分层图最短路
分层图
分层图确实是个不难的东西我也确实是一个菜鸡...
简要介绍
分层图常在图论问题中出现可任选K条边更改边权(变为0或是原来一半等)时应用。
分层图,就是在应对这种问题时,把原图复制K层(总共K+1层)
每相邻层之间用更改边权后的边连接对应的点(代表进行一次操作)
然后就可以在这个新图中处理,得到问题的最优解
图例如下
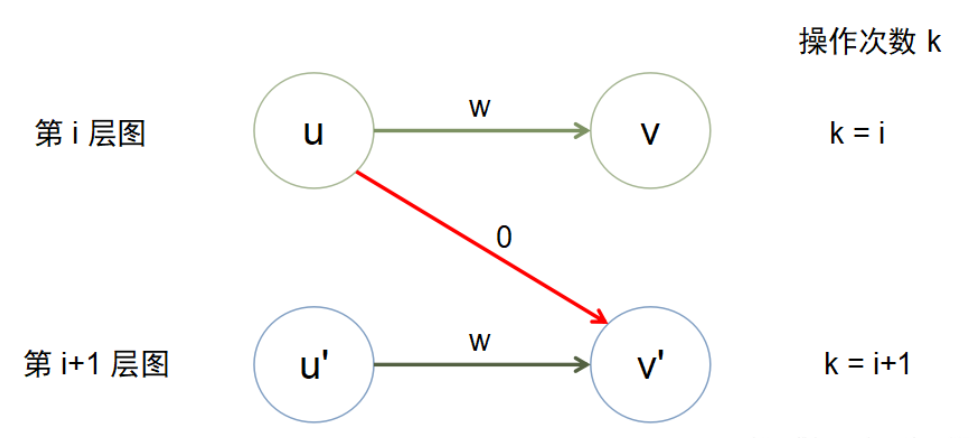
因为连接两层的边代表的是进行了一次不可逆的边权操作,所以都是有向边
每层图内部的边就是和原图一样了
简单说明
可能有人会有疑问,把图复制K层后,空间和时间不会爆炸嘛?
虽然分层图总共有K+1层图
但因为每层都只是单纯的复制原图
所以内容都是一样的,一般没有必要新建图
我们只需要用一个二维数组表示点编号及其所在层数
例如在求最短路时,用 dis[x][k] 表示分层图中在k层的x点的最短距离
即原图中进行了k次边权操作的 x 点最短距离
这样就不需要新建图了
(如果最后还是炸了,说明正解大概不是分层图)
例题
题目描述
Your are given an undirect connected graph.Every edge has a cost to pass.You should choose a path from S to T and you need to pay for all the edges in your path. However, you can choose at most k edges in the graph and change their costs to zero in the beginning. Please answer the minimal total cost you need to pay.
您将获得一个无向连通图。每条边都有成本要通过。您应该选择一条从S到T的路径,并且需要为路径中的所有边付费。但是,您可以在图中选择最多k个边,并在开始时将其成本更改为零。请回答您需要支付的最低总费用。(机翻)
输入描述:
The first line contains five integers n,m,S,T,K.
For each of the following m lines, there are three integers a,b,l, meaning there is an edge that costs l between a and b.
n is the number of nodes and m is the number of edges.
第一行包含五个整数n,m,S,T,K。
对于以下m行中的每一行,有三个整数a,b,l,这意味着在a和b之间存在成本为l的边。
n是节点数,m是边数。
输出描述:
An integer meaning the minimal total cost.
一个整数表示最小总成本。
示例1
输入
3 2 1 3 1
1 2 1
2 3 2
输出
1
备注:
1≤n,m≤1e3,1≤S,T,a,b≤n,0≤k≤m,1≤l≤1e6
Multiple edges and self loops are allowed.
来源:牛客网暑期多校第四场J题

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <queue> using namespace std; #define M 1000100 struct node { int to,next,w; }e[2*M]; typedef pair <int,int> p; priority_queue <p,vector<p>,greater<p> > q; int dis[1010][1010],head[M],s,t,n,m,k=0; int path[1010],cnt; bool vis[1010][1010]; void add(int u,int v,int w) { e[k].to=v; e[k].next=head[u]; e[k].w = w; head[u]=k++; } void dij() { for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for (int j=0;j<=k;j++) dis[i][j] = 0x7f7f7f7f; } memset(vis,0,sizeof vis); int now,son,x; dis[s][0] = 0; q.push(make_pair(0,s)); while ( q.size() ) { now = q.top().second; q.pop(); if ( now%n == 0 ) x = now/n-1,now=n; else x=now/n,now%=n; if ( vis[now][x] ) continue; vis[now][x] = 1; for (int i=head[now];~i;i=e[i].next) { son = e[i].to; if ( dis[now][x]+e[i].w<dis[son][x]) { dis[son][x] = dis[now][x]+e[i].w; q.push(make_pair(dis[son][x],son+n*x)); } if ( x != cnt ) { if ( dis[son][x+1] > dis[now][x]) { dis[son][x+1] = dis[now][x]; q.push(make_pair(dis[son][x+1],son+x*n+n)); } } } } } int main() { int a,b,c; memset(head,-1,sizeof head); scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s,&t,&cnt); for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); add(a,b,c); add(b,a,c); } dij(); printf("%d\n",dis[t][cnt]); return 0; }


