ES6_Day-2-变量的解构赋值
ES6中对数据进行解构赋值,若等号右边的不是数组或者对象,将自动转换为对象。由于 undefined与 null 无对应对象,因此无法对其进行解构赋值。
数组的解构赋值
- 解构赋值本质属于模式匹配,只要等号左右两边模式相同,即能够进行赋值操作。
if(true){ let [a,b,c] = [1,2,3] console.log(a,b,c) let [head, ...tail] = [1,2,3] console.log(head, tail) let [one, two, ...three] = [1] // 当匹配失败时,变量为 undefined,数组为 空数组 console.log(one,two,three) let [d,[f]] = [1,[2,3]] // 不完全解构 console.log(d,f) }
- 等号右边为可迭代对象即可
- 可对待解构的变量设置默认值
1 if(true){ 2 let [a=1] = [] 3 // 变量默认值设置,只有变量在赋值过程中严格等于 undefined 时默认值才会有效 4 console.log(a) 5 let [b=1] = [null] 6 console.log(b)
// b = null 7 }
对象的解构赋值
- 由于对象是无序的,因此在解构过程中,变量名与属性名相同才能够取得正确的值。对象中不存在的属性名为 undefined
1 if(true){ 2 let {name, age, gender} = {'name': 'PB','age': 24} 3 console.log(name, age) 4 console.log(gender)// undefined 5 }
- 通过以下方式改变解构变量名
1 let {name : N} = {'name':'P'} 2 console.log(N)
- 可以通过对象的解构将对象的方法赋值到某个变量
1 let {cos, sin} = Math 2 console.log(cos(10))
- 在对已经声明的变量进行解构赋值时注意,由于ES6会将 {} 看作代码块,而代码块无法赋值,会报错,因此不能将 {} 放在首行
1 let x 2 ({x} = {'x':1}) 3 console.log(x)
- 数组是一种对象,因此可以以对象的解构方式对数组进行解构
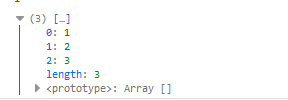
1 let arr = [1,2,3] 2 let {length, 0:first} = arr 3 console.log(length, first)
字符串的解构赋值
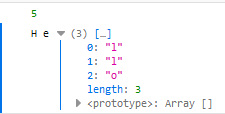
- 字符串进行解构赋值时,被转换为一个类似于数组的对象
1 let s = 'Hello' 2 let {length} = s 3 let [a,b, ...c] = s 4 console.log(length) 5 console.log(a,b,c)
数值和布尔值的解构赋值
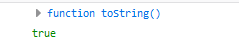
- 若等号右边为数值或者布尔值会先转换为对象。
1 let {toString: s} = 123 2 console.log(s) 3 console.log(s === Number.prototype.toString)
函数参数的解构赋值
- 当函数的参数为数组或者对象时,在传入实参的后,就会发生函数参数的解构。
1 function test({x=0,y=0} = {}){ 2 return [x,y] 3 } 4 console.log(test()) 5 console.log(test({x:100})) 6 7 function Test({x,y}= {x:100}){ 8 return [x,y] 9 } 10 console.log(Test()) 11 console.log(Test({x:100,y:100}))
- 注意以上两种为函数参数设置默认值的方式并不相同,第二种是为函数的整个形参赋值,不是解构赋值,因此不传入实参不完全时会为 undefined
圆括号问题
- 赋值语句的模式:即包含 [] 或者 {} 的部分。
- 变量的声明不能够使用圆括号(函数参数也属于一种变量的声明)
- 可以使用圆括号的只有一种情况:赋值语句的非模式部分
用途
- 交换变量的值:
1 let x = 1; 2 let y = 2; 3 [x, y] = [y, x] 4 console.log(x,y)
- 从函数返回多个值
- 通过解构赋值来对函数返回的数组或者对象进行操作。
- 多个函数参数的实参传递、函数参数的默认值
- JSON数据的提取
- 遍历Map结构
- 输入模块的指定方法




