Vue.js学习笔记--进阶之路
vue框架介绍
框架,framework,是能够让程序开发人员更好的专注于业务逻辑的开发,而无需关心底层功能的实现。
vue是一个渐进式 JavaScript 框架,Vue (读音 /vjuː/,类似于 **view**) 是一套用于构建用户界面的**渐进式框架**。与其它大型框架不同的是,Vue 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。
国人自己的开发的框架,作者是:尤雨溪vue有两大核心:数据驱动页面、组件化
vue框架学习内容
vue、vue-cli脚手架、vue-router路由、ui库、样式预处理器stylus、网络请求axios、状态管理vuex、服务器端渲染
vue优点-缺点
优点:易学、速度快、采用虚拟DOM、数据双向绑定、指令系统、生态圈活跃
缺点:兼容性,不支持ie8及以下的浏览器、语法报错提示不是特别的准确
vue基本使用
安装方式一:引入js文件使用
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
安装方式二:结合node环境,下载vue使用(进入一个指定的目录,然后执行命令进行下载)
npm install vue
注:下载慢--设置淘宝镜像
npm config set registry "https://registry.npm.taobao.org"
vue常用配置选项
速查表
new Vue({
el:'#app', //设置挂载点 类似于querySelector
data:{}, //初始数据
methods:{}, //自定义函数
watch:{}, //监听
computed:{}, //计算属性
filters:{}, //过滤器
components:{}, //自定义组件
beforeCreate(){}, //创建之前
created(){}, //创建完成
beforeMount(){}, //挂载之前
mounted(){}, //挂载完成
beforeUpdate(){}, //更新之前
updated(){}, //更新完成
beforeDestroy(){},//销毁之前
destroyed(){}, //销毁完成
})el配置选项
指定vue的作用范围,相当于js中querySelector,只会配到满足条件的第一个标签,所以我们一般使用id选择器(不适用class或者标签选择器)。
data配置选项
初始化页面数据,初始化的数据会直接挂在vue实例上
methods 自定义函数
methods,用来存放用户自定义函数
常用指令
内容展示
mustache 语法
mustache 语法(文本插值) { { 变量名或者单行JS语法 }}
v-text
可以解析data中设置的初始值,v-text把初始值设置到指定的标签内。
和mustache的区别
如果要展示的内容是固定的,可以使用v-text
如果要展示的内容中的一部分是固定的,可以是使用mustache注意:所有v-xxx指令都要写标签的开始标签上
v-html
可以解析带有html标签的内容
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- 1 引入vue.js 核心文件 -->
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 2 设置挂载点 -->
<div id="box">
<!-- mustache语法 -->
<!-- 文本插值 -->
<h3>{
{ `小豪:${txt}` }}</h3>
<p>{
{ nu + 10 }}</p>
<!-- 布尔值 -->
<p>{
{ isshow ? 'true' : 'false' }}</p>
<!-- 对象类型 -->
<p>{
{ `姓名:${user.name}` }}</p>
<!-- 数组对象 -->
<p>{
{ `姓名:${users[1].name}` }}</p>
<hr>
<!-- v-text 替换源标签内所有内容-->
<p v-text="user.name">我被v-text内容覆盖了</p>
<hr>
<!-- v-html -->
<p v-text="ele">我不能识别html标签</p>
<p v-html="ele"></p>
<hr>
<!-- 数据双向绑定 -->
<input type="text" v-model="txt">
<p>{
{ txt }}</p>
</div>
<script>
// 3 示例化vue
new Vue({
el: '#box',
data: {
txt: 'vue基础学习',
nu: 20,
isshow: false,
ele:'<b>你好,我要加粗显示</b>',
user: {
name: '小代',
age: 20
},
users: [
{
name: '小代',
age: 20
},
{
name: '小代2',
age: 22
}
]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>条件判断
v-if v-else-if v-else
根据条件表达式或者布尔值的结果来展示或者不展示指定标签
当表达式的结果为true时,在页面结构中才会存在指定的标
v-show
不论条件表达式或者布尔值的结果是什么,v-show指定的标签都会在页面结构中存在
当表达式的结果为true时,在页面结构中会显示指定的标签
当表达式的结果为false时,在指定的标签上会添加一个display:none属性
使用场景:
当页面中,要根据指定的内容来频繁的切换某些内容时,要使用v-show
列表渲染--循环
v-for语法格式
<标签 v-for="(每次遍历的变量名[,每次遍历的元素在数组的下标]) of/in 要遍历的数据源"></标签>
可以根据数组元素数量来生成指定数量的标签
v-for key属性
遍历的数据源类型是数组时:
第一个参数是数组中每一项元素,第二个参数是数组中每项元素的下标
<ul>
<li v-for="(user,index) of users">
<!-- 字符串拼接方式 -->
<!-- <p>{
{ '姓名:'+user.name+',年龄:'+${user.age} }}</p> -->
<!-- 模板语法方式 -->
<p>{
{ index }}----{
{ `姓名:${user.name},年龄:${user.age}` }}</p>
</li>
</ul>遍历的数据源类型是对象时:
第一个参数是对象中每一项元素的value属性,第二参数是每一项元素的key属性,第三个参数是每一项元素的下标
<p v-for="(fruite,index,val) of fruites">{ { val }}---{ { index }}---{ { fruite }}</p>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="islogin">已登录</div>
<div v-else>未登录</div>
<div v-show="islogin">显示</div>
<div v-show="!islogin">隐藏</div>
<!--
注意:v-if有更高的切换开销
v-show有更高的初始渲染开销。
因此,如果要非常频繁的切换,则使用v-show较好;如果在运行时条件不太可能改变,则v-if较好
-->
<hr>
<ul>
<li v-for='(item,idx) of arr'>
{
{ idx }}--->{
{ item }}
</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<!-- 数组 -->
<li v-for="(item,idx) of arrObj">
<p>{
{ idx }}--{
{ item }}</p>
<!-- 对象 -->
<p v-for="(item,key,idx) of item">{
{ `${idx}-${key}-姓名:${item}` }}</p>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
islogin:true,
arr:[11,22,33,44,55,66],
obj:{
name:'小豪',
age:22
},
arrObj:[
{
name:'dyh',
age:19
},
{
name:'dyh1',
age:14
},
{
name:'dyh2',
age:12
}
]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>事件绑定
v-on
语法格式:<标签 v-on:事件名=“自定义函数名”></标签>
简写:<标签 @事件名="自定义函数"></标签>
//=========事件绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- <button v-on:click="toggle">{
{ !isshow ? '显示' : '隐藏' }}</button> -->
<!-- 简化版 -->
<button @click="toggle">{
{ !isshow ? '显示' : '隐藏' }}</button>
<div class="box" v-show="isshow">使用行内样式控制显示隐藏</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
isshow:true
},
methods:{
toggle(){
//Vue中的this 指向Vue实例
this.isshow = !this.isshow;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
//=========选项卡练习
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>选项卡-vue</title>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="page">
//根据按钮数组遍历出指定数量的按钮
//给按钮绑定点击事件,并把当前遍历的元素下标赋值给指定的变量
<button v-for="(btn,btnidx) of btns" @click="showidx = btnidx">{
{ btn }}</button>
//根据按钮数组遍历出指定数量的内容标签
//遍历时,拿当前数组下标与指定遍历进行比较,如果相等则显示,否则不显示
<div class="content" v-for="(btn,index) of btns" v-show="index == showidx">
//根据数组下标来遍历对象内容
<p v-for="con of news[index]">{
{ con }}</p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#page",
data:{
showidx:0,//默认显示哪个新闻内容
btns:[
'北京新闻1','中国新闻2','国际新闻3'
],
news:[
{
'新闻1':'北京新闻内容1',
'新闻2':'北京新闻内容2',
'新闻3':'北京新闻内容3'
},
{
'新闻1':'中国新闻内容1',
'新闻2':'中国新闻内容2',
'新闻3':'中国新闻内容3'
},
{
'新闻1':'国际新闻内容1',
'新闻2':'国际新闻内容2',
'新闻3':'国际新闻内容3'
}
]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>属性绑定
v-bind
语法格式:<标签 v-bind:属性名=“属性值”></标签>
可以简写:<标签 :属性名=“属性值”></标签>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>样式绑定</title>
<style>
#box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.red{
color:red;
}
.blue{
color:blue;
}
</style>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<p v-bind:style="styleA">v-bind绑定样式</p>
<button @click="green">绿色</button>
<img v-bind:src="imgUrl">
<!-- v-bing简写方式 : -->
<p :class="className">简写</p>
<button @click="toggle">切换</button>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{
styleA:{
'background-color':'#f00'
},
className:'red',
imgUrl:'https://cn.vuejs.org/images/logo.png'
},
methods:{
green(){
this.styleA = {
'background-color':'green'
}
},
toggle(){
this.className = 'blue'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Vue常见错误解析
vue.js:634 [Vue warn]: Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.
vue实例只能挂在到普通的元素标签上,不能是html、body标签,而且推荐使用id选择器来获取标签
[Vue warn]: Property or method "XXX" is not defined on the instance but referenced during render.
vue框架是一个声明式的框架,所以在挂载点内要使用变量时,要定义才能使用。
属性绑定
style
第一种用法:直接使用变量
<标签 v-bind:sytle="styleA"></标签>
<script>
new Vue({
...
data:{
styleA:{
'background-color':'#f00'
}
}
})
</script>
第二种用法:使用对象
<标签 v-bind:style="{ 属性名:属性值,... }"
注意:如果属性名中包含"-“,把横杠去掉,并横杠后的字母变成驼峰法命名,或者把属性名用引号引起来
如果属性值是一个单词,也要用引号引起来
比如:font-size、background-color...
fontSize、backgroundColor...
第三种用法:使用数组
<标签 v-bind:style="[变量1,变量2]"class
第一种用法:直接使用变量
<标签 :class="变量名"></标签>
第二种用法:使用对象
<标签 :class="{ 类名:表达式或者布尔值 }"></标签>
当表达式或者布尔值的结果为true时,表示使用该类名,否则就不使用该类名
第三种用法:使用数组
<标签 :class="[‘类名1’,‘类名N’,...]"
class使用数组时,每一个类名都要加上引号才会被解析成class属性。表单元素双向绑定
设计模式
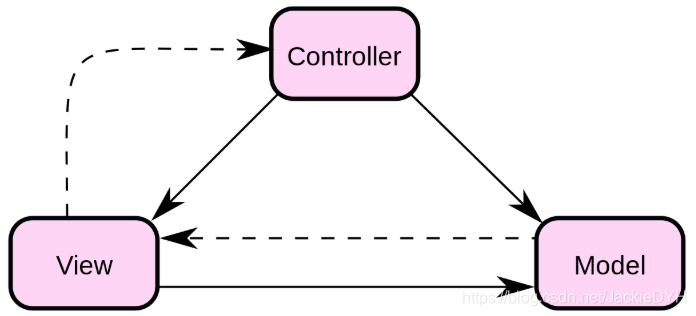
MVC:
Model 数据模型层
View 视图层
Controller 控制器层
强制的把程序的输入、输出和处理分开
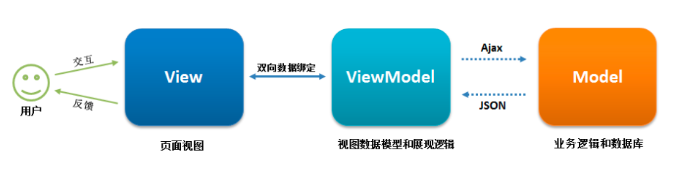
MVVM:
Model 数据模型层
View 视图层
ViewModel 视图模型层
内容展示
输入框
<div id="box">
<!-- view -->
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
<p>{
{ msg }}</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{ //可以理解为是model
msg:""
}
})
</script>文本域
<!-- 文本域 -->
<textarea v-model="article"></textarea>
<p>{
{ article }}</p>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{ //可以理解为是model
msg:"",
article:"这是一篇技术文章"
}
})
</script>checkbox
数组
语法格式:<input type="checkbox" v-model="变量名" value="属性值" />内容
//数组
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="看电影">看电影
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="打游戏">打游戏
<input type="checkbox" v-model="hobbies" value="运动">运动
<p>{
{ hobbies }}</p>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{ //可以理解为是model
msg:"",
article:"这是一篇技术文章",
hobbies:["打游戏"]
}
})
</script>
//布尔值
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isagree">是否同意协议
<!-- 不使用v-model实现单选 -->
<input type="checkbox" :checked="isagree" @click="isagree = !isagree">是否同意协议
<p>{
{ isagree }}</p>radio
radio和checkbox使用v-model一定要加上value属性
<div>
<span>性别:</span>
<input type="radio" v-model="sex" value="男">男
<input type="radio" v-model="sex" value="女">女
</div>
<p>{
{ sex }}</p>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{ //可以理解为是model
...
sex:'男'
}
})
</script>select
select双向绑定不需要添加到option标签中,只需要在select的开始标签里写v-model即可。
<select v-model="course">
<option value="">请选择</option>
<option value="0">web前端</option>
<option value="1">java</option>
<option value="2">ui</option>
</select>
<p>{
{ course }}</p>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{
...,
course:0
}
})
</script>自定义指令
vue支持我们自定义一些指令来完成一定的操作
Vue.directive('指令名称',{
inserted:function(el){
el.focus();//让元素获得焦点
//其他操作...
}
})
new Vue({...})
注意,自定义指令,需要写在vue被实例化之前
//========示例
// 自定义命令需要在vue实例化前定义
Vue.directive('test',{
//inserted 当指定插入到标签中时
inserted:function(e){
//e 是形参,名字可以自定义,此时e就代表添加了自定义指定v-test那个元素
e.focus();
e.value = '测试自定义指令'
console.log(e)
}
})
new Vue({
el:'#app'
})用户信息收集功能
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-BVYiiSIFeK1dGmJRAkycuHAHRg32OmUcww7on3RYdg4Va+PmSTsz/K68vbdEjh4u" crossorigin="anonymous">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css">
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box" class="container">
<form class="form-horizontal" autocomplete="off">
<h3 class="text-center">用户信息收集</h3>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name" class="col-sm-2 control-label">姓名:</label>
<div class="col-sm-6">
<input type="text" id="name" class="form-control" v-model.trim="info.name">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="age" class="col-sm-2 control-label">年龄:</label>
<div class="col-sm-6">
<input type="text" id="age" class="form-control" v-model.trim="info.age">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="age" class="col-sm-2 control-label"></label>
<div class="col-sm-6">
<input type="button" value="提交" class="btn btn-primary" @click="add()">
<input type="button" value="重置" class="btn" @click="clear()">
<input type="button" value="删除所有用户" class="btn btn-warning" @click="delAll">
</div>
</div>
</form>
<!-- 表格 -->
<table class="table table-bordered table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(obj,idx) of users" :idx="idx">
<td>{
{ obj.name }}</td>
<td>{
{ obj.age }}</td>
<td class="col-sm-3 text-center">
<button class="btn btn-primary" @click="edit(idx)">编辑</button>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="del(idx)">删除</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr v-show="users.length==0" class="text-center">
<td colspan="3">尚无用户信息显示!!</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#box',
data: {
isidx:-1,//记录数组项
info: {
name: '',
age: ''
},
users: JSON.parse(sessionStorage.getItem('users')) || [],
// users: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('users')) || [],
},
methods: {
add() {//添加 push 是把指定的内容追加到数组的末尾
//为空判断
if(this.info.name == '' || this.info.age == ''){
alert("请输入完整内容再提交表单!!!");
return false;
}
//判断是 提交 修改
if(this.isidx == -1){
//添加
this.users.push(JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.info)));
}else{
// 修改替换
this.users.splice(this.isidx,1,(JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.info))));
// this.users[this.isidx] = this.info;
}
//对象的浅拷贝问题
this.session();
this.clear();
},
session(){//本地临时存储
sessionStorage.setItem("users",JSON.stringify(this.users));
},
clear() {//重置
this.isidx = -1; //恢复提交状态
this.reset();
},
reset() {//清空
this.info = {
name: '',
age: ''
}
},
edit(id){//编辑信息
console.log(this.users[id])
// 深浅拷贝
this.info = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.users[id]));
this.isidx = id; //赋值数组下标
},
del(id){//删除
this.users.splice(id,1);
this.session();
},
delAll(){
// 把数组赋值空
this.users = [];
// 1删除本地存储中指定key的内容
sessionStorage.removeItem('users');
// localStorage.removeItem('users');
// 2还可以清空本地存储所有数据
// sessionStorage.clear();
// localStorage.clear();
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>修饰符
事件修饰符
阻止默认事件
<标签 @事件名.prevent></标签>阻止事件冒泡
<标签 @事件名.stop></标签>捕获事件冒泡
<标签 @事件名.capture></标签>
注意:.capture修饰符不会阻止或者改变事件冒泡,但是会改变冒泡函数执行的顺序。self修饰符
<标签 @事件名.self></标签>
注意:.self强调的是当前操作的元素只有是它自己本身时,才会触发指定的函数。只执行一次
<标签 @事件名.once></标签>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>修饰符</title>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<style>
.box,.big{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.small{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 阻止默认事件 -->
<div class="box" @contextmenu.prevent="menu"></div>
<hr>
<!-- 阻止事件冒泡 -->
<div class="big" @click="bigClick">
<div class="small" @click.stop="smallClick"></div>
</div>
<hr>
<!-- 捕获事件冒泡 -->
<div class="big" @click.capture="bigClick">
<div class="small" @click="smallClick"></div>
</div>
<hr>
<!-- self修饰符 -->
<div class="big" @click.self="bigClick">
<div class="small" @click="smallClick"></div>
</div>
<hr>
<!-- once修饰符 -->
<div class="big" @click.self.once="bigClick">
<div class="small" @click="smallClick"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
methods:{
menu(){
// if(e){
// e.preventDefault();
// }else{
// }
// return false;
console.log("鼠标右键执行了")
},
bigClick(){
console.log("大盒子被点击了")
},
smallClick(e){
// e.stopPropagation();
console.log("小盒子被点击了")
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>表单元素修饰符
.lazy
不再对数据进行实时双向绑定,而是在执行change事件时才进行双向绑定.number
number修饰符不强制页面用户输入的内容,而是转变数据类型为number
如果写的内容是数字开头,字符串结尾,那么number修饰符会把字符串过滤掉
如果写的内容是字符串开通,数字结尾,那么number修饰符不做任何操作。.trim
过滤输入内容左右两边的空格,不包含中间的空格。
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- lazy修饰符 -->
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="msg">
<p>{
{ msg }}</p>
<hr>
<!-- number修饰符 -->
<input type="text" v-model.number="num">
<button @click="getType">获取数据类型</button>
<hr>
<!-- trim修饰符 -->
<input type="text" v-model.trim="str">
<p>{
{ str }}</p>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
msg:'',
num:0,
str:''
},
methods:{
getType(){
console.log(typeof this.num)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>其他修饰符
@事件.enter 回车键
@事件.down 下键
@事件.up 上键
@事件.left
@事件.right
@事件.esc
@事件.tab
数据本地存储
localStorage
sessionStorage
方法
数据添加:setItem('key',value)
sessionStorage.setItem("users",JSON.stringify(this.users))数据读取:getItem('key')
sessionStorage.getItem('users')删除数据:removeItem('key')
根据指定的key来进行删除
sessionStorage.removeItem('users');
localStorage.removeItem('users');删除本地存储中所以数据:clear()
sessionStorage.clear();
localStorage.clear();
模拟跨域请求
基本步骤
第一步:创建一个script标签
var s = document.createElement("script");第二步:设置script标签的src属性
s.src = "http://suggestion.baidu.com/su?cb=getwd&wd="+this.ipt;第三步:把生成好的script标签追加到页面中
document.body.append(s)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.select{
background-color: coral;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
<!-- <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> -->
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- @input="search" -->
<input type="text" v-model="ipt" @keydown.down="down" @keydown.up.prevent="up" @keydown.enter="enter">
<button @click="search">搜索</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,idx) of arr" :class="{select:idx==isid}">{
{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
arr:[],
ipt:'',
isid:-1
},
methods:{
search(){
if(this.ipt == '')return;
// cb 回调函数名称
// wd 要搜索的关键词
var s = document.createElement("script");
s.src="http://suggestion.baidu.com/su?cb=callback&wd="+this.ipt;
// s.src="https://sp0.baidu.com/5a1Fazu8AA54nxGko9WTAnF6hhy/su?cb=callback&wd="+this.ipt;
document.body.append(s);
},
down(){
this.isid++;
if(this.isid>3){
this.isid=-1;
}
},
up(){
this.isid--;
if(this.isid<0){
this.isid=4;
}
},
enter(){
console.log(this.arr[this.isid],this.isid)
if(this.isid == -1 || this.isid == 4){
window.open("https://www.baidu.com/s?wd="+this.ipt);
}else{
window.open("https://www.baidu.com/s?wd="+this.arr[this.isid]);
}
}
},
watch:{//监听
// ipt:function() 简写
ipt(newVal,oldVlal){
if(newVal == ''){
return false;
}
console.log(newVal);
console.log(oldVlal);
var s = document.createElement("script");
s.src="http://suggestion.baidu.com/su?cb=callback&wd="+newVal;
document.body.append(s);
}
}
});
function callback(res){
//现在收索显示条数
res.s.length=4;
vm.arr = res.s;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>侦听/监听器watch
可以对页面中已经定义好的变量进行监听,一旦变量值发生了改变,那么就可以执行一定操作。
本文来自博客园,作者:JackieDYH,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/JackieDYH/p/17633994.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现