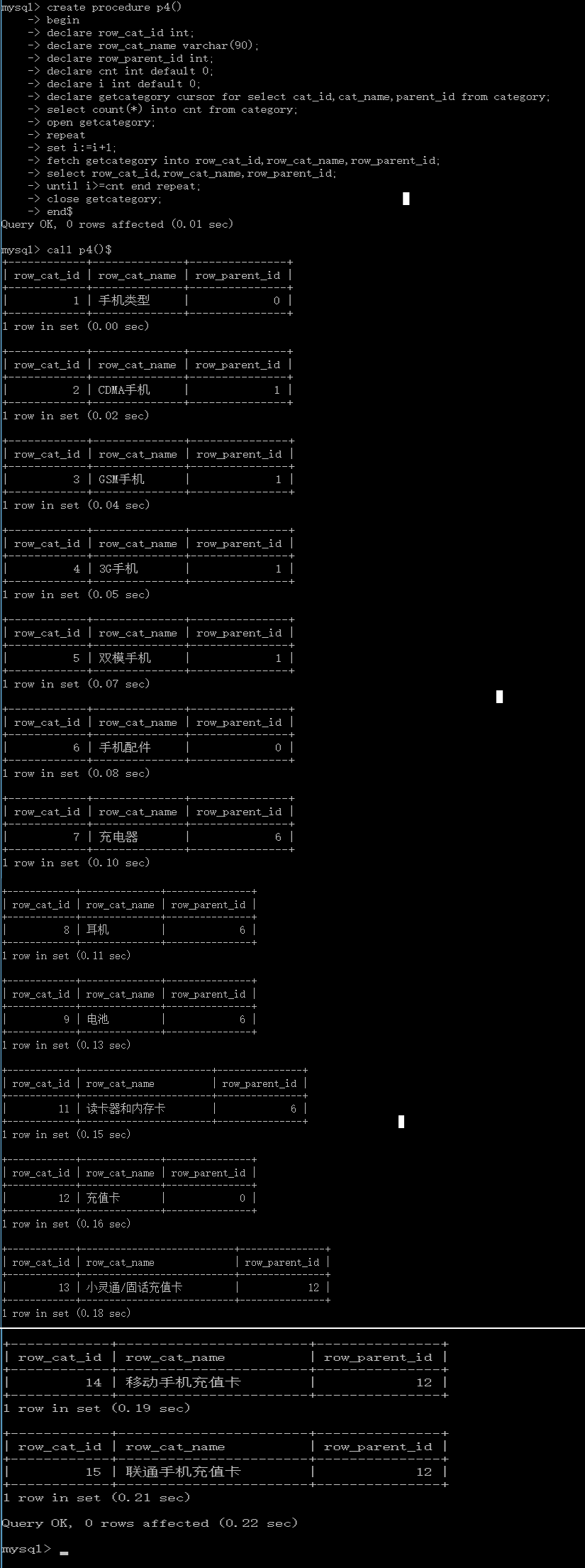
由此可见已经一条条得到表中结果,再次强调游标在此处的意义在于它把取出每一行的权利交给了你,你可以在每取出这一行的repeat中再做其他判断。
2.给游标定义一个越界的标识
//在mysql游标(cursor)中,可以定义continue handler来操作一个越界标识,使用语法:declare continue handler for NOT FOUND statemet(当没数据的时候要执行的语句)
//这句话的意思是说,我要声明一个句柄事件,你往后取,一旦发生NOT FOUND 事件就会出发set ergodic:=0这个语句
create procedure p5()
begin
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name varchar(90);
declare row_parent_id int;
declare ergodic int default 1;//声明一个变量表明还有数据可遍历
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
declare continue handler for NOT FOUND set ergodic:=0;
open getcategory;
repeat
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
until ergodic=0 end repeat;
close getcategory;
end$
call p5()$
执行结果为:
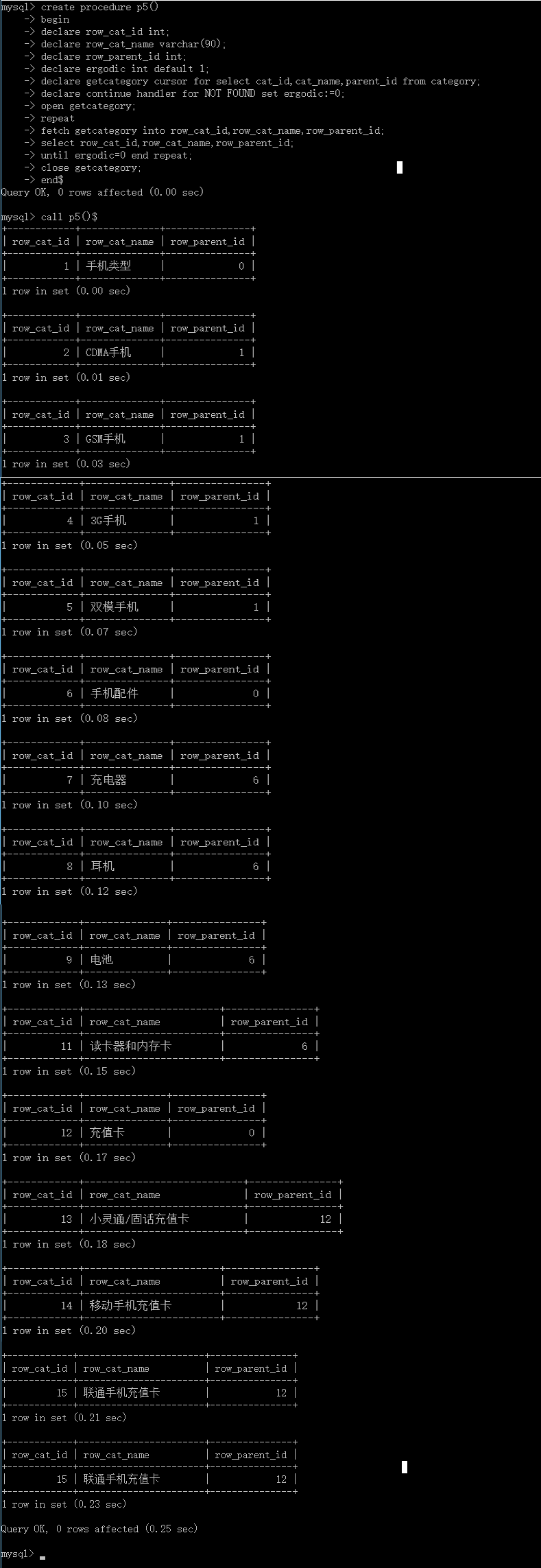
发现问题没有?为啥第最后一个查了两次?这是什么原因?我们不妨来分析一下我们写的语句:
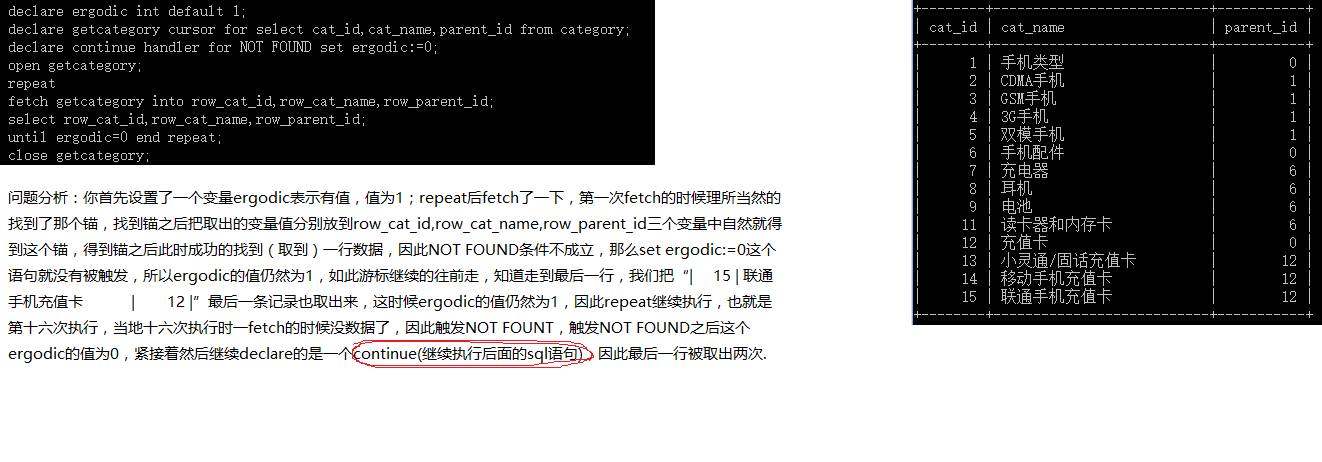
既然问题已经分析出来后,我们如何处理这个问题呢?
解决方案:声明处理的hanlder不再是continue,而是exit即可达到目的。即:declare exit handler for NOT FOUND set ergodic:=0;
//exit与continue的区别是:exit触发后,后面的语句不再执行,而continue还需要继续执行。
注意:除了这exit与continue两种方式外,还有一种方式就是undo handler。
//采用undo handler方式触发后,前面的语句直接撤销。【但目前好像这种方式,mysql还不支持】
create procedure p6()
begin
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name varchar(90);
declare row_parent_id int;
declare ergodic int default 1;
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
declare exit handler for NOT FOUND set ergodic:=0;
open getcategory;
repeat
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
until ergodic=0 end repeat;
close getcategory;
end$
call p6()$
执行结果为:
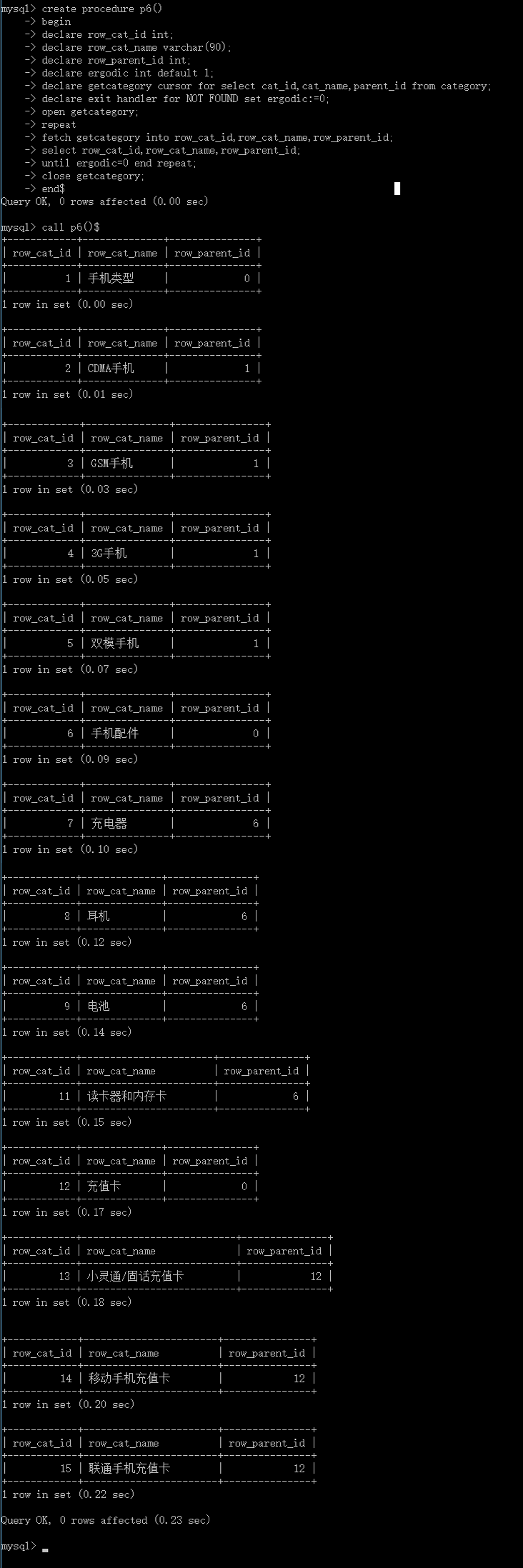
由此,问题解决。
题外话:如果我们还是使用continue的方式去实现不重复的话,我们应该怎么做呢?这时候我们可以在我们代码逻辑上处理这种问题,我们先来分析一下代码:
提示:
你有没有考虑过,你第一次fetch取值的时候会不会存在没有数据(值为空)的情况,因此我们可以先手动的fetch一行出来,紧接着repeat下面的数据。
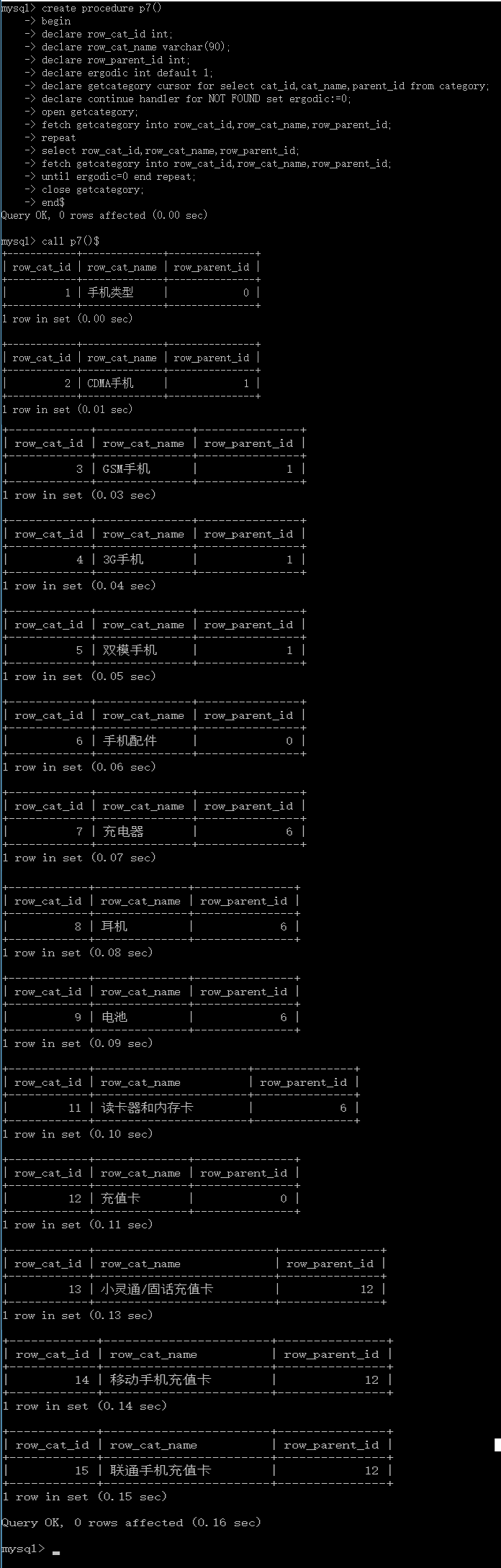
create procedure p7()
begin
declare row_cat_id int;
declare row_cat_name varchar(90);
declare row_parent_id int;
declare ergodic int default 1;
declare getcategory cursor for select cat_id,cat_name,parent_id from category;
declare continue handler for NOT FOUND set ergodic:=0;
open getcategory;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
repeat
select row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
fetch getcategory into row_cat_id,row_cat_name,row_parent_id;
until ergodic=0 end repeat;
close getcategory;
end$
call p7()$
执行结果为:
附件:
测试数据库与数据表:
create table category (
cat_id smallint unsigned auto_increment primary key,
cat_name varchar(90) not null default '',
parent_id smallint unsigned
)engine myisam charset utf8;
INSERT INTO `category` VALUES
(1,'手机类型',0),
(2,'CDMA手机',1),
(3,'GSM手机',1),
(4,'3G手机',1),
(5,'双模手机',1),
(6,'手机配件',0),
(7,'充电器',6),
(8,'耳机',6),
(9,'电池',6),
(11,'读卡器和内存卡',6),
(12,'充值卡',0),
(13,'小灵通/固话充值卡',12),
(14,'移动手机充值卡',12),
(15,'联通手机充值卡',12);




