教育后台管理系统:后台系统搭建
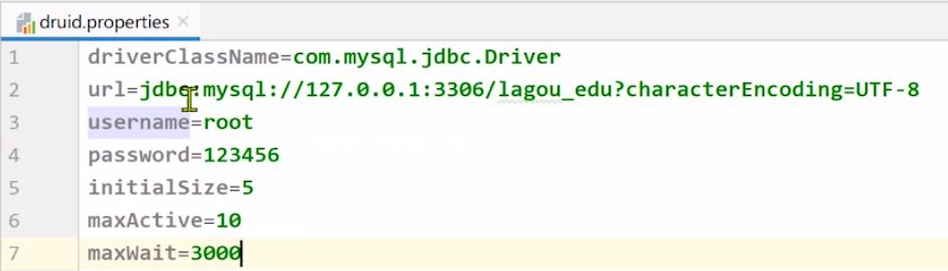
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.lagou</groupId> <artifactId>lagou_edu_home</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <!-- properties 是全局设置,可以设置整个maven项目的编译器 JDK版本 --> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- Servlet --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.13</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- Beanutils --> <dependency> <groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId> <artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId> <version>1.8.3</version> </dependency> <!-- DBUtils --> <dependency> <groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId> <artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId> <version>1.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.1.1</version> </dependency> <!-- 数据库相关 --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.37</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.0.9</version> </dependency> <!--fastjson工具包 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.colobu</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson-jaxrs-json-provider</artifactId> <version>0.3.1</version> </dependency> <!-- 文件上传 --> <dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>1.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId> <artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId> <version>1.2.1</version> </dependency> <!-- Lombok --> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <!-- maven编译插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <configuration> <release>11</release> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
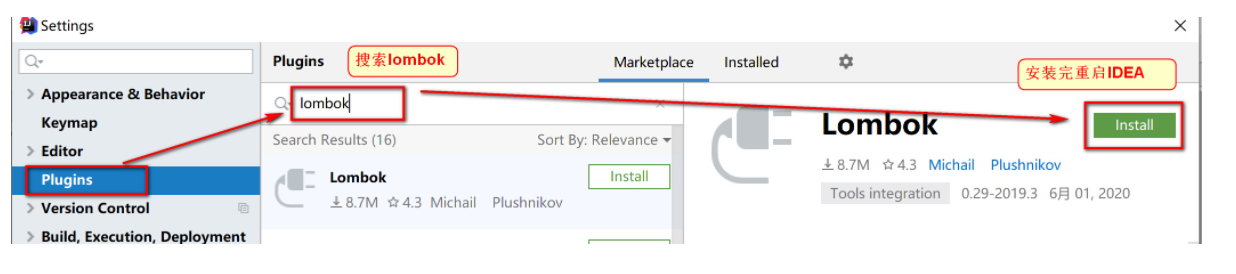
打开IDEA的Setting –> 选择Plugins选项 –> 搜索lombok –> 点击安装 –> 安装完成,重启IDEA
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
4) Lombok常用注解
@NoArgsConstructor:生成无参构造器
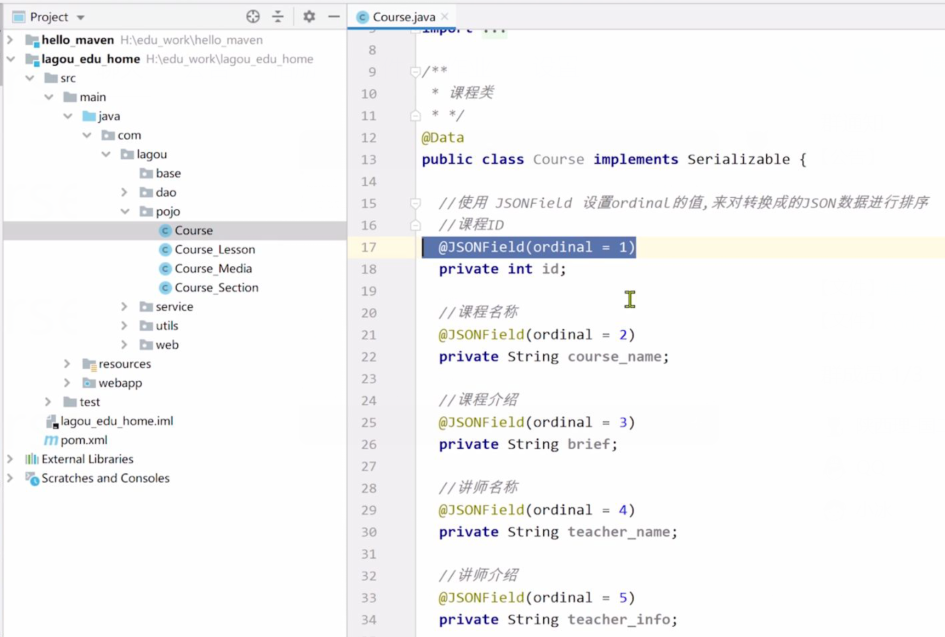
@Data: 该注解使用在类上,该注解会提供 getter、setter、equals、hashCode、toString
-
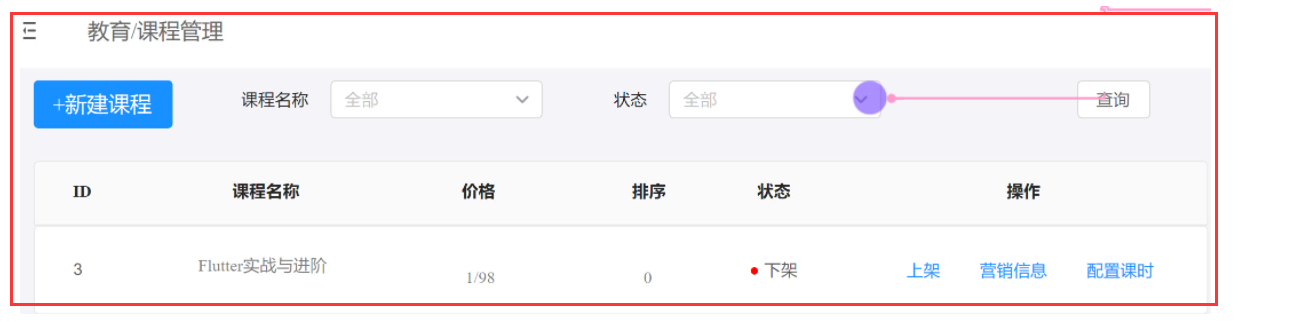
课程模块下有两个子模块:
-
-
课程模块
-
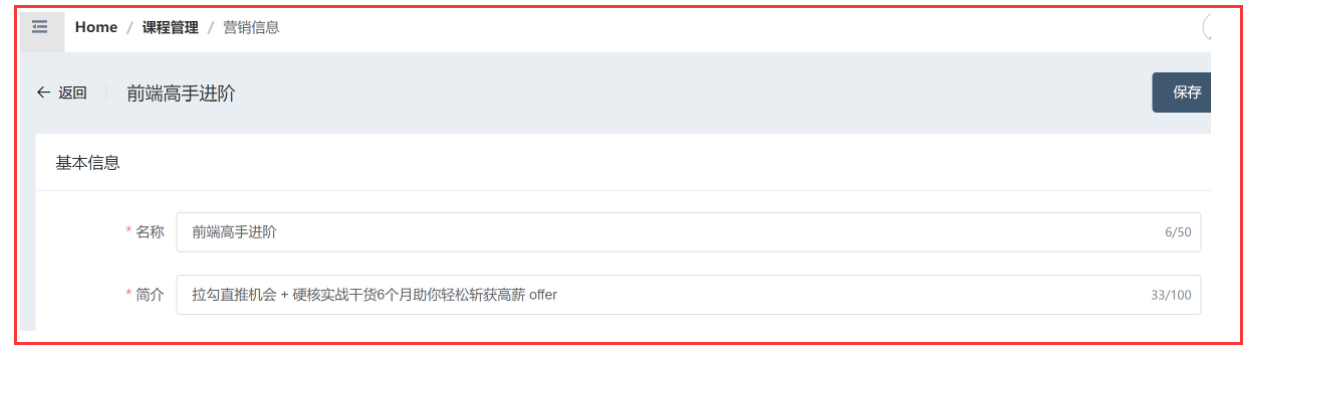
营销信息
-
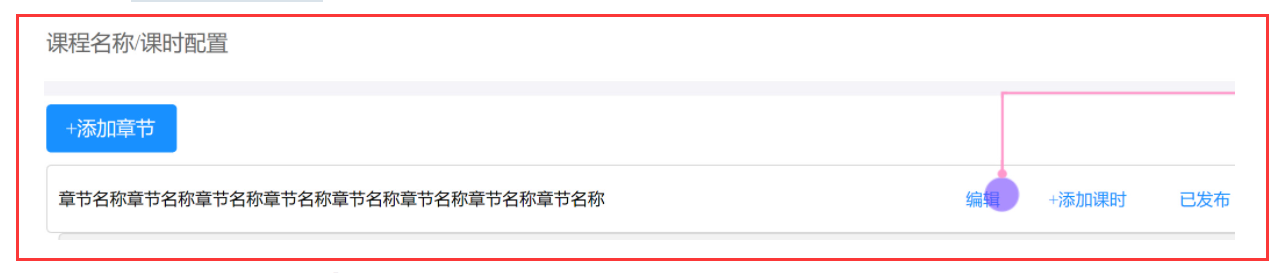
配置课时(课程内容管理)
-
-
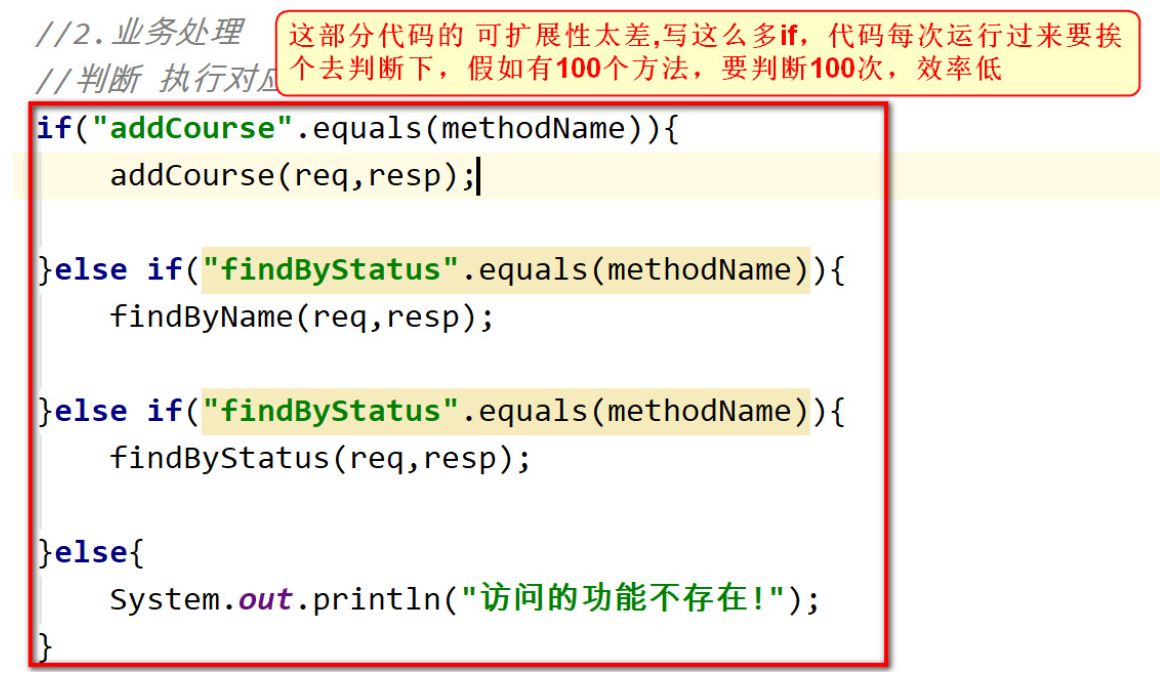
每个模块下都有很多的功能, 比如课程模块 的 新建课程, 上架课程,下架课程,根据课程名查询等等功能 , 每一个功能都是一个Servlet.
-
问题: 一个功能就是一个Servlet, 那么一个项目下有海量的Servlet, 这种方式好吗 ?
-
Servlet太多了,不好管理, 而且Servlet越多 服务器运行就越慢,资源消耗就越多.
我们使用一个Servlet对应一个模块的方式进行开发
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>$Title$</title> </head> <body> <%-- 一个模块对应一个Servlet --%> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/test?methodName=addCourse">新建课程</a> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/test?methodName=findByName">根据课程名查询</a> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/test?methodName=findByStatus">根据状态查询</a> </body> </html>
TestServlet
/** * 模拟课程模块 ,模块中有很多功能 * */ @WebServlet("/test") public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet { /** * doGet()方法作为调度器 控制器,根据请求的功能不同,调用对应的方法 * * */ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { //1.获取参数 //获取要调用的方法名 String methodName = req.getParameter("methodName"); //2.业务处理 //判断 执行对应的方法 if("addCourse".equals(methodName)){ addCourse(req,resp); }else if("findByStatus".equals(methodName)){ findByName(req,resp); }else if("findByStatus".equals(methodName)){ findByStatus(req,resp); }else{ System.out.println("访问的功能不存在!"); } } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req,resp); } /** * 2.模块对应的功能部分 * */ public void addCourse(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){ System.out.println("新建课程"); } public void findByStatus(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){ System.out.println("根据状态查询"); } public void findByName(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){ System.out.println("根据课程名称查询"); } }
反射的知识回顾:
第一步:先获取请求携带的方法参数值
第二步:获取指定类的字节码对象
第三步:根据请求携带的方法参数值,再通过字节码对象获取指定的方法
第四步:最后执行指定的方法
/** * 模拟课程模块 ,模块中有很多功能 * */ @WebServlet("/test") public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet { /** * doGet()方法作为调度器 控制器,根据请求的功能不同,调用对应的方法 * * */ @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { try { //1.获取参数 //获取要调用的方法名 String methodName = req.getParameter("methodName"); //2.业务处理 if(methodName != null){ //通过反射优化代码,提升代码的可维护性 //1.获取字节码对象 this = TestServlet对象 Class c = this.getClass(); //2.根据传入的方法名, 获取对应方法对象,执行方法即可 Method method = c.getMethod(methodName, HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class); //3.调用Method对象的 invoke()方法,执行对应的功能 method.invoke(this,req,resp); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("请求的功能不存在! !"); e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req,resp); } /** * 2.模块对应的功能部分 * */ public void addCourse(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){ System.out.println("新建课程"); } public void findByStatus(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){ System.out.println("根据状态查询"); } public void findByName(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){ System.out.println("根据课程名称查询"); } }
当前代码依然存在问题:
每个Servlet都需要写一份相同的反射代码
解决方案:
-
BaseServlet
public class BaseServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { try { //1.获取参数 //获取要调用的方法名 String methodName = req.getParameter("methodName"); //2.业务处理 if(methodName != null){ //通过反射优化代码,提升代码的可维护性 //1.获取字节码对象 this = TestServlet对象 Class c = this.getClass(); //2.根据传入的方法名, 获取对应方法对象,执行方法即可 Method method = c.getMethod(methodName, HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class); //3.调用Method对象的 invoke()方法,执行对应的功能 method.invoke(this,req,resp); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("请求的功能不存在! !"); e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(req,resp); } }
- 修改 TestServlet,继承 BaseServlet
@WebServlet("/test")
public class TestServlet extends BaseServlet {
/**
* 在模块对应的Servlet中只保留 业务相关代码
* 当有请求访问到 TestServlet时, 发现没有doGet和doPost方法,就回去父类中找,从而执行BaseServlet中的
* doGet方法
* */
public void addCourse(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){
System.out.println("新建课程");
}
public void findByStatus(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){
System.out.println("根据状态查询");
}
public void findByName(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp){
System.out.println("根据课程名称查询");
}
}